Health
Heavy drinking linked to increased risk of brain lesions


Heavy drinkers who have eight or more alcoholic drinks per week have an increased risk of brain lesions called hyaline arteriolosclerosis, signs of brain injury that are associated with memory and thinking problems, according to a study published on April 9, 2025, online in Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study does not prove that heavy drinking causes brain injury; it only shows an association.
Hyaline arteriolosclerosis is a condition that causes the small blood vessels to narrow, becoming thick and stiff. This makes it harder for blood to flow, which can damage the brain over time. It appears as lesions, areas of damaged tissue in the brain.
Heavy alcohol consumption is a major global health concern linked to increased health problems and death. We looked at how alcohol affects the brain as people get older. Our research shows that heavy alcohol consumption is damaging to the brain, which can lead to memory and thinking problems.”
Alberto Fernando Oliveira Justo, PhD, study author of University of Sao Paulo Medical School, Brazil
The study included 1,781 people who had an average age of 75 at death. All had brain autopsies.
Researchers examined brain tissue to look for signs of brain injury including tau tangles and hyaline arteriolosclerosis. They also measured brain weight and the height of each participant.
Family members answered questions about participants’ alcohol consumption.
Researchers then divided the participants into four groups: 965 people who never drank, 319 moderate drinkers who had seven or fewer drinks per week; 129 heavy drinkers who had eight or more drinks per week; and 368 former heavy drinkers. Researchers defined one drink as having 14 grams of alcohol, which is about 350 milliliters (ml) of beer, 150 ml of wine or 45 ml of distilled spirits.
Of those who never drank, 40% had vascular brain lesions. Of the moderate drinkers, 45% had vascular brain lesions. Of the heavy drinkers, 44% had vascular brain lesions. Of the former heavy drinkers, 50% had vascular brain lesions.
After adjusting for factors that could affect brain health such as age at death, smoking and physical activity, heavy drinkers had 133% higher odds of having vascular brain lesions compared to those who never drank, former heavy drinkers had 89% higher odds and moderate drinkers, 60%.
Researchers also found heavy and former heavy drinkers had higher odds of developing tau tangles, a biomarker associated with Alzheimer’s disease, with 41% and 31% higher odds, respectively.
Former heavy drinking was associated with a lower brain mass ratio, a smaller proportion of brain mass compared to body mass, and worse cognitive abilities. No link was found between moderate or heavy drinking and brain mass ratio or cognitive abilities.
Justo noted that, in addition to brain injuries, impaired cognitive abilities were observed only in former drinkers.
Researchers also found that heavy drinkers died an average of 13 years earlier than those who never drank.
“We found heavy drinking is directly linked to signs of injury in the brain, and this can cause long-term effects on brain health, which may impact memory and thinking abilities,” said Justo. “Understanding these effects is crucial for public health awareness and continuing to implement preventive measures to reduce heavy drinking.”
A limitation of the study was that it did not look at participants before death and did not have information on the duration of alcohol consumption and cognitive abilities.
The study was supported by The São Paulo Research Foundation.
American Academy of Neurology
Shu, L., et al. (2025). Incidence Trends and Risk of Recurrent Stroke of Cervical Artery Dissections in the United States Between 2005 and 2019. Neurology. doi.org/10.1212/wnl.0000000000213548.
Health
Sisters in Sports fundraiser supports women with disabilities


When four-time Paralympic alpine skier Danelle Umstead talks about the power of sport, she speaks from her lived experience in finding community through isolation and hardship.
“Skiing gave me purpose and independence when I was losing my sight,” said Umstead, who is visually impaired and competed with her husband as her guide across four Paralympic Games. “It gave me community when I felt isolated, and it taught me that sometimes the biggest barriers aren’t the ones on the mountain. They’re the ones in our minds and in society.”
This need for community became the spark for the Sisters in Sports Foundation, which Umstead launched in 2020 to ensure that women and girls with disabilities have a place to belong, thrive and lead.
For Umstead, skiing represented a space she could turn to when she felt isolated by vision loss. Now, she is giving a platform to a generation of girls with disabilities, aiming to help them find that same sense of belonging and grow into leaders who will lift others in turn.
“We hope that this is a movement. If we start now, by the time 2034 comes, we can really rally the Paralympic side of things and show what we’ve accomplished together here as a community and as Sisters in Sports,” said Umstead.
On Saturday, the foundation is hosting Bella Notte, a fundraising gala named in the spirit of the 2026 Milano Cortina Games at the Grand Hyatt Deer Valley. The evening brings together Olympians, Paralympians and community members for a celebration of sport and resilience, raising funds to sustain and expand Sisters in Sports’ impact.
With a fundraising goal of $250,000, the event will feature a silent auction, appearances from Olympians including Picabo Street, Erin Jackson and Brittany Bowe alongside Sisters in Sports athletes.
Olympian Shannon Bahrke will host the evening, and Bella Notte will give the community a chance to meet the young women whose futures the foundation is helping to shape.
“This is more than just a fundraiser,” said Umstead. “It’s about rallying together as a community and showing these women and girls that they belong.”
Sisters in Sports was born from the gaps Umstead felt in her own support system as an athlete.
“I knew there was something that really needed to change for women in sports, and that is community. Having a community is really important. That’s what sports are all about, right? It teaches you to collaborate and encourage and empower each other, and it wasn’t there for women,” said Umstead.
When Umstead founded Sisters in Sports, she built it around two priorities: mental wellness and storytelling. Through the foundation’s programs, athletes gain access to psychologists and wellness specialists offering one-on-one sessions, group workshops and curriculum designed to strengthen mental health long before an athlete reaches the elite level.
“I thought that was really lacking in sports,” Umstead said. “The only way you’d get that mental health support was if you made the national team. That leaves out quite a bit of people who are trying to either get involved in sport or who live with a disability and want to excel in life. It was really important to me to have a healthy mind just as much as a healthy body.”
Athletes also work with coaches to learn how to tell their stories in a way that feels true to their experience, and prepares them to advocate confidently with coaches, sponsors and employers.
“We want to help women tell their story in their own authentic way, so they could really hold themselves as a strong disabled woman. And that was really, really important to me,” said Umstead.
Despite launching during the coronavirus pandemic, Sisters in Sports has now supported more than 50 athletes, funding training, travel and equipment while also fostering a culture of mentorship.
Paralympians, including co-founders Oksana Masters and Kendall Gretsch, lead roundtables on topics from nutrition and social media branding to resilience and leadership. The round tables are about offering advice and connection, but also a way to meet and find community among other women with disabilities, regardless of level or discipline.
Umstead explained that while she often found herself informally mentoring teammates during her career, what was missing in women’s sports, especially for athletes with disabilities, was a structured, lasting community to lean on. Through roundtables and the foundation’s Big SIS program, where experienced athletes step in as mentors to newer members, Sisters in Sports is working to create a lasting outlet for community and belonging.
“Once you’re a part of sisters in sports, it’s something you stay with forever. We continue to rally for you and your needs and help you in wherever your path is going,” said Umstead. “Once a sister, always a sister. We really want them to know they have a community that they can rely on, and we hope they’ll bring up the next generation of sisters too.”
Guests at Saturday night’s Bella Notte will be able to bid in the public silent auction featuring experiences and items, including local wine tastings, resort stays and U.S. Ski Team merch.
The silent auction also offers a rare piece of alpine history, featuring Mikaela Shiffrin’s autographed custom helmet from her 2022-23 World Cup season. Shiffrin surpassed Ingemar Stenmark’s all-time World Cup victories record while wearing the helmet, earning the title of the greatest skier of all time.
The gala will also feature an Olympic-style pin trading, where each guest receives a lanyard and collectible pins to swap throughout the reception. Inspired by traditions from the Games, the activity is designed to spark connections among attendees while nodding toward both Milano Cortina 2026 and the 2034 Games in Utah.
Umstead envisions Sisters in Sports becoming a household name by the Winter Olympics, when the Paralympic Games come to town. The foundation recently strengthened its leadership with new board members Beth Armstrong, Gil Mandelzis and Steve Scruton, joining an existing board that includes Susan Cattozzo and Jeannie Goldstein.
“By the time 2034 comes around, I would love for Sisters in Sports to be a staple — for it to be a name that everybody knows. And for the movement of the Paralympics, maybe to know that we were a part of it, even if it’s a small part, we all have to give to make it better in our communities and for our athletes.”
Bella Notte begins at 6:30 p.m. with the VIP reception, followed by the general reception at 7:30 p.m. and dinner at 8 p.m. on Saturday. Tickets start at $250 with sponsorship opportunities also available starting at $2,500. Visit tinyurl.com/4j89ypce for details.
 Bella Notte supports Sisters in Sports’ mission to support women with disabilities in sport, offering funding, community and mentorship. Credit: Photo courtesy of the Sisters in Sports Foundation
Bella Notte supports Sisters in Sports’ mission to support women with disabilities in sport, offering funding, community and mentorship. Credit: Photo courtesy of the Sisters in Sports FoundationHealth
Stamford Teens to Watch 2025


PORTRAITS BY KATHARINE CALDERWOOD
FORGET THE STEREOTYPES. Today’s teens aren’t waiting for adulthood to make a difference—they’re leading with clarity, creativity and conscience right now. In Stamford, these young leaders are coding cleaner futures, researching lifesaving breakthroughs, amplifying unheard voices and mentoring the next generation. They navigate complexity with grace, resilience and relentless curiosity—balancing late-night studying with early-morning swim practices, or scientific discoveries with classical dance. WHAT UNITES THEM ISN’T JUST AMBITION-IT’S CARE. For each other, for their communities and for the world they’re inheriting.
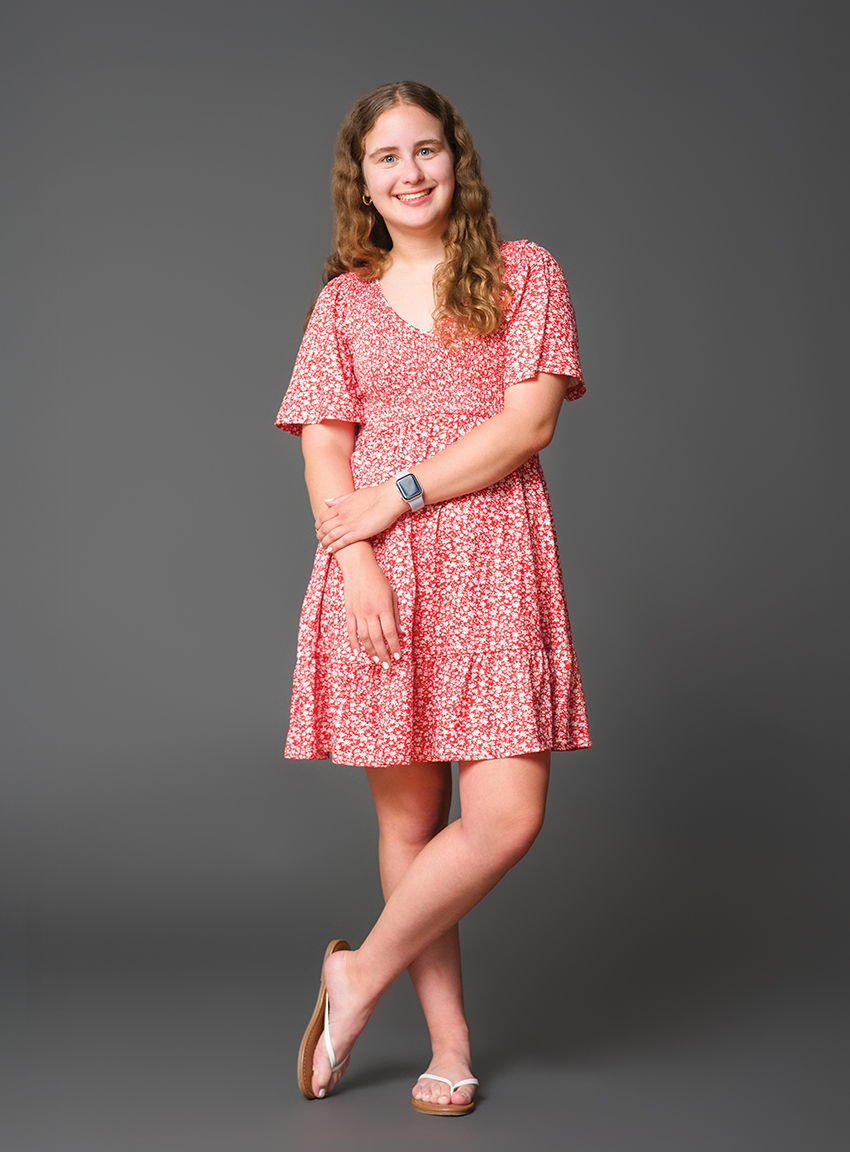
CHRISTINA DEMATT
ST. JOSEPH HIGH SCHOOL
11th Grade / Competitive Swimming, Youth Mentorship, Community Service, Yearbook
From early mornings at swim practice to late nights designing her school’s yearbook, Christina moves through her days with quiet purpose. She knows that making a difference isn’t always about grand gestures—it’s about showing up for others, especially kids who need a little extra support. Whether she’s leading activities as a camp counselor or assembling food bags for children facing hunger, Christina finds meaning in the small moments that build confidence, joy and hope. Balancing academics and athletics, she carries the same determination into every role she takes on. Her passion for helping young children grows from personal experience and a desire to make kindness a ripple that reaches far beyond her community. Through empathy and steady commitment, Christina is proving that even the smallest acts can spark big change.

Between your MVP swim season and various community service groups, how do you balance creativity, athletics and academics—and what keeps you motivated?
Balancing creativity, athletics and academics can be challenging, especially with big assignments and competitions, but prioritizing is key. For me, school always comes first, even if I don’t want it to. As much as I love swimming and yearbook, my studying usually takes over and has to be done before anything else. Swimming is the part of my day I look forward to the most, and even when I don’t feel like going, I know I’ll be glad I did once I get there. My motivation comes from thinking about the payoff—hard tests or swim meets. I don’t always want to study or push through practice, but when I try my hardest and get good results, it’s worth it.
You’ve volunteered both as a camp counselor and with Filling in the Blanks—what do you love most about working with kids and giving back to your community?
As a counselor, I love seeing the kidsevery day and spending time with them. I remember how much fun I had with my counselors growing up and try to give that experience to the kids now. Counselors can make all the difference at camp. With Filling in the Blanks, even though we don’t directly interact with kids, making food bags to help children in Fairfield County means a lot. Taking a couple hours to help may seem small, but it really makes a difference. Knowing I’m helping so many kids is the best feeling.
What draws you to working with young children in the future, and how have your experiences so far shaped that goal?
Having younger siblings, and being around kids as a counselor, has shown me how much I love working with them. They brighten my day even if they’re not always happy. These experiences deepened my passion, and I can’t imagine doing anything without children in my life.
Who’s someone you admire—and what do you admire about them?
I admire my friends and family for their hard work and dedication. Whether in school or their dream jobs, they persevere and always support and encourage me to be my best.
What’s your dream job—or dream impact?
I want to help kids feel confident and loved, and show them what they’re capable of. Whatever job I have, I hope to help children grow into better versions of themselves and make positive changes.
What’s a song/movie/show/book you can’t stop thinking about lately?
Taylor Swift, Dear Evan Hansen, Manifest, The Summer I Turned Pretty.
What’s your go-to comfort snack or meal?
Dark chocolate.
Where do you hope to be in 10 years?
Graduated from college with a job I love, still swimming, proud of my life, with a dog near the beach.
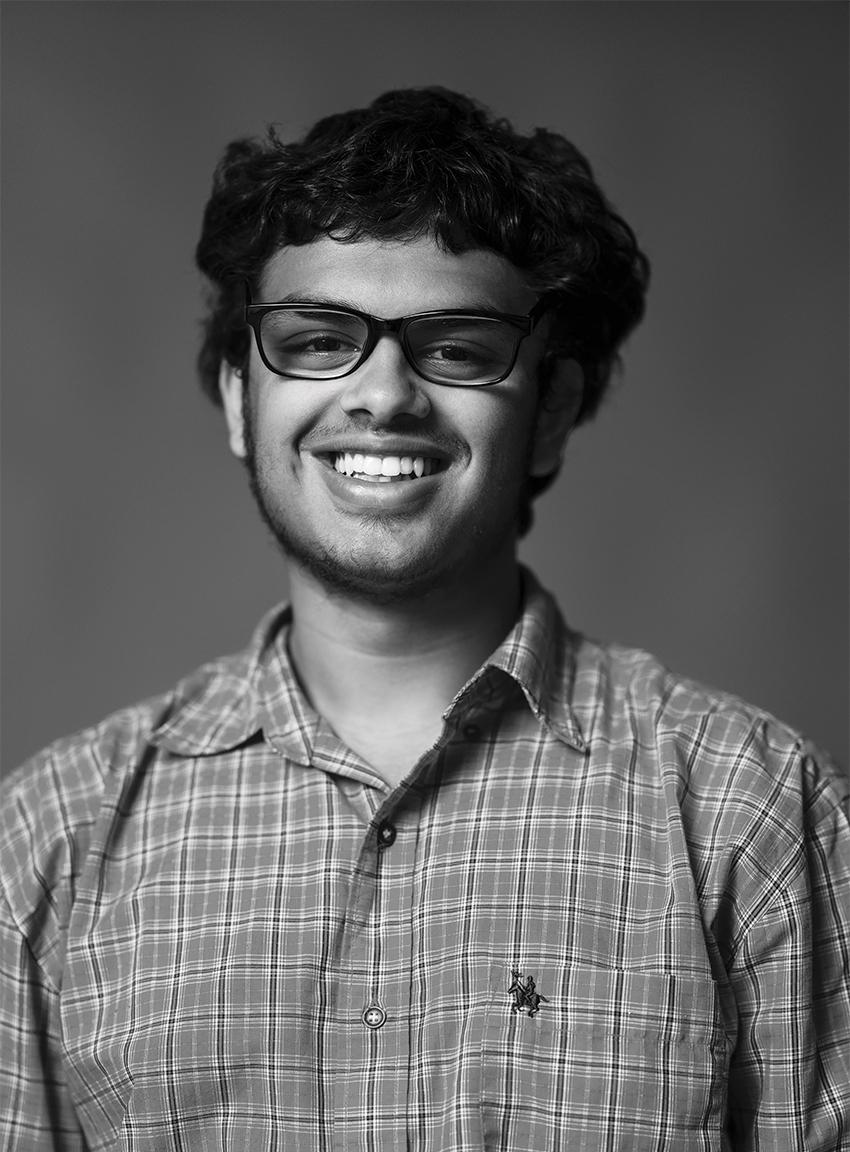
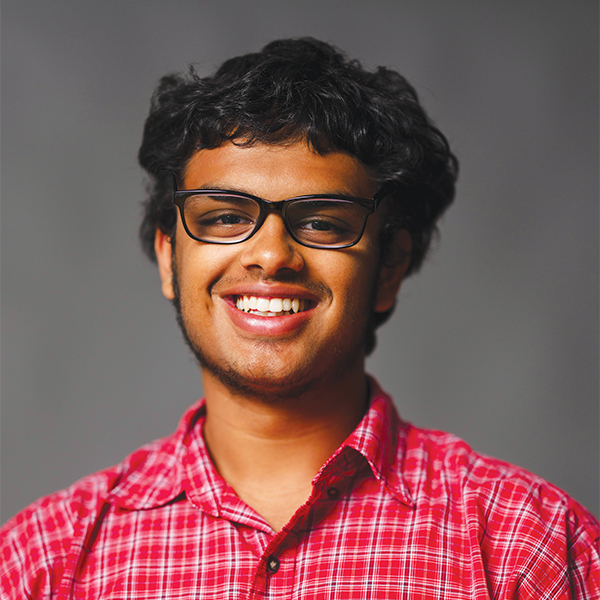
SAZID ROB
ACADEMY OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY & ENGINEERING
12th Grade / AI and Biotechnology, Debate, Community Leadership
At his school, Sazid Rob is a changemaker in every sense— quietly confident, driven by purpose and always thinking ahead. Whether he’s leading conversations on mental health with the Mayor’s Leadership Council, mentoring peers through Future 5, or competing in debate, he approaches every effort with a clear mission: to better the world around him. Fascinated by AI and biotechnology, Sazid hopes to use future innovations to create a more just and compassionate society. His leadership style isn’t about the spotlight—it’s about showing up, speaking up and lifting others along the way. With Sazid, it’s not just about potential—it’s about progress already in motion.

You’ve been a voice for activism at school. How do you find the courage to lead on issues that matter to you?
I didn’t really “find” courage— it came through action. What I did find was the understanding that if no one speaks up, nothing changes. That quote, “You miss 100% of the shots you don’t take,” stuck with me. I realized I had to step outside my comfort zone if I truly cared. That mindset—of action over comfort—continues to guide me.
You’ve talked about using AI and biotech to make the world a better place. What’s one problem you dream of helping to solve—and how would you start?
We’ve made major strides in science and tech, but one of the biggest issues still holding us back is bias—especially in AI. My dream is to create collaborative AI tools that help accelerate research in medicine and tech without reinforcing harmful systems. I want to use AI to support— not replace—human problem-solving, specially in areas like accessible healthcare and under-resourced education. Whether it’s mentoring, debate or Future 5, you spend a lot of time helping others grow. What’s one lesson you’ve learned about yourself while supporting others? Helping others has shown me the real power of guidance and collaboration. It’s not just about solving problems—it’s about creating an environment where people feel seen and supported. I’ve learned how much happiness and motivation I draw from that. It keeps me grounded, and it reminds me how grateful I am for the people who’ve supported me, too.
What’s one passion or cause that drives you?
Right guidance, love and compassion. When people are met with those values, they can achieve incredible things. I’ve seen how they lead to real change—justice, peace, personal growth—and those are the outcomes I want to be part of.
What’s your favorite way to express yourself?
Through positive, constructive interaction. That might mean a good conversation, helping with a project, debating respectfully, or even just collaborating on something creative. I enjoy hands-on connection—it helps me grow and understand others better.
What’s a book you can’t stop thinking about lately?
Restart by Gordon Korman. It’s about a boy who gets a second chance at life after memory loss, and he changes from a bully into someone with purpose. That transformation really stuck with me—it showed how change is always possible.
If you could create one new school subject, what would it be?
Principles of Emotional Intelligence. With everything going on—technology, social pressure—we’re losing our ability to connect emotionally. This class would help students build self-awareness and empathy, skills that are just as important as academics in today’s world.
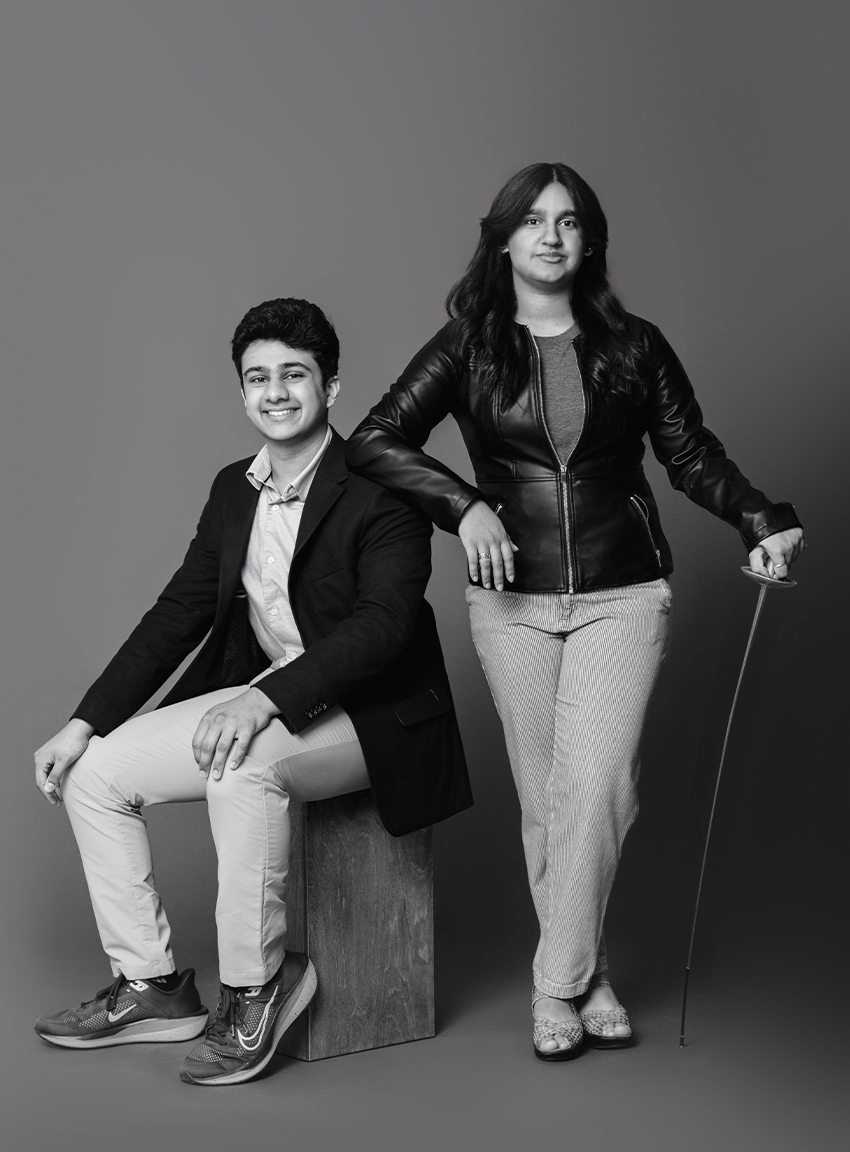
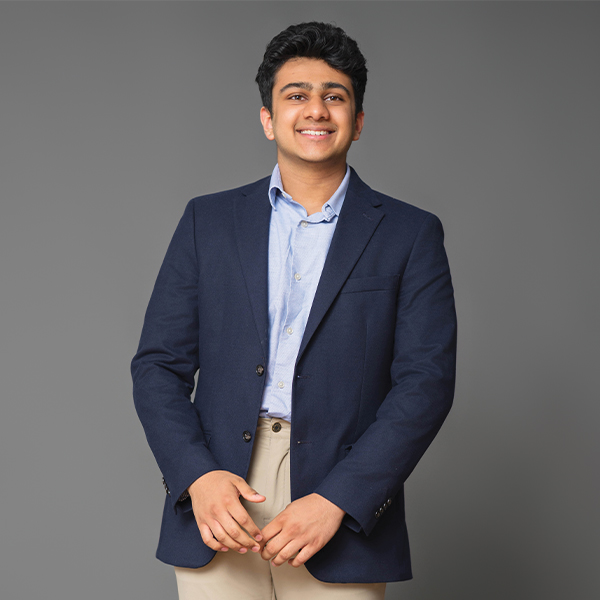
CHAARANATH BADRINATH
RYE COUNTRY DAY
12th Grade / Mathematical Oncology, Robotics, Origami, STEM Mentorship
ISHANA KUMAR
RYE COUNTRY DAY
12th Grade / Music, STEM Research, Invention, Fencing, Cross-Cultural Leadership

CHAARANATH BADRINATH
When Chaaranath folds a sheet of paper, he’s not just creating art—he’s solving puzzles that blend math and creativity. His passion reflects a scientific approach—precise, innovative and curious. At Rye, he combines robotics, physics, and origami with cutting-edge cancer research. Whether designing intricate paper models or building mathematical frameworks at Moffitt Cancer Center, he uses creativity and science to tackle real-world problems. As a leader, he fosters collaboration—doubling club attendance through cultural partnerships and mentoring younger students. Driven to transform cancer care with machine learning, Chaaranath inspires curiosity and innovation across disciplines.
You’ve explored the intersection of math and cancer biology through research at Moffitt Cancer Center—what inspired that focus?
My interest in mathematical oncology started by accident through my school’s Science Research Program, where I developed skills in reading and explaining scientific papers. I became fascinated by mathematical oncology, where models help understand cancer cell microenvironments. I found a program at Moffitt Cancer Center that combined math and oncology, and I was fortunate to be accepted. There, I worked on tumor growth models using approaches like differential equations and network theory. These models provided insights that could directly influence patient care, not just cancer understanding. The experience was transformative, inspiring me to focus on translational research to have real-world impact on patients.
How have your leadership roles shaped the way you think?
Leading robotics and co-presiding over the physics and origami clubs reshaped how I understand collaboration and creativity. Innovation comes from unexpected places. I include new team members early to hear their ideas and help them grow. Leadership requires creativity—not just technical, but solving issues like boosting origami
club attendance. I partnered with APIDA to co-host origami sessions during cultural holidays, doubling attendance and creating meaningful connections. This taught me that creative solutions come from looking beyond boundaries. I now focus less on having all the answers and more on enabling others to discover solutions together.
What impact do you hope to make?
I want to create ripple effects of curiosity and collaboration. Inspired by Sal Khan’s Khan Academy, I aim to open doors for others to discover their interests. When mentoring origami, I hope to spark wonder and math appreciation, so students explore independently. In math competitions, sharing diverse approaches strengthens everyone. Ultimately, I want to build a culture where knowledge flows freely, and curiosity is contagious, equipping others to solve problems beyond my own reach.
What’s one passion thatdrives you?
Bridging mathematical cancer research and patient care drives me. After Moffitt, I developed a machine learning project for adaptive treatment frameworks, aiming to translate life-saving insights from computer models to patients’ bedsides. I’m excited that math can save lives not just in theory, but in practice.
What’s your dream job?
I want to transform cancer treatment with personalized medicine that evolves in real-time through math and machine learning, combined with technology to monitor tumors continuously. The goal is a new paradigm where math and AI are integral to healing, and care is as unique as biology.
ISHANA KUMAR
Ishana Kumar’s world is where melodies meet mathematics, and compassion drives invention. A musician, she blends Indian bhajans with jazz flute, creating a unique fusion she now teaches to immigrant youth. Offstage, Ishana’s curiosity pushes boundaries in science and innovation: She researches health disparities in breast cancer care and co-invented a patent-pending technology aiming to reduce environmental impact in shipping. As fencing captain and student leader, she balances precision with empathy, inspiring peers and advocating for equity. Whether composing a new jazz arrangement or developing tools for accessible healthcare, Ishana weaves creativity, intellect and heart into every challenge she embraces.
You’re blending Indian bhajans with jazz and teaching cross-cultural music to others—what sparked that idea, and how has it evolved?
I’ve always loved how music tells stories. Though I trained in classical piano and flute, I was drawn to the Indian bhajans I heard at family gatherings. One day, I brought my flute to a devotional session and tried playing along—it was hard at first, with no sheet music and shifting keys. But over time, I learned to let go of structure and play by feel. When I later joined jazz band, I noticed the same kind of fluidity. Jazz and bhajans both embrace imperfection and improvisation, which made me fall in love with jazz. Now I blend the two and even teach jazz to immigrant students at a local nonprofit—helping others see how music connects cultures and unlocks self-expression.
From fencing captain to a patent-pending inventor and public health researcher, how do you stay grounded while balancing so many roles?
Weekly Dunkin’ runs, Bananagrams with my family, and noodling on the flute help me stay grounded. I’m endlessly curious, and everything I do started with wanting to try something new. Even after practicing my fencing parry-riposte for the hundredth time, I still feel like I’m discovering something.
What does “equity” mean to you—whether in healthcare, music, or your broader vision for the future?
To me, equity means meeting people where they are. That might look like tailoring a health plan or simply playing a student’s favorite song in jazz class to build confidence. Everyone deserves a path to what makes life special.
What’s one passion or cause that drives you?
Health equity for underserved women. It’s not just about services—it’s about making sure those services work for real people. That means early intervention, accessible resources, and empowering women to make informed decisions.
What’s something about your generation that makes you proud?
I’m really proud to be in the same generation as Malala Yousafzai and Greta Thunberg—activists who have kept fighting for what they believe in despite setbacks. I really admire their resilience and how they have brought about meaningful change.
What’s your favorite way to express yourself?
I love using my hands to craft with clay. I enjoy designing pieces that are both aesthetically pleasing and practical—like a stack of pancakes that also serves as a ring box. When I make animals, I enjoy coming up with whimsical background stories for each one of them with my brother. Ducks are my favorite!
What’s a song/movie/show/book you can’t stop thinking about lately?
Law & Order. I love how it shows the complexity of justice from all sides.
What’s your go-to comfort snack or meal?
My mom’s pasta carbonara—it blends her time in India and Italy and always reminds me of home.
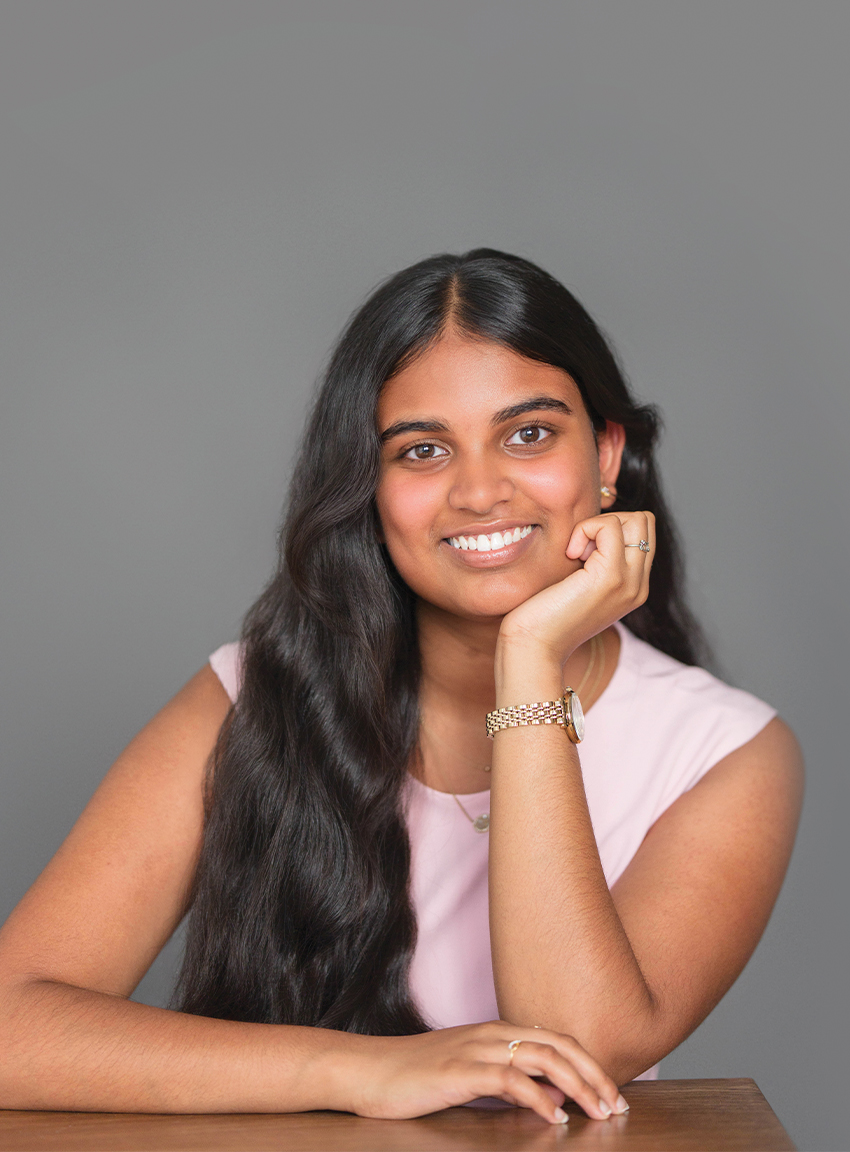
TANISHA ALILAIKANNAN
ACADEMY OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY & ENGINEERING
12th Grade / STEM, Community Advocacy, Civil Air Patrol, Dance
Tanisha Alilaikannan is a powerhouse of empathy, intellect and initiative. A trilingual STEM scholar and passionate performing artist, she’s also a devoted caregiver at home and a Cadet Commander for the Civil Air Patrol, leading a squadron of more than 70. Inspired by her father’s rare genetic disease, she has raised thousands of dollars for medical research and women’s health, founded a Junior Leadership Board, and interned at Stamford Health’s Interventional Radiology Department. Last spring, she had an internship with a UCONN science professor in a chemical laboratory doing research in molecular networking. Whether she’s debating, dancing, fundraising or mentoring, Tanisha’s work is rooted in compassion and her vision for the future is nothing short of life-changing, from gene editing breakthroughs to community service.

You’ve raised thousands of dollars for causes close to your heart—including one inspired by your father’s health. What’s one lesson your fundraising work has taught you about strength or community?
I used to think success came from how much effort I put in—designing fliers, promoting events, setting up tables. But what surprised me was how many people stepped up to help. Some I barely knew hung fliers, helped run my stand, and spread the word. That’s when I realized true community strength comes from people lifting each other up.
Your interests are wide and deep. How do you stay grounded while doing so much?
It’s not always easy, but music and reading keep me grounded. Fantasy books have been my go-to since I was little. They give my mind space to reset and reconnect with the sense of wonder that fuels everything I do.
You’ve turned empathy into action, launching a Junior Leadership Board and organizing a supply drive. What advice would you give another student who wants to start something but doesn’t know where to begin?
Trust that a community exists around you—even if it doesn’t feel like it. Start by identifying what you want to accomplish, and go from there. Cold-email that person. Walk up to that stranger. It might feel awkward, but discomfort usually means you’re growing.
Who’s someone you admire—and what do you admire about them?
My mom. Her strength comes from enduring so much, but never letting anything wear her down. She’s taught me to move forward no matter the hardship—and I carry that lesson every day.
What does being a leader mean to you?
Leadership means being the driving force behind a team—knowing people’s strengths, helping them grow and creating synergy. As Cadet Commander, I’ve had to shift from taking direction to giving it—and being the person others turn to. A strong leader makes others stronger too.
What’s your dream job—or dream impact?
I want to work in gene editing and help remove multi-generational diseases. It’s not just about science—it’s about giving people a chance to reclaim their lives. That would be my dream impact.
What’s a “life hack” or piece of advice you swear by?
Email etiquette! A simple “Good morning” and a kind sign-off go a long way. It shows profession-alism, earns respect and builds connections.
What’s your favorite comfort snack or meal?
Curd rice. It’s simple—cooked rice mixed with yogurt—and I could eat it every day. It’s comfort food in the truest sense.
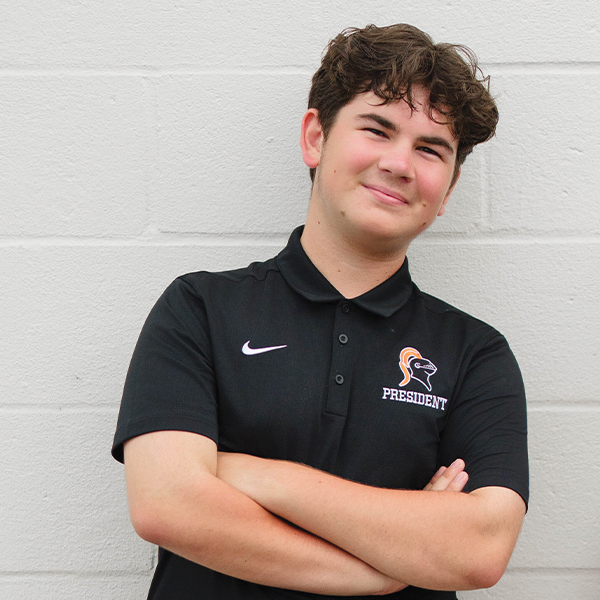
MICHAEL FAHERTY
STAMFORD HIGH SCHOOL
2025 Graduate / Student Government, Journalism, Theater, Eagle Scouts, Community Service
Michael doesn’t wait for opportunity—he builds it. At Stamford High School, he led as Class President and Editor-in-Chief, shaping senior milestones and headline stories with equal parts vision and drive. He spent weekends restoring a trail railing at the Bartlett Arboretum for his Eagle Scout project, and brought that same commitment to the stage as a four-year member and senior board leader of the Strawberry Hill Players, his school’s drama club. Last spring, he was honored to serve as a student reporter at the Stephen Sondheim Awards—Connecticut’s top celebration of high school musical theater and a gateway to the national Jimmy Awards. Michael’s leadership thrives at the intersection of service, creativity and conviction. Now a first-year student at Northwestern University studying journalism and political science, he continues his mission to inform, empower and lead.

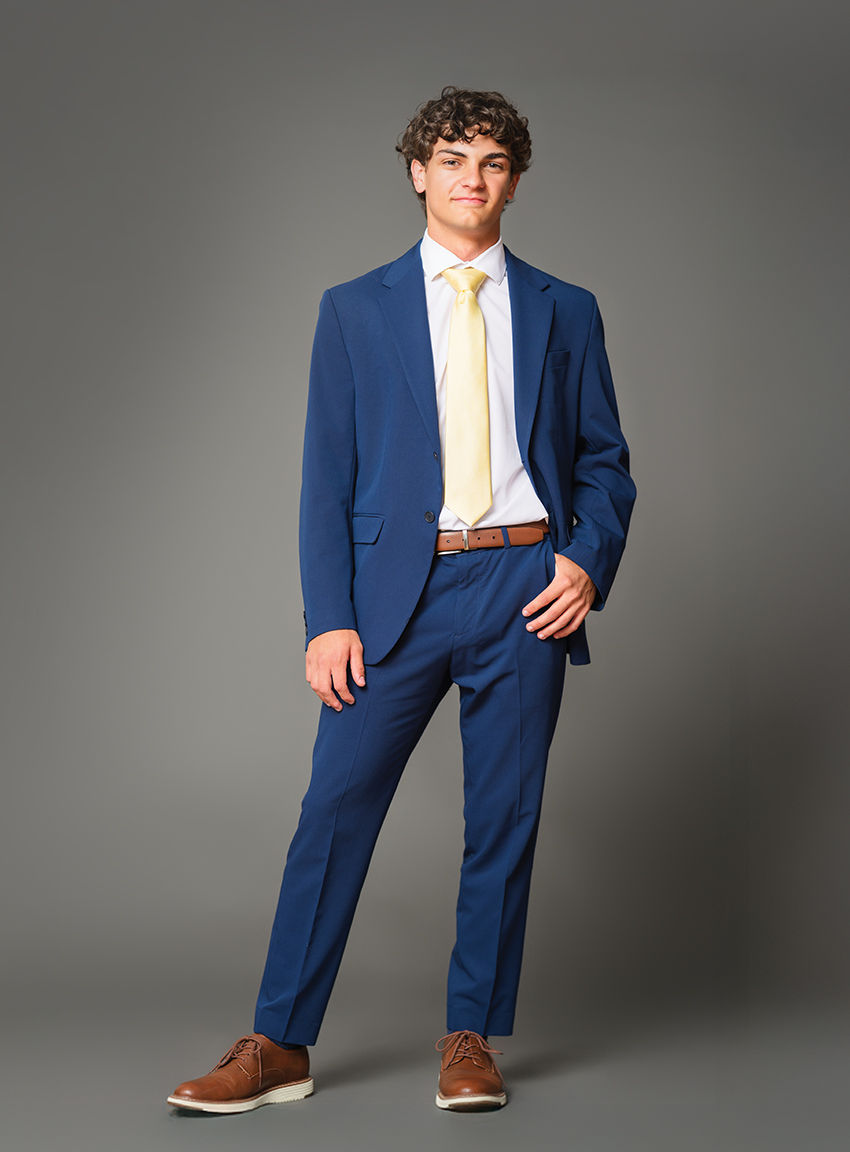
As Senior Class President and Editor-in-Chief of your school newspaper, how do you balance leadership and academics?
It’s easy to want to work hard when I love what I do. Leading my class means being part of some truly big moments—prom, senior sunsets, graduation—and I find a lot of joy in helping make those memories special for my 490 classmates. There have been plenty of late nights, but I don’t see these roles as tiring obligations—they’re exciting opportunities. What keeps me going is the passion behind it and the people I get to work with.
You’ve used your Eagle Scout project to give back to the Stamford community by building a walking trail at the Bartlett Arboretum—what inspired you to choose this project, and what impact do you hope it has on the community?
I grew up going to the Bartlett for field trips, and always loved its role as a sanctuary in our busy city. When it came time for my Eagle Scout Project, I knew I wanted to give back there. After meeting with the CEO, we decided to restore the Native Shade Garden. After 125+ hours of volunteer work, we rebuilt the rotted wooden railings. Thousands walk those trails each month, and I hope the new railings help them do so safely.
With plans to double major in journalism and political science at Northwestern, what are your aspirations in those fields, and how do you hope to use your platform to make a difference?
Being Editor-in-Chief of The Round Table confirmed my journalism path, but my D.C. trip as an Al Neuharth Free Spirit Scholar sparked a passion for politics. I’d love to write political columns—or maybe even represent Connecticut’s 4th District in Congress. Whether I’m writing or legislating, I want to give voice to those who need one. My leadership experiences in high school are the foundation for wherever that path takes me.
What’s one passion or cause that drives you?
Protecting the 1st Amendment. As a future journalism major, it’s vital to me that stories can be published freely. Censorship is, in my opinion, one of our nation’s greatest internal threats.
What’s something about your generation that makes you proud?
Our ambition. In Stamford Public Schools, I’ve seen students head to Top 20 schools, the military and the workforce. As class president, I’ve watched these achievements unfold, and I’m hopeful because of the people building our future.
What’s your favorite way toexpress yourself?
Onstage. I am a proud alumni of Stamford High’s drama club The Strawberry Hill Players, where I served as a board member during my senior year. I participated in four spring musicals, a fall play, and directed my own scene when I had the opportunity to direct underclassmen in my adaptation of Tony Kushner’s Angels in America.
What’s a song/movie/show/book you can’t stop thinking about lately?
I’m a really huge Beyoncé fan; I just saw her on tour this past May and have her most recent album Cowboy Carter on repeat.
KATELYN LAUREANO-RIKARDSEN
STAMFORD HIGH SCHOOL
2025 Graduate / Student Government, Journalism, Theater, Eagle Scouts, Community Service
When a torn ACL sidelined Katelyn her freshman year, she turned that setback into purpose—founding Stamford High’s chapter of Morgan’s Message to support student-athlete mental health. Under her leadership, the initiative expanded across three schools, hosting 15+ dedication games and reaching athletes, coaches and families. As Varsity Lacrosse captain and a member of the Dominican Republic Women’s National Team, Katelyn led with grit on and off the field. She also helped revise Stamford’s student suicide prevention policy through the Mayor’s Youth Leadership Program and launched the school’s AI in Business Club. A National Honor Society member and IB Diploma recipient, she blends data-driven thinking with deep empathy. This fall, she heads to Northwestern University to pursue a dual degree in economics and data science—ready to lead, uplift and prove that she’s just getting warmed up.
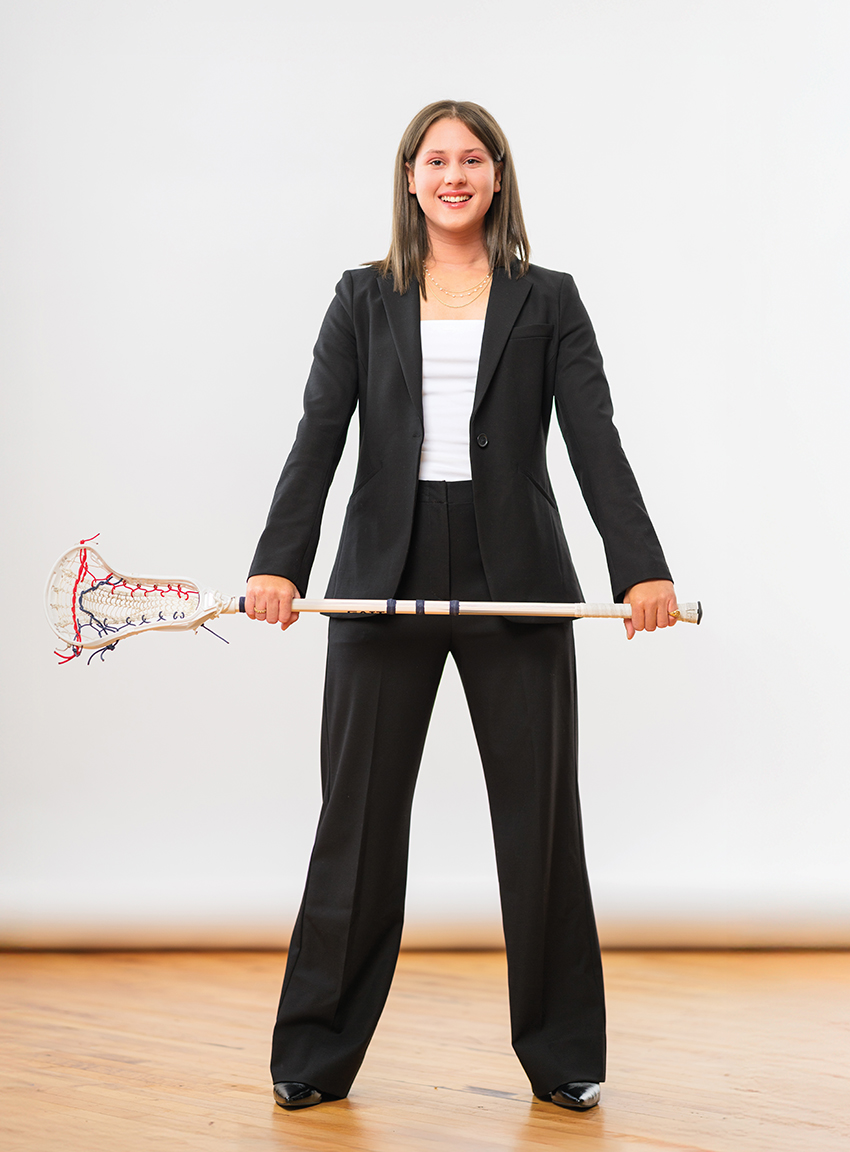

As a leader in both athletics and advocacy, how did you balance founding Morgan’s Message at SHS and expanding its reach across multiple schools, and what impact do you hope it has on student-athlete mental health?
Morgan’s Message came at a pivotal time in my life. My goals were almost instantly derailed by a torn ACL my freshman year, and Morgan’s Message and the lacrosse community picked up the pieces. I hope the impact we’ve had on Stamford has reached a wide group of student athletes, coaches, family and others—helping them recognize the importance of mental health awareness.
How do you plan to integrate your passion for sports with your career goals in private equity and data analytics?
Every time I step onto a lacrosse field, I feel renewed. That passion can carry over into financial services, where team building, grit, and endurance matter. I love analyzing games—each strategy is like a puzzle, and no one approach works every time. That ability to adapt and outsmart an opponent is what makes sports so special. I hope to bring that same mindset to private equity and data analytics—whether reshaping companies or studying network patterns.
Through your work with the Mayor’s Youth Leadership Program, what changes or improvements do you think are essential for supporting student well-being in schools?
More than anything, attention, awareness and resources. We need to pay attention to student well-being, facilitate more in-depth check-ins and provide our administrators and teachers with uniform response plans as well as resources to support these efforts.
Who’s someone you admire—and what do you admire about them?
Coco Gauff—for her drive, kindness and poise under pressure. And Rio Ferdinand, from Manchester United, who inspired me as a leader and defender. I continue to wear his number 5 for both Stamford High and the Dominican Republic Women’s National Team.
What does being a leadermean to you?
Being a conduit for your peers, a motivator, and a listener. My advice: Listen with empathy, never turn a blind eye and trust your gut. I live by “focus on the solution, not the problem.”
What’s your favorite way to express yourself?
Writing short stories—from tailored gentlemen to chunky chipmunks—everyone has a story.
What’s a song/movie/show/book you can’t stop thinking about lately?
“Non-Stop” from Hamilton and Ted Lasso—especially the “Believe” sign moment. It really resonated with our team.
What’s one thing you want to be remembered for?
My positivity—an infectious energy I hope inspires others.
LEON WANG
KING SCHOOL
12th Grade / Biomedical Research, Debate, Community Service, Nonprofit Leadership
Leon Wang isn’t just curious—he’s committed. A junior at King School and Stamford resident, Leon blends biomedical research with community service and award-winning debate. After his grandfather’s Alzheimer’s diagnosis, Leon joined the Blanchard Lab at Mount Sinai to study FDA-approved drugs as potential treatments, earning top honors at CT STEM and Science Fairs. Whether leading King’s debate team, helping immigrant families through Building One Community, or co-founding a nonprofit, Leon leads with intellect and empathy. Co-captain of debate and co-leader of numerous clubs, he brings focus and heart everywhere. With goals to study biomedical research and become a surgeon, he is already making a meaningful impact in both science and his community.
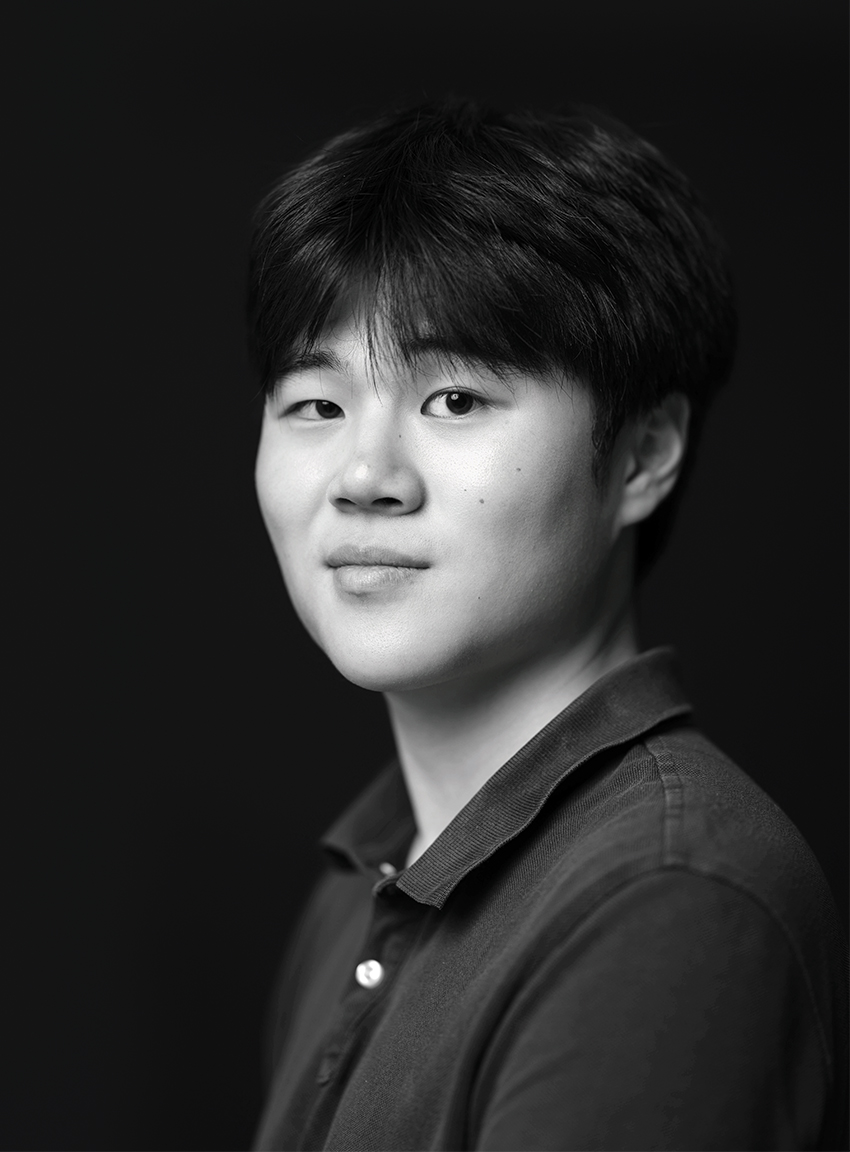

What inspired your interest in biomedical research, particularly in Alzheimer’s disease?
When my grandfather was diagnosed with Alzheimer’s, watching him slowly lose his memory—and eventually his own name—was heartbreaking. I joined my school’s Advanced Science Research program with one goal: to work on Alzheimer’s. At the Blanchard Lab at Mount Sinai, I’ve been testing FDA-approved drugs for new use in treating the disease. I hope this work can lead to better, more accessible treatments for patients like my grandfather.
Debate, research and leadership all require different types of thinking—how do they complement each other in your daily life?
Research taught me to ask better questions. Debate gave me the confidence to advocate for ideas. Together, they’ve helped me think critically, speak persuasively and lead effectively—whether that’s running a club or proposing a project in the lab.
What does “impact” mean to you—and how do you measure it in your work so far?
Impact means improving someone’s life—whether that’s a smile on the subway or progress in Alzheimer’s research. Right now, it means pushing my project one step closer to the goal. Some of my recent results are promising: the drugs I’m testing may help regenerate healthy brain cells. I hope to publish this work so it can inspire further research—and maybe one day, help patients directly.
What’s one passion or cause that drives you?
Closing healthcare access gaps. Repurposed drugs are about 160 times cheaper to bring to market than new ones, which can make treatments more affordable. That’s especially important in Alzheimer’s, where low income is a top risk factor. I want to help make cutting-edge care accessible—through advocacy or research.
What’s something about your generation that makes you proud?
Gen Z is resilient. From COVID to AI, we’ve had to adapt quickly—and I think that flexibility will serve us well going forward.
What’s your favorite way to express yourself?
The piano. I’ve been playing for 12 years, and it’s how I decompress and reset.
What’s a song/movie/show/book you can’t stop thinking about lately?
Succession is my current obsession, but Grey’s Anatomy is still my comfort show.
Where do you hope to be in 10 years?
I hope to be making a meaningful impact in healthcare—whether as a doctor, researcher, policymaker, or in biotech. I’m looking forward to narrowing my path in college and grad school.
AIDAN MULCAHEY
WESTHILL HIGH SCHOOL
12th Grade / Baseball, Coding, Volunteering, Engineering, Community Service
Aidan Mulcahey steps up to the plate with a rare blend of grit, brains and heart. As a senior at Westhill High School, he’s not just swinging for the fences in baseball and golf—he’s also knocking it out of the park academically with a 4.0 GPA and a rigorous load of Honors and AP courses. Off the field, Aidan coaches the next generation of coders at Code Ninjas and volunteers tirelessly, umpiring Stamford Little League and mentoring at EST Baseball Camp. His passion for problem-solving drives his dream of becoming an engineer focused on sustainable energy and cutting-edge technology. With awards like the Mickey Lione Jr. Fund Youth Excellence and a black belt in Tang Soo Do, Aidan’s leadership hits every base—from community service to academic excellence—setting him up to engineer solutions that could change the world.

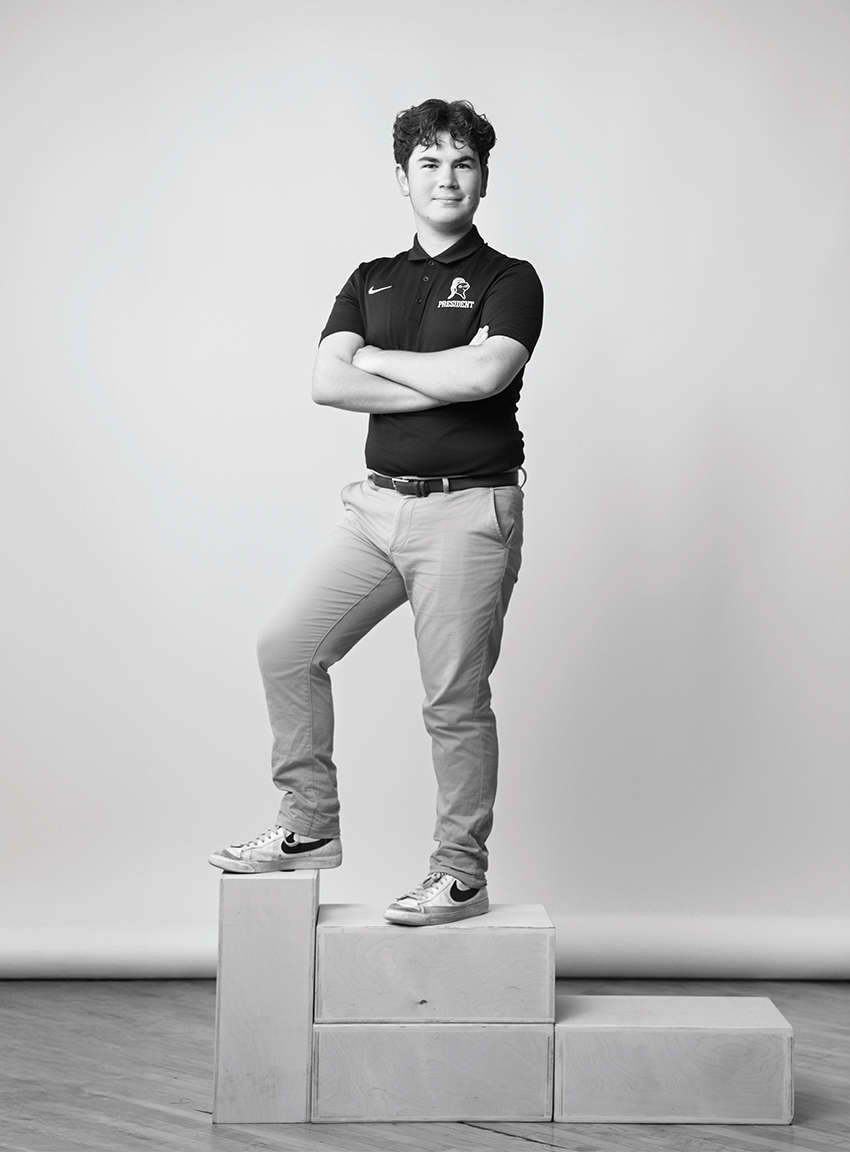
You’re involved in so many activities, from teaching coding at Code Ninjas to volunteering at EST Baseball Camp—how do you manage to balance your rigorous academics with all your extracurriculars, and how has this experience shaped your leadership skills?
Finding balance comes easily because I enjoy everything I do. From baseball to volunteering to AP Physics, each one is something I love. Of course, doing what you love brings pressure, but those moments build character. Learning to handle stress and diversify my interests help me understand myself—and bring out the best in others. Helping others also means learning from their experiences, shaping me into a better leader.
With your interest in engineering and passion for problem-solving, what area of technology or innovation are you most excited to explore, and what kind of impact do you hope to make in that field?
Presented with a world riddled with waste and pollution, I am most excited to innovate in the field of energy—especially nuclear. It’s one of the cleanest, safest forms of energy, yet only 20% of U.S. energy comes from nuclear power. I believe it’s the future for both cities and rural areas. While the industry faces challenges, I see them as problems to solve. I hope to make nuclear energy more efficient and raise awareness of its benefits.
As a dedicated volunteer and mentor, how do you think giving back to the community has shaped your personal growth and influenced your future aspirations?
Volunteering has taught me a lot about values—especially community, health and education. At the Stamford Little League Challenger Division, I’ve helped bring baseball to kids with mental and physical disabilities. I’ve also mentored at EST Baseball Camp and Code Ninjas. The baseball community shaped me, and I want others to have the same chance. Inclusion and support are key—and I hope to keep giving back as I grow.
What’s one passion or cause that drives you?
My biggest passion is my thirst for knowledge. I love learning—in class and on my own—and want to absorb as much as I can from everyone and everything.
What’s something about your generation that makes you proud?
When I look at my generation, I would say that our ability to innovate and adapt to technology stands tall as our best feature. We understand its power and use it to create life-changing ideas.
What’s your favorite way to express yourself?
Through clothing—especially things that show what I love, like baseball, golf, or my favorite artists and shows.
What’s a song/movie/show/book you can’t stop thinking about lately?
Succession. The concept of splitting work and personal life is fascinating—and full of symbolism and foreshadowing.
What’s your go-to comfort snack or meal?
Super easy microwave nachos. They’ve been a favorite for years!
ANYA ANDERSON
KING SCHOOL
2025 Graduate / Track & Field, Ninja Warrior, Medicine, Youth Leadership, Women in STEM, Environmental Conservation
Leaping past limits is second nature to Anya Anderson. A senior at King School, Anya is a nationally ranked track star, elite Ninja Warrior competitor and aspiring emergency room doctor who thrives in high-pressure moments—both on and off the course. Whether she’s vaulting over hurdles or leading younger girls through faith-based mentorship, she pushes herself for something greater. From her leadership in King’s Future Medical Professionals and Girls Advancing in STEM clubs to her work conserving endangered frogs and empowering girls in science, Anya brings bold energy and deep care to every challenge. With plans to compete on American Ninja Warrior and pursue a career in medicine, she’s training to make an impact in every arena.

What drives you to keep pushing your physical and mental limits?
What drives me is the pursuit of growth—physically, mentally and emotionally. Competing at a national level demands focus, discipline and resilience, but I thrive in the process of learning what I’m capable of. I find purpose in challenges that push me beyond my comfort zone. I’m also deeply motivated by the community around me. The friendships I’ve built through both track and Ninja Warrior are a constant source of encouragement and inspiration. Knowing that I’m not pushing limits alone—but alongside people who believe in me—makes every challenge more meaningful.
How have your experiences in youth group leadership shaped how you want to help others, both now and in your future career?
In youth group, I learned that real leadership isn’t about being the loudest voice—it’s about listening, building trust, and showing up for people. Whether I was leading a service project or mentoring younger students, I saw how small actions could make someone feel seen and valued. In medicine, I want to carry that same sense of empathy and connection—treating patients as whole people, not just cases. Helping others starts with understanding them.
From frog conservation to empowering girls in STEM—what connects all these passions for you?
At first glance, these interests might seem unrelated, but they’re all rooted in a deep desire to protect and uplift life—whether it’s endangered species or underrepresented voices. I care about what’s overlooked: the fragile ecosystems that need advocates, the young girls who need someone to tell them they belong in science. For me, it’s all about creating a better future—one where every life, big or small, has a chance to thrive.
Who’s someone you admire—and what do you admire about them?
My track and field coach, Avi Thomas, is someone I really admire. He’s incredibly dedicated to our team—not just in the way he pushes us to improve, but in how much he genuinely cares about us as people. He always goes the extra mile, whether it’s staying late after practice to talk or helping us navigate school-life balance. That kind of support and consistency really sticks with you.
What’s your dream job—or dream impact?
I want to be a doctor, and right now, I’m leaning toward emergency medicine. I like the fast pace and how every day brings something new. But more than that, I want to be someone people can rely on in a crisis, who brings calm and confidence when things feel out of control.
What’s your favorite way to express yourself?
Working out is 100% my favorite way to express myself. Whether it’s on the track, Ninja Warrior, or just moving my body—it helps me process everything and feel more grounded. Also, I have “Runaway by Galantis” on repeat—it’s the kind of song that makes you feel like you can do anything.
What’s a song/movie/show/book you can’t stop thinking about lately?
The OC.
If you could make one new school subject, what would it be?
I’d create a class on sports science. I think athletes (and honestly, everyone) would benefit from learning how our bodies and minds actually work when we move.
THE FUTURE ACCORDING TO US
OUR TEENS SHARE THEIR HOPES, FEARS AND WILDEST DREAMS FOR THE WORLD IN 10 YEARS

ISHANA KUMAR
Closing the Gap Between Innovation and Access
Ishana’s hope is that medical tech breakthroughs reach those who need them most, shrinking healthcare disparities. Her invention wish? Clean-energy personal jetpacks to travel freely and reconnect with loved ones. And she admires activists’ relentless drive to make a difference—hoping their fire never burns out.

CHRISTINA DEMATT
Dreaming Big, Hoping for Heart
Flying cars are Christina’s pick for the next big invention, but she’s most hopeful that human love and hard work never fade. “I hope love and the drive to achieve our goals never go away,” she says. While concerned about climate change, Christina believes it’s our support for each other that will help us face the future.

ANYA ANDERSON
The Human Side of a Tech-Heavy Future
Anya imagines a future where self-driving cars are everywhere, and AI is more than a tool—it’s a daily companion. “The job market will be unrecognizable,” she predicts, “and we’ll all need to learn how to work with technology, not around it.” But for all the tech advances, she values one thing above all else: in-person connection. “Nothing beats a late-night hang with friends, laughing and being present. I hope tech never replaces that magic.” Anya also dreams of a life-organizing AI that’s part personal trainer, therapist, and calendar—a little help to keep the chaos of school, sports, and life in check.
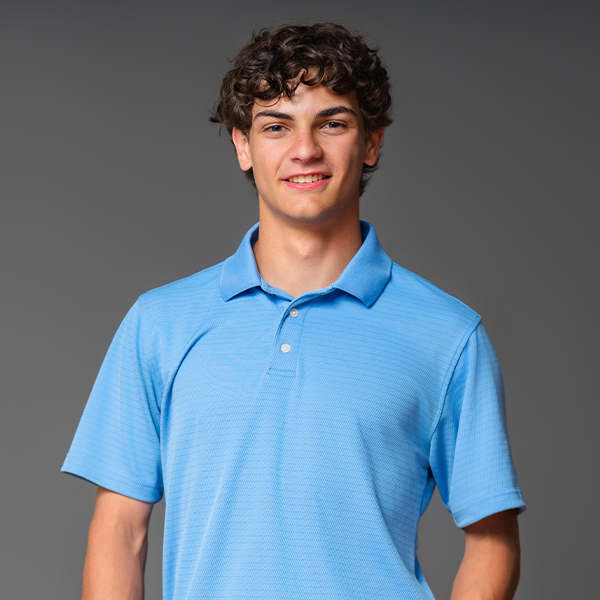

AIDAN MULCAHEY
Balancing Innovation with Responsibility
As a 12th grader who’s equally at home on the baseball field and behind a computer screen, Aidan sees the next ten years as a high-stakes game. “AI will power everything—from healthcare to transportation—making life faster and more efficient,” he says. Like a curveball that can trick even the best batter, AI carries risks. “It could replace jobs or raise ethical questions that we’re not ready for yet.” Aidan believes two conversations must happen soon: how far we let AI shape our world, and how seriously we respond to climate change. “Ignoring it won’t make it go away.” His dream invention? Controlled nuclear fusion—a clean, near-limitless energy source that could rewrite the planet’s future. Aidan hopes this remains a constant: his insatiable love for learning. “It’s what drives me and connects me with others.”
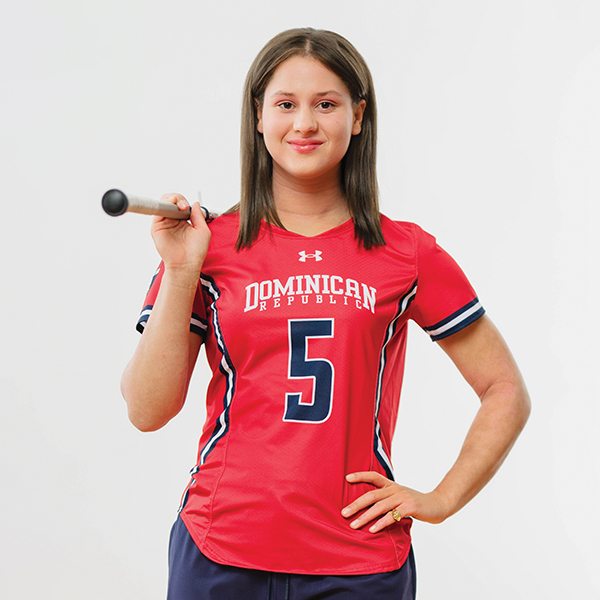

KATELYN LAUREANO-RIKARDSEN
Cultivating Curiosity and Connection
For Katelyn, the future is about appreciating both people and places more deeply. She envisions a “Cultural Adapter,” a machine helping people understand and celebrate differences. And she holds tight to the simple beauty of West Beach sunsets—something she hopes never changes.
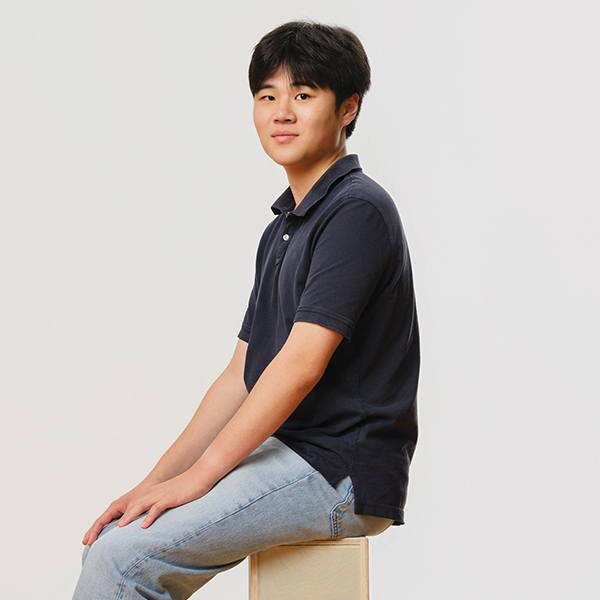

LEON WANG
Guarding Truth in the Age of AI
Leon sees AI transforming how we study, work and communicate but urges caution. “Humans won’t be replaced, but AI should help us work smarter.” What worries him most is misinformation. “We need tools that can detect fake news and AI-generated content to protect our ability to make informed decisions.” His hope? That life’s simple joys—picnics, books, quiet moments—never lose their charm, no matter how much technology advances.
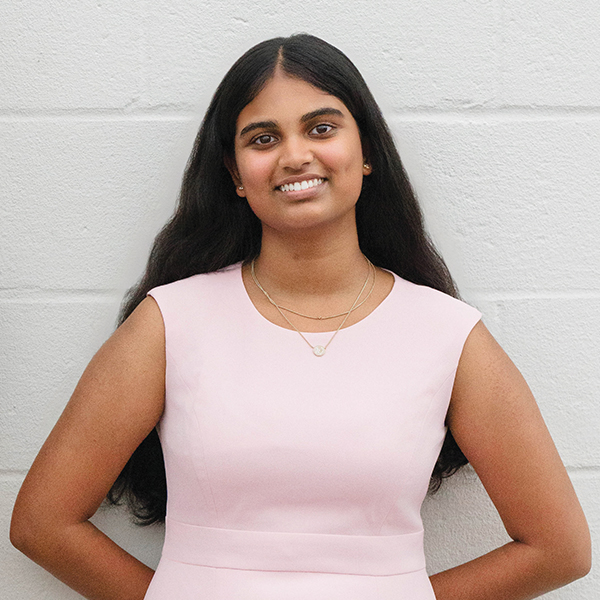

TANISHA ALILAIKANNAN
Celebrating Connection and Culture
From pioneering gene editing to virtual reality classrooms, Tanisha envisions a tech-heavy, health-focused future. But she also wants a device that bridges divides—an inclusive language translator that could help erase prejudice embedded in everyday speech. “Language shapes belonging and productivity,” she explains. And what does she hope lasts forever? Family game nights around the board. “There’s nothing like moving pieces, reading faces, and sharing laughter that no video game can match.”

CHAARANATH BADRINATH
The Microsurgeon of Tomorrow
Chaaranath’s vision of 2035 is a world where AI blends into daily life like electricity—almost invisible but indispensable. He dreams of intelligent microsurgeons: tiny robots patrolling our bodies, stopping diseases before symptoms appear. “This could transform medicine from reactive to preventive care,” he says. Above all, he hopes human curiosity—the drive to ask “why” and imagine new possibilities—never fades. “Our hunger for understanding is what makes us beautifully human.”

SAZID ROB
Bridging Divides with Openness
Sazid senses a future of intense technological growth but hopes we don’t lose our capacity to love and stay open-minded. “These qualities make us human and help us grow,” he says, even as logic and emotion dance a delicate dance in a tech-driven world.

MICHAEL FAHERTY
Community and Progress Hand in Hand
Michael balances hope and caution about the future’s tech advances, wanting AI to serve global peace and progress. His invention wish? A compact water filtering generator to bring clean water to underserved communities. And he cherishes Stamford’s close-knit culture—hoping its warmth and opportunities endure.
Health
Athlete Resilience as a Stabilizing Force in Sports Investments
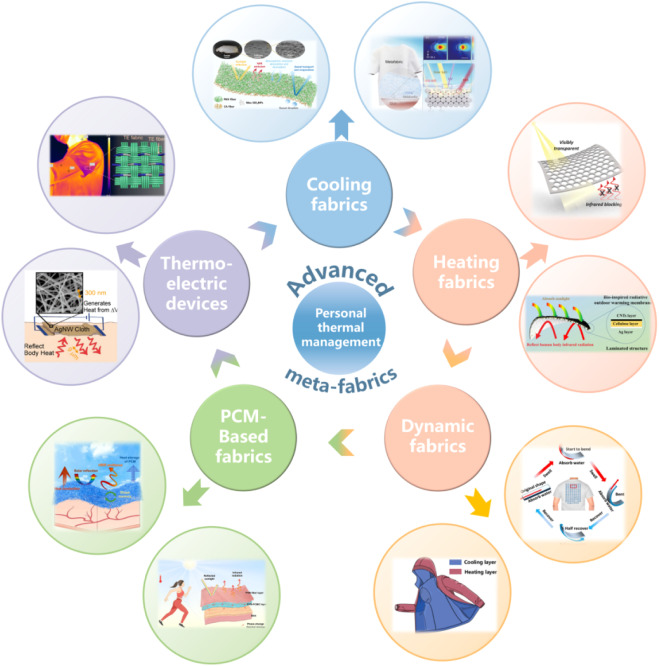


The sports investment landscape has long grappled with the inherent volatility of athlete performance. In 2025, however, a paradigm shift is emerging: athlete resilience is proving to be a critical stabilizing factor for sponsorship deals and media rights valuations. This resilience—defined as an athlete’s ability to recover from setbacks, maintain mental fortitude, and adapt to pressure—has become a linchpin for investors seeking to mitigate risks in a sector where performance fluctuations are inevitable.
Resilience as a Catalyst for Sponsorship Stability
Sponsorship deals in professional sports are no longer solely tied to on-field success. Instead, brands are prioritizing athletes who demonstrate resilience, as these individuals foster deeper emotional connections with audiences. A 2024 Czech Republic case study revealed that sponsored athletes showed a 20% improvement in competition results compared to non-sponsored peers, with access to elite training facilities further boosting performance by 15% [1]. This data underscores how sponsorship not only enhances athletic output but also cultivates resilience through structured support systems.
Moreover, brands are recognizing that resilient athletes act as buffers against performance volatility. For instance, Powerade’s 2024 initiative, The Athletes Code, legally protects athletes’ mental health by allowing them to take breaks from obligations without jeopardizing sponsorships [2]. This model has set a precedent for how brands can align with athletes’ long-term stability, ensuring that short-term performance dips do not erode the value of partnerships. By 2025, campaigns featuring athletes generated a 7x return on ad spend, far outpacing traditional influencers [3], a metric that directly ties resilience-driven authenticity to financial returns.
Media Rights Valuations and the Resilience Premium
Media rights valuations have also been reshaped by athlete resilience. The rise of Name, Image, and Likeness (NIL) rights in college sports has empowered athletes to build personal brands, with platforms like Instagram and TikTok amplifying their reach. College athletes leveraging these tools have attracted $2.5 billion in projected media rights value for women’s sports by 2030 [3], driven by their ability to sustain fan engagement even during off-peak seasons.
Professional athletes like Caitlin Clark and Simone Biles exemplify this trend. Their resilience—evident in overcoming injuries, societal pressures, and performance slumps—has translated into record-breaking viewership for events such as the NCAA Women’s Basketball Championship and the WNBA Finals [1]. This loyalty translates into $30.5 billion in U.S. sports rights spending in 2025, a 122% increase from 2015 [4], as media rights holders capitalize on the “resilience premium” embedded in athlete narratives.
The Investment Implications
For investors, the interplay between athlete resilience and valuation stability offers a compelling opportunity. Sponsors and media rights holders that prioritize resilient athletes are better positioned to weather performance volatility. For example, the NFL’s Game Pass International achieved 80% annual subscriber retention by leveraging data-driven strategies to deepen fan relationships, a tactic rooted in the enduring appeal of resilient athlete personas [2]. Similarly, clubs like Paris St. Germain saw a 15-fold increase in Google searches after signing Lionel Messi, demonstrating how top-tier athletes act as “insurance policies” against market downturns [1].
However, risks remain. Over-reliance on a single athlete’s resilience can backfire if injuries or off-field controversies arise. The solution lies in diversifying investments across athletes with proven mental and physical durability. The Czech case study highlights this: while sponsorship obligations can introduce stress, resilient athletes are 30% more likely to meet contractual expectations without burnout [1].
Conclusion
Athlete resilience is no longer a soft metric—it is a hard asset in the sports investment ecosystem. By stabilizing sponsorship returns and amplifying media rights valuations, resilient athletes provide a hedge against the inherent unpredictability of performance. As the global sports sponsorship market surges toward $160 billion by 2030 [1], investors who prioritize resilience will find themselves at the forefront of a sector where emotional capital and financial returns are inextricably linked.
**Source:[1] Impact of sports sponsorship on early career athlete performance: Czech case study [https://www.researchgate.net/publication/385446532_Impact_of_sports_sponsorship_on_early_career_athlete_performance_Czech_case_study][2] The Athletes Code (case study) [https://www.adsoftheworld.com/campaigns/the-athletes-code-case-study][3] Athletes Rule the Influencer World in 2025 [https://blog.opensponsorship.com/athletes-rule-the-influencer-world-in-2025][4] US sports rights spending hits US$30.5bn in 2025 [https://www.sportspro.com/news/sports-broadcast-rights-spending-usa-uk-nfl-nba-ampere-analysis-august-2025/]
Health
Welcome Back, Naomi Osaka!



A couple of years ago Naomi Osaka, the four-time Grand Slam champion who last won the U.S. Open in 2020, came to Arthur Ashe Stadium as a spectator, just two months after giving birth to her first child, daughter Shai. Osaka was in New York City with Olympic champion Michael Phelps to participate in a forum, along with then U.S. surgeon general Vivek Murthy, on mental health in sports. The next evening, she watched American Coco Gauff beat Karolína Muchová in the semifinals, during Gauff’s run to the 2023 U.S. Open title.
Advertisement
In that moment watching Gauff, Osaka, now 27, had doubts as to whether she’d be able to play at such a high level again. But she could still picture returning to Arthur Ashe Stadium, late in a U.S. Open, to compete for another major championship. “Maybe I’m crazy or something,” Osaka said after dispatching Gauff, the third-ranked player in the world and the defending French Open champion, 6-3, 6-2 in a Monday fourth- round match that took barely an hour to complete. “But I always feel like you have to imagine it, and then you have to believe it for it to actually come true.”
“You’re also speaking to the kid that visualized playing Serena too,” Osaka went on, referencing her memorable 2018 breakout win over Serena Williams in the U.S. Open final. “So I feel like there’s a lot of power in dreaming and believing.”
She needed all of it. Since winning the 2021 Australian Open, Osaka had trouble returning to the top after public challenges with her mental health and other difficulties. She’s said she had “extremely bad” postpartum after Shai’s birth, and since returning to pro tennis in 2024, she’d reached the third round of a major championship just twice before this year’s U.S. Open: in fact, Osaka has been bounced out of the first round of last year’s Australian and U.S. Opens, and this year’s French. In the press conference following that loss in Paris, she made a reference to her then-coach Patrick Mouratoglou, who used to work with Serena Williams. “He goes from working with, like, the greatest player ever to, like, ‘What the (expletive) is this?’” Osaka said. She walked away in tears.
Advertisement
Osaka’s performance, however, at this year’s U.S. Open should go a long way toward eliminating any uncertainty—self-inflicted or otherwise—about her chances to win again. Her decisive victory over Gauff, Osaka’s successor as the highest-paid female athlete in the world, puts Osaka in the quarterfinals on Tuesday, against 11th-seeded Karolina Muchovia of Czechia.
Four times, Osaka has reached the quarterfinals of a major tournament. All four times, she’s won the championship.
Osaka’s influence in athletics is secure: another run to the title, after becoming a mom and taking a few years to find her rhythm, would just add flourish to her legacy, both on and off the court. In protest of the 2020 police shooting of Jacob Blake in Wisconsin, Osaka—who is Black and Japanese and grew up in the U.S. but competes under the Japanese flag—announced she would not play her next match: the entire tournament soon paused before Osaka and others returned to compete.
Advertisement
During her run to the U.S. Open championship that year, she memorably wore facemasks bearing the names of a Black victims of alleged police or racist violence. The next year, she pulled out of the French Open to tend to her well-being, a decision that helped destigmatize mental health struggles in sports. “It’s O.K. to not be O.K.,” Osaka wrote in a TIME essay after the 2021 French Open. At the same time, critics derided her stance and the subsequent decision of U.S. gymnast Simone Biles to back out of the all-around competition at that year’s Tokyo Olympics, where Osaka lit the cauldron, for her mental well-being.
Osaka has continued to serve as a lightning rod in some circles: during this year’s Canadian Open final, she failed to congratulate Victoria Mboko on the court following their match, which Mboko won. Critics called her out. Osaka later said she inadvertently forgot to do so.
Advertisement
That Canadian Open, in Montreal in July and August, seemed to turn Osaka’s season around. She points to a second round match against Liudmila Samsonova, in which she saved two match points, as a key moment. “I was really frustrated for a long time because I felt like I was playing well, but there was just something that I don’t know if I was missing or it was just, like, a mentality thing,” said Osaka. “Then I played Samsonova, and I didn’t give up until the very last point. Obviously, I ended up winning that. I think from that moment on I just tried to be the biggest fighter that I can be.”
As strongly as Osaka performed in her highly anticipated duel with Gauff, the American contributed to her own undoing in the match, with 33 unforced errors to Osaka’s 12. Before the U.S. Open, Gauff made the surprising decision to switch coaches, bringing on biomechanics expert Gavin MacMillan to fine-tune Gauff’s struggling serve. And while Gauff served well—she only double-faulted five times (to Osaka’s zero), matched Osaka’s ace count (3 each), and even hit more first-serves in than Osaka (66% vs 42%) while essentially matching her first-serve speed (104.1 miles per hour compared to 104.8 miles per hour for Osaka)—the parts of her game in which she had the most confidence, groundstrokes and service return, faltered.
Advertisement
“I woke up today thinking, ‘Oh, this is going to be a good day for me where I’m going to play well,’ and then out there I just don’t know what happened,” Gauff said after the match. “I felt so discombobulated on the court, because it’s, like, I’m serving well, but not returning well. The last two years everybody can agree that’s like a weird thought.”
Gauff’s partnership with MacMillan is in its infant stages, and with her serve already showing signs of improvement, and her age–21–portending potential prime years ahead for her, she promises not to hang her head too long after losing to Osaka. “I am not going to let this crush me,” Gauff said.
When it comes to resilience, Osaka can now show Gauff the way. Osaka hasn’t let the disappointments and detractors of the last nearly five years derail her. She’s clearly enjoying herself in New York. On Monday she revealed her latest Labubu, a sparkling plush toy from the viral Chinese company Pop Mart that she named Althea Glitterson (other bejeweled Labubus accompanying her at the U.S. Open include Billie Jean Bling and Arthur Flashe).
Advertisement
With Gauff out of the tournament, Osaka is certain to be the sentimental crowd favorite in the women’s draw going forward. Her comeback story is just too compelling.
“This is my favorite court in the world,” she told the Ashe Stadium fans after the match. “And it means so much to me to be back here.”
Health
For some Chattanooga athletes, making room for equipment is its own exercise
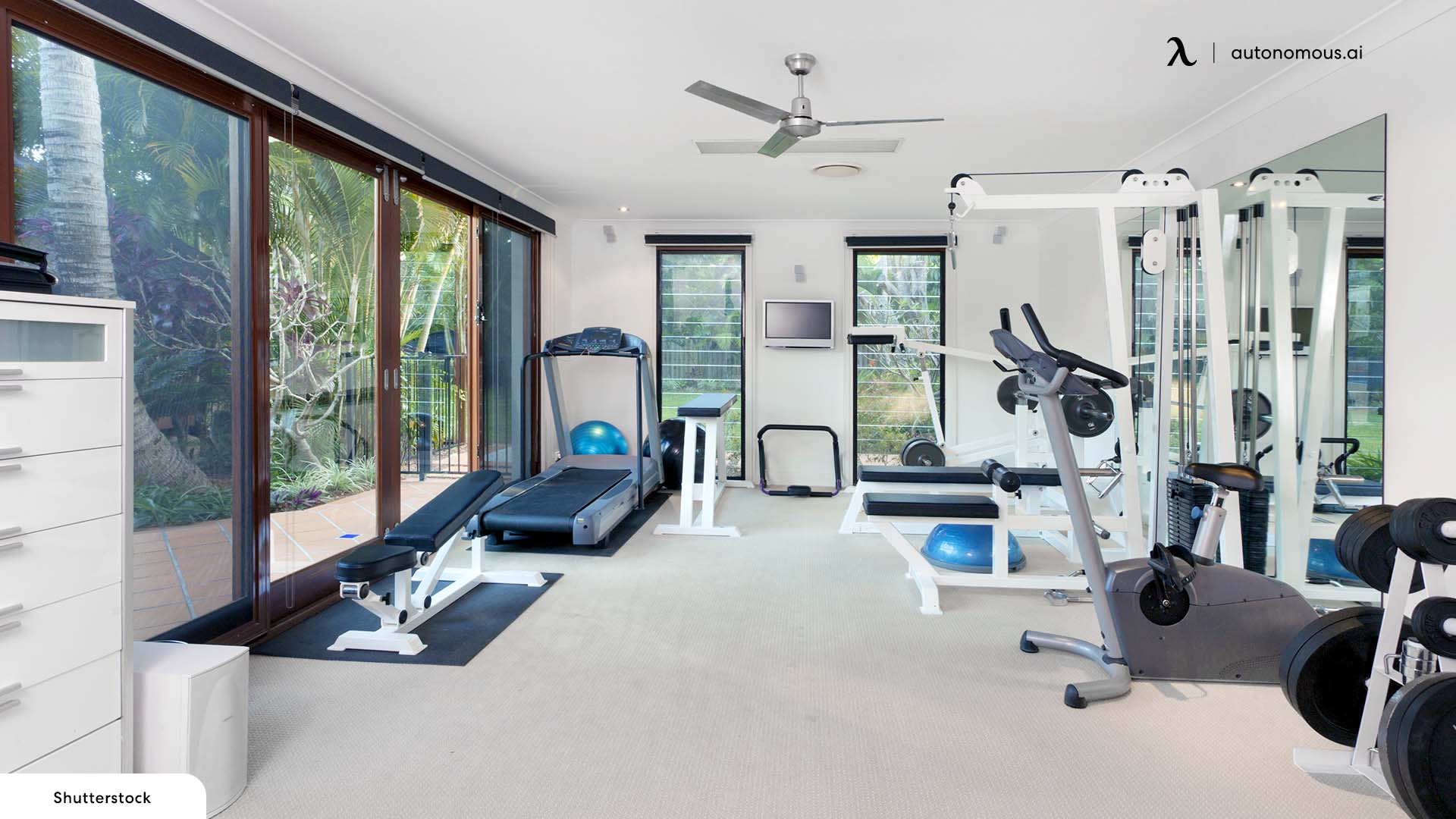



Racks, bins and shelves may organize most sports paraphernalia, but not every weekend warrior’s collection is average. Some athletes can fill entire rooms, sheds or garages with the accoutrements of their particular sport.
Sometimes the gear is just large. Sometimes progressing in the sport means acquiring more equipment. And sometimes nostalgia kicks in, with memories attached to a first medal or first set of skis.
We checked in with four Chattanoogans who’ve had to get creative to corral their vast collections. Here’s how they do it.
Kayaks in the Living Room
Taylor Gauthreaux, 25, says he’s lucky to live with a “chill” roommate who spends most of his free time in his bedroom playing video games. That’s because Gauthreaux’s collection of outdoor equipment is slowly taking over their 924-square-foot condo.
“Our living room is basically a gear closet,” Gauthreaux says. “It’s organized, but it’s definitely a gear closet.”
In his downtime, Gauthreaux can be found whitewater kayaking, rock climbing, bouldering, track climbing, lead climbing, backpacking, open-water swimming, fly fishing or playing disc golf.
All of those interests require particular equipment, which means the self-proclaimed adrenaline junkie has four whitewater boats in the living room, whitewater gear hanging on a banister, paddles in a corner of the laundry room and a bike beneath a stairwell — just for starters. The smaller stuff gets tucked into any empty spot.
“I’m making do with the space,” he says. “It’s quite a scene.”
And, yes, he needs all four boats, he says, as each is geared to different styles of whitewater paddling, his main interest.
Gauthreaux, who works in the mental health field, moved here from West Georgia to earn his graduate degree, “but also for the outdoor potential,” he says.
With Chattanooga’s easy access to outdoor adventures and a community of like-minded enthusiasts, “that made the gear problem worse,” he says. “I want to be prepared for any adventure.”
2,000 Medals … and Counting
An accomplished triathlete, Danny Tolliver requires little more than a bicycle, wetsuit and running shoes to be ready for competition.
But coming home with a finisher medal after each race has posed problems.
“I have all kinds,” says Tolliver. “I have running medals, Ironman, ultramarathon, duathlon, triathlon, marathon, half-marathon. I’ve probably got over 2,000 medals.”
Tolliver, who turns 60 on September 8, took up running in 2015 and cycling about five years later. The combination of skills led him to Ironman competitions (swimming, cycling and running), gran fondos (long-distance road cycling) and all-night ultramarathons (a 100-mile run in Georgia lasted from 8:00 at night to 8:00 the next morning, though “we could stop and rest as long as we got the 100 miles in,” he says).
The result of all this sweat equity is a wall full of colorful ribbons weighted with gleaming medals. They stay in a downstairs den.
“When I first started getting them, I was hanging them on my wall,” he says. “After 20-something medals, I started looking at pictures of how people were putting their medals up. They were getting these ladders from Amazon.”
He ordered three and now keeps his medals looped across each ladder’s six rungs. Top rungs are also a place to prop plaques, occasionally given in addition to or instead of medals, as well as photos of him in competition.
Tolliver, who works as an IT professional for the city of Chattanooga and as a freelance photographer, says at first, he filled the ladders with “maybe 10 or 12 medals across each row, then started going down. Then they just started overlapping. I tried to keep all the biking medals together, but I lost out on that battle a long time ago. Now I just put them where I can.”
Bikes (and Socks) to Spare
Cycling is a shared passion for Melanie Blake, 51, and Ed Kulbis, 48, who combined two large bike collections when they married last year.
“We met on a bike ride,” says Blake. “He showed up wearing bright socks that matched his jersey and helmet. I said, ‘Who’s that guy?” His whole kit [cycling attire] was bright and colorful, and it all matched. That was great. That’s my thing, too.”
Their initial interest grew when they learned they shared not only a love of cycling and socks but also a love of bikes.
“We have mountain bikes. We have road bikes. We have gravel bikes. We have single-speed bikes. And we’ve got multiples of these, depending on where we’re going to ride,” Blake says. “Every bike has a specific use.”
They keep their “daily drivers” in the basement, but the basement can’t hold them all. Others are housed in an office, multipurpose room and storage room on their property, along with various camping and paddling gear.
“We’re building a garage in the next year to put everything in,” says Blake, who works in marketing and website strategy design. Her husband is a process manager in the aerospace industry.
Blake says they hope to eventually add electric bikes to their multitude.
“I’ll never complain about his bikes and gear because I have just as much,” she says.
Coordinating their cycling attire is still a shared passion as well.
“Our sock collection is more ridiculous than our bike collection,” she says.
Health
Van Wert community holds first Hope Walk for Overdose and Suicide Awareness


VAN WERT, Ohio (WLIO) — Van Wert is working to bring hope to those struggling with overdoses, suicide, or the loss of loved ones.
For International Overdose Awareness Day, and to kick off Suicide Awareness and Recovery Month in September, the Tri County Alcohol, Drug Addiction, and Mental Health Services Board held their first-ever Hope Walk. The Van Wert community came together to raise awareness, celebrate recovery and support those grieving the loss of family members or friends.
Speakers shared personal stories of battling mental health or addiction, or reflected on loved ones who died too soon and how they coped with the loss. Organizers said they hope the event helps break down the stigma surrounding these issues.

“Sometimes we don’t want to talk about it, or we’re scared to talk about it. There’s shame and stigma around it, and in order for us to show that, you know, we can talk about it, we got to create opportunities for people to come together to know that it’s okay to not be okay. It’s okay to talk about the people that we’ve lost, to use their stories to to help other people and to know that they can recover and that we’re here to support,” said Anne Dunn, outreach coordinator for Tri County ADAMHS.
The event also connected people to resources available in Van Wert County.
“You can text chat or call with #988 which is a suicide hotline and crisis line. It’s an easy thing to remember, #988. But then we also have partners such as Foundations Behavioral Health, Westwood Behavioral Health and Angel Intervention that are here in Van Wert County, that are all ready and able to help people that are struggling,” Dunn said.
Dunn added that organizers hope to make the Hope Walk an annual event in Van Wert County.
-

 Rec Sports3 weeks ago
Rec Sports3 weeks agoFirst Tee Winter Registration is open
-

 Rec Sports2 weeks ago
Rec Sports2 weeks agoFargo girl, 13, dies after collapsing during school basketball game – Grand Forks Herald
-

 Motorsports2 weeks ago
Motorsports2 weeks agoCPG Brands Like Allegra Are Betting on F1 for the First Time
-

 Motorsports3 weeks ago
Motorsports3 weeks agoF1 Las Vegas: Verstappen win, Norris and Piastri DQ tighten 2025 title fight
-

 Sports2 weeks ago
Sports2 weeks agoTwo Pro Volleyball Leagues Serve Up Plans for Minnesota Teams
-

 Sports2 weeks ago
Sports2 weeks agoUtah State Announces 2025-26 Indoor Track & Field Schedule
-

 Sports2 weeks ago
Sports2 weeks agoSycamores unveil 2026 track and field schedule
-

 Motorsports2 weeks ago
Motorsports2 weeks agoRedemption Means First Pro Stock World Championship for Dallas Glenn
-

 Motorsports2 weeks ago
Motorsports2 weeks agoJo Shimoda Undergoes Back Surgery
-

 Sports2 weeks ago
Sports2 weeks agoTexas volleyball vs Kentucky game score: Live SEC tournament updates