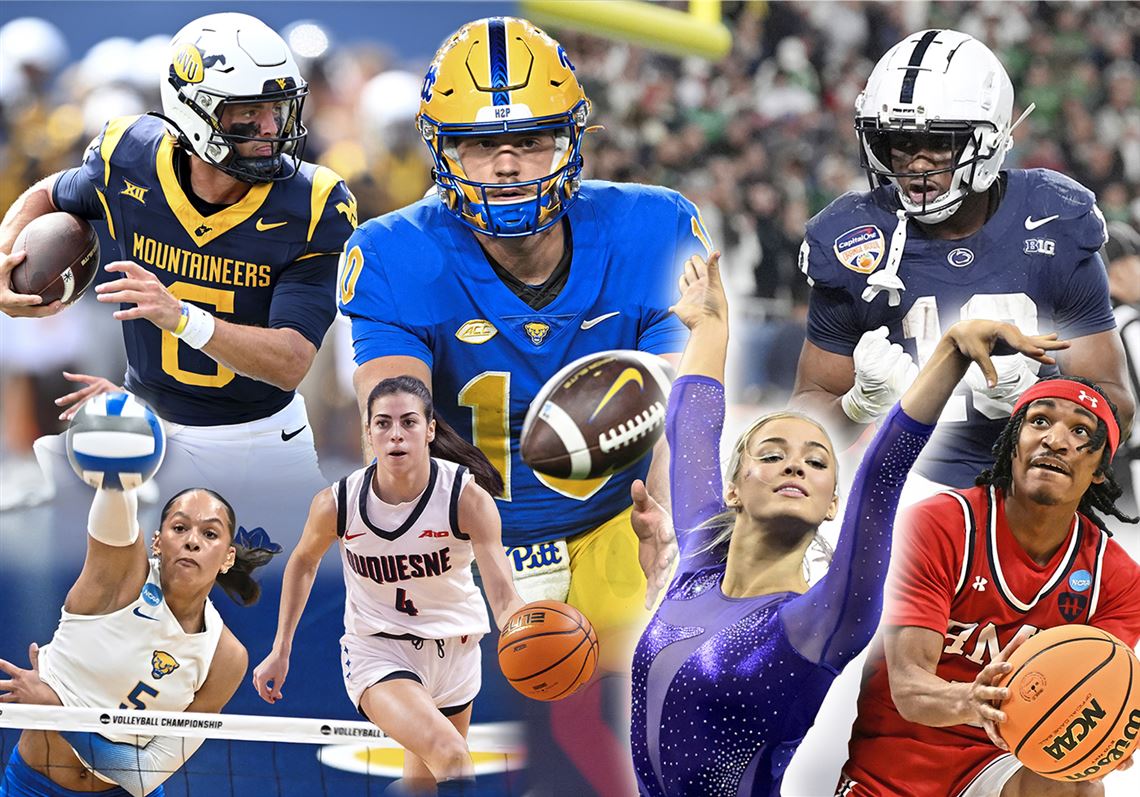
Nazareth Area High School recognized 47 college-bound senior athletes with a signing event last month.
Click the gallery atop this post to see photos from the ceremony and find the full list of signees below:
1/45 2025 Nazareth Area High School signing ceremony Nazareth Area High School recognized 47 college-bound senior athletes with a signing event last month. Click the gallery atop this post to see photos from the ceremony and find the full list of signees below: If you purchase a product or register for an account through a […]
Nazareth Area High School recognized 47 college-bound senior athletes with a signing event last month.
Click the gallery atop this post to see photos from the ceremony and find the full list of signees below:
If you purchase a product or register for an account through a link on our site, we may receive compensation. By using this site, you consent to our User Agreement and agree that your clicks, interactions, and personal information may be collected, recorded, and/or stored by us and social media and other third-party partners in accordance with our Privacy Policy.
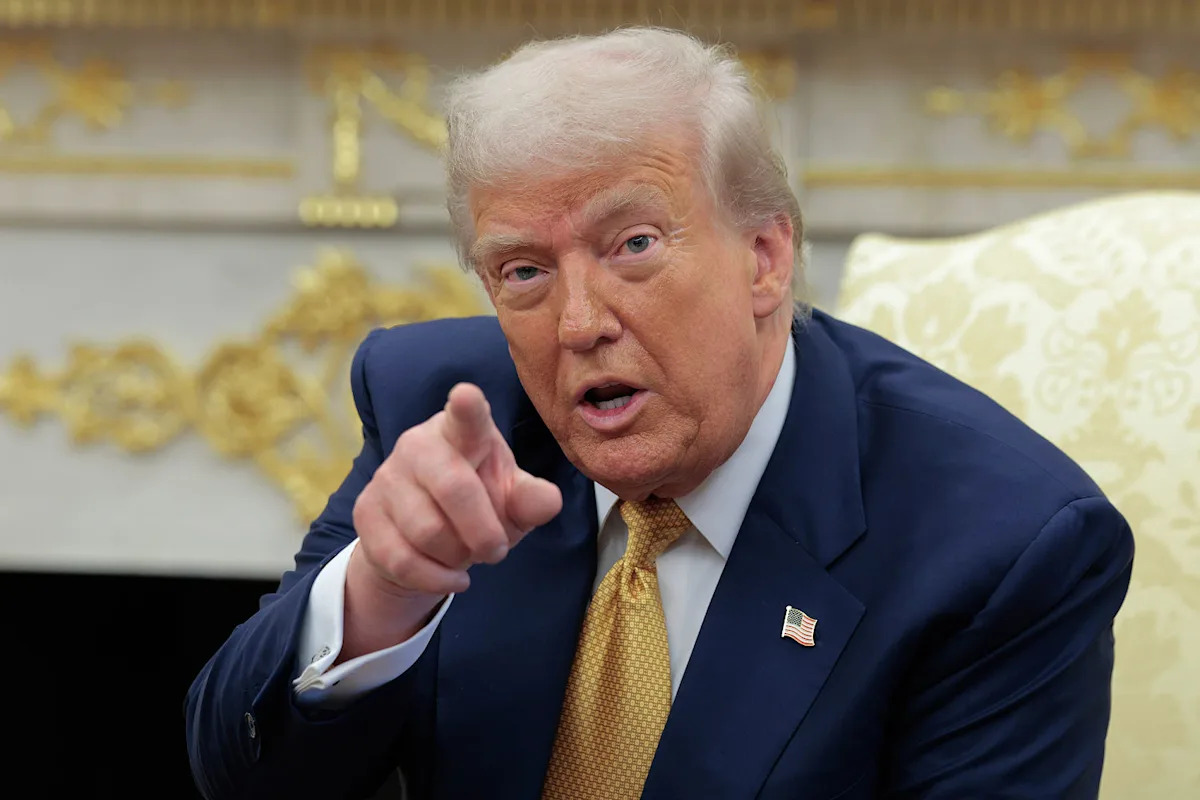
By WILL WEISSERT, Associated Press WASHINGTON — WASHINGTON (AP) — President Donald Trump on Thursday signed an executive order mandating that federal authorities clarify whether college athletes can be considered employees of the schools they play for in an attempt to create clearer national standards in the NCAA’s name, image and likeness era. Trump directed […]

WASHINGTON — WASHINGTON (AP) — President Donald Trump on Thursday signed an executive order mandating that federal authorities clarify whether college athletes can be considered employees of the schools they play for in an attempt to create clearer national standards in the NCAA’s name, image and likeness era.
Trump directed the secretary of labor and the National Labor Relations Board to clarify the status of collegiate athletes through guidance or rules “that will maximize the educational benefits and opportunities provided by higher education institutions through athletics.” The order does not provide or suggest specifics on the controversial topic of college athlete employment.
The move comes after months of speculation about whether Trump will establish a college sports commission to tackle some of the thorny issues facing what is now a multibillion-dollar industry. He instead issued an order intended to add some controls to “an out-of-control, rudderless system in which competing university donors engage in bidding wars for the best players, who can change teams each season.”
“Absent guardrails to stop the madness and ensure a reasonable, balanced use of resources across collegiate athletic programs that preserves their educational and developmental benefits, many college sports will soon cease to exist,” Trump’s order says. “It is common sense that college sports are not, and should not be, professional sports, and my administration will take action accordingly.”
There has been a dramatic increase in money flowing into and around college athletics and a sense of chaos. Key court victories won by athletes angry that they were barred for decades from earning income based on their celebrity and from sharing in the billions of revenue they helped generate have gutted the amateurism model long at the heart of college sports.
Facing a growing number of state laws undercutting its authority, the NCAA in July 2021 cleared the way for athletes to cash in with NIL deals with brands and sponsors — deals now worth millions. That came mere days after a 9-0 decision from the Supreme Court that found the NCAA cannot impose caps on education-related benefits schools provide to their athletes because such limits violate antitrust law.
The NCAA’s embrace of NIL deals set the stage for another massive change that took effect July 1: The ability of schools to begin paying millions of dollars to their own athletes, up to $20.5 million per school over the next year. The $2.8 billion House settlement shifts even more power to athletes, who have also won the ability to transfer from school to school without waiting to play.
At Big Ten Conference football media days in Las Vegas, Purdue coach Barry Odom was asked about the Trump order.
“We’ve gotten to the point where government is involved. Obviously, there’s belief it needs to be involved,” he said. “We’ll get it all worked out. The game’s been around for a hundred years and it’s going to be around 100 more.”
The NCAA has been lobbying for several years for limited antitrust protection to keep some kind of control over this new landscape — and avoid more crippling lawsuits — but a handful of bills have gone nowhere in Congress. Trump’s order makes no mention of that, nor does it refer to any of the current bills in Congress aimed at addressing issues in college sports.
NCAA President Charlie Baker and the nation’s largest conferences both issued statements saying there is a clear need for federal legislation.
“The association appreciates the Trump administration’s focus on the life-changing opportunities college sports provides millions of young people and we look forward to working with student-athletes, a bipartisan coalition in Congress and the Trump administration,” said Baker, while the conferences said it was important to pass a law with national standards for athletes’ NIL rights as soon as possible.
The 1,100 universities that comprise the NCAA have insisted for decades that athletes are students who cannot be considered anything like a school employee. Still, some coaches have recently suggested collective bargaining as a potential solution to the chaos they see.
It is a complicated topic: Universities would become responsible for paying wages, benefits, and workers’ compensation and schools and conferences have insisted they will fight any such move in court. While private institutions fall under the National Labor Relations Board, public universities must follow labor laws that vary from state to state and it’s worth noting that virtually every state in the South has “right to work” laws that present challenges for unions.
Trump’s order also:
— Calls for adding or at least preserving athletic scholarships and roster spots for non-revenue sports, which are those outside football and basketball. The House settlement allows for unlimited scholarships but does impose roster limits, leading to a complicated set of decisions for each program at each school that include potential concerns about Title IX equity rules. Trump said “opportunities for scholarships and collegiate athletic competition in women’s and non-revenue sports must be preserved and, where possible, expanded.”
— Asks the Justice Department and Federal Trade Commission to “preserve college athletics through litigation” and other actions to protect the rights and interests of athletes — a stance that could influence ongoing lawsuits filed by athletes over eligibility and other issues.
— Directs White House staff to work with the U.S. Olympic and Paralympic Committee to protect the collegiate pipeline feeding Team USA. College sports programs produce around three-quarters of U.S. Olympians at a typical Summer Games, but some are on uncertain footing as schools begin sharing revenue with athletes and the lion’s share going to football and basketball.
___
AP National Writer Eddie Pells contributed.
___
AP college sports: https://apnews.com/hub/college-sports
By WILL WEISSERT WASHINGTON (AP) — President Donald Trump on Thursday signed an executive order mandating that federal authorities clarify whether college athletes can be considered employees of the schools they play for in an attempt to create clearer national standards in the NCAA’s name, image and likeness era. Trump directed the secretary of labor […]



By WILL WEISSERT
WASHINGTON (AP) — President Donald Trump on Thursday signed an executive order mandating that federal authorities clarify whether college athletes can be considered employees of the schools they play for in an attempt to create clearer national standards in the NCAA’s name, image and likeness era.
Trump directed the secretary of labor and the National Labor Relations Board to clarify the status of collegiate athletes through guidance or rules “that will maximize the educational benefits and opportunities provided by higher education institutions through athletics.” The order does not provide or suggest specifics on the controversial topic of college athlete employment.
The move comes after months of speculation about whether Trump will establish a college sports commission to tackle some of the thorny issues facing what is now a multibillion-dollar industry. He instead issued an order intended to add some controls to “an out-of-control, rudderless system in which competing university donors engage in bidding wars for the best players, who can change teams each season.”
“Absent guardrails to stop the madness and ensure a reasonable, balanced use of resources across collegiate athletic programs that preserves their educational and developmental benefits, many college sports will soon cease to exist,” Trump’s order says. “It is common sense that college sports are not, and should not be, professional sports, and my administration will take action accordingly.”
There has been a dramatic increase in money flowing into and around college athletics and a sense of chaos. Key court victories won by athletes angry that they were barred for decades from earning income based on their celebrity and from sharing in the billions of revenue they helped generate have gutted the amateurism model long at the heart of college sports.
Facing a growing number of state laws undercutting its authority, the NCAA in July 2021 cleared the way for athletes to cash in with NIL deals with brands and sponsors — deals now worth millions. That came mere days after a 9-0 decision from the Supreme Court that found the NCAA cannot impose caps on education-related benefits schools provide to their athletes because such limits violate antitrust law.
The NCAA’s embrace of NIL deals set the stage for another massive change that took effect July 1: The ability of schools to begin paying millions of dollars to their own athletes, up to $20.5 million per school over the next year. The $2.8 billion House settlement shifts even more power to athletes, who have also won the ability to transfer from school to school without waiting to play.
At Big Ten Conference football media days in Las Vegas, Purdue coach Barry Odom was asked about the Trump order.
“We’ve gotten to the point where government is involved. Obviously, there’s belief it needs to be involved,” he said. “We’ll get it all worked out. The game’s been around for a hundred years and it’s going to be around 100 more.”
The NCAA has been lobbying for several years for limited antitrust protection to keep some kind of control over this new landscape — and avoid more crippling lawsuits — but a handful of bills have gone nowhere in Congress. Trump’s order makes no mention of that, nor does it refer to any of the current bills in Congress aimed at addressing issues in college sports.
NCAA President Charlie Baker and the nation’s largest conferences both issued statements saying there is a clear need for federal legislation.
“The association appreciates the Trump administration’s focus on the life-changing opportunities college sports provides millions of young people and we look forward to working with student-athletes, a bipartisan coalition in Congress and the Trump administration,” said Baker, while the conferences said it was important to pass a law with national standards for athletes’ NIL rights as soon as possible.
The 1,100 universities that comprise the NCAA have insisted for decades that athletes are students who cannot be considered anything like a school employee. Still, some coaches have recently suggested collective bargaining as a potential solution to the chaos they see.
It is a complicated topic: Universities would become responsible for paying wages, benefits, and workers’ compensation and schools and conferences have insisted they will fight any such move in court. While private institutions fall under the National Labor Relations Board, public universities must follow labor laws that vary from state to state and it’s worth noting that virtually every state in the South has “right to work” laws that present challenges for unions.
Trump’s order also:
— Calls for adding or at least preserving athletic scholarships and roster spots for non-revenue sports, which are those outside football and basketball. The House settlement allows for unlimited scholarships but does impose roster limits, leading to a complicated set of decisions for each program at each school that include potential concerns about Title IX equity rules. Trump said “opportunities for scholarships and collegiate athletic competition in women’s and non-revenue sports must be preserved and, where possible, expanded.”
— Asks the Justice Department and Federal Trade Commission to “preserve college athletics through litigation” and other actions to protect the rights and interests of athletes — a stance that could influence ongoing lawsuits filed by athletes over eligibility and other issues.
— Directs White House staff to work with the U.S. Olympic and Paralympic Committee to protect the collegiate pipeline feeding Team USA. College sports programs produce around three-quarters of U.S. Olympians at a typical Summer Games, but some are on uncertain footing as schools begin sharing revenue with athletes and the lion’s share going to football and basketball.
___
AP National Writer Eddie Pells contributed.
Originally Published:
WASHINGTON — President Donald Trump on Thursday signed an executive order mandating that federal authorities clarify whether college athletes can be considered employees of the schools they play for in an attempt to create clearer national standards in the NCAA’s name, image and likeness era. Trump directed the secretary of labor and the National Labor […]

WASHINGTON — President Donald Trump on Thursday signed an executive order mandating that federal authorities clarify whether college athletes can be considered employees of the schools they play for in an attempt to create clearer national standards in the NCAA’s name, image and likeness era.
Trump directed the secretary of labor and the National Labor Relations Board to clarify the status of collegiate athletes through guidance or rules “that will maximize the educational benefits and opportunities provided by higher education institutions through athletics.” The order does not provide or suggest specifics on the controversial topic of college athlete employment.
The move comes after months of speculation about whether Trump will establish a college sports commission to tackle some of the thorny issues facing what is now a multibillion-dollar industry. He instead issued an order intended to add some controls to “an out-of-control, rudderless system in which competing university donors engage in bidding wars for the best players, who can change teams each season.”
“Absent guardrails to stop the madness and ensure a reasonable, balanced use of resources across collegiate athletic programs that preserves their educational and developmental benefits, many college sports will soon cease to exist,” Trump’s order says. “It is common sense that college sports are not, and should not be, professional sports, and my administration will take action accordingly.”
There has been a dramatic increase in money flowing into and around college athletics and a sense of chaos. Key court victories won by athletes angry that they were barred for decades from earning income based on their celebrity and from sharing in the billions of revenue they helped generate have gutted the amateurism model long at the heart of college sports.
Facing a growing number of state laws undercutting its authority, the NCAA in July 2021 cleared the way for athletes to cash in with NIL deals with brands and sponsors — deals now worth millions. That came mere days after a 9-0 decision from the Supreme Court that found the NCAA cannot impose caps on education-related benefits schools provide to their athletes because such limits violate antitrust law.
The NCAA’s embrace of NIL deals set the stage for another massive change that took effect July 1: The ability of schools to begin paying millions of dollars to their own athletes, up to $20.5 million per school over the next year. The $2.8 billion House settlement shifts even more power to athletes, who have also won the ability to transfer from school to school without waiting to play.

Wake Forest running back Demond Claiborne (1) runs back a kick return for a touchdown during the first half of an NCAA college football game against Miami, Saturday, Nov. 23, 2024, in Miami Gardens, Fla. Credit: AP/Lynne Sladky
At Big Ten Conference football media days in Las Vegas, Purdue coach Barry Odom was asked about the Trump order.
“We’ve gotten to the point where government is involved. Obviously, there’s belief it needs to be involved,” he said. “We’ll get it all worked out. The game’s been around for a hundred years and it’s going to be around 100 more.”
The NCAA has been lobbying for several years for limited antitrust protection to keep some kind of control over this new landscape — and avoid more crippling lawsuits — but a handful of bills have gone nowhere in Congress. Trump’s order makes no mention of that, nor does it refer to any of the current bills in Congress aimed at addressing issues in college sports.
NCAA President Charlie Baker and the nation’s largest conferences both issued statements saying there is a clear need for federal legislation.

North Carolina coach Bill Belichick speaks with a group of reporters during the Atlantic Coast Conference’s NCAA college football media days, Thursday, July 24, 2025, in Charlotte, N.C. Credit: AP/Aaron Beard
“The association appreciates the Trump administration’s focus on the life-changing opportunities college sports provides millions of young people and we look forward to working with student-athletes, a bipartisan coalition in Congress and the Trump administration,” said Baker, while the conferences said it was important to pass a law with national standards for athletes’ NIL rights as soon as possible.
The 1,100 universities that comprise the NCAA have insisted for decades that athletes are students who cannot be considered anything like a school employee. Still, some coaches have recently suggested collective bargaining as a potential solution to the chaos they see.
It is a complicated topic: Universities would become responsible for paying wages, benefits, and workers’ compensation and schools and conferences have insisted they will fight any such move in court. While private institutions fall under the National Labor Relations Board, public universities must follow labor laws that vary from state to state and it’s worth noting that virtually every state in the South has “right to work” laws that present challenges for unions.
Trump’s order also:
— Calls for adding or at least preserving athletic scholarships and roster spots for non-revenue sports, which are those outside football and basketball. The House settlement allows for unlimited scholarships but does impose roster limits, leading to a complicated set of decisions for each program at each school that include potential concerns about Title IX equity rules. Trump said “opportunities for scholarships and collegiate athletic competition in women’s and non-revenue sports must be preserved and, where possible, expanded.”
— Asks the Justice Department and Federal Trade Commission to “preserve college athletics through litigation” and other actions to protect the rights and interests of athletes — a stance that could influence ongoing lawsuits filed by athletes over eligibility and other issues.
— Directs White House staff to work with the U.S. Olympic and Paralympic Committee to protect the collegiate pipeline feeding Team USA. College sports programs produce around three-quarters of U.S. Olympians at a typical Summer Games, but some are on uncertain footing as schools begin sharing revenue with athletes and the lion’s share going to football and basketball.
___
AP National Writer Eddie Pells contributed.
Story Links 2024-25 CSCAA Scholar All-America Team Release Spring 2025 CSCAA Scholar All-America Teams Release Three Hamilton College women’s swimmers earned College Swimming & Diving Coaches Association of America (CSCAA) Scholar All-America Team honors for the 2024-25 […]

Three Hamilton College women’s swimmers earned College Swimming & Diving Coaches Association of America (CSCAA) Scholar All-America Team honors for the 2024-25 season on Thursday, July 10 when the organization released its list.
Ashlyn Blessey ’26 (Fairfield, Conn./Academy of Our Lady of Mercy, Lauralton Hall), Jade Matthias ’26 (Reading, Pa./Mercersburg Academy) and Carolyn Miner ’27 (Manchester, Conn./Manchester HS) collected first team awards. To qualify for first team Scholar All-America, student-athletes must have earned a grade point average of 3.5 or better and participated in their national championship.
Blessey, Matthias and Miner qualified for the 2025 NCAA Division III Swimming and Diving Championships as part of a 200-yard freestyle relay. They also competed in the 400 free relay at the championships. Matthias has been a scholar all-American all three years and Blessey previously was honored in 2023.
The Continentals were recognized as a CSCAA Scholar All-America Team for the 2025 spring semester. Teams were required to achieve a grade point average of 3.00 or better during the semester in order to earn the prestigious honor. The Hamilton women posted a 3.70 GPA and picked up the award for the eighth straight semester under Head Coach John Geissinger.
WASHINGTON — President Donald Trump on Thursday signed an executive order prohibiting “third party, pay-for-play” payments to college athletes, a move the White House is taking to curb “bidding wars” that have roiled college sports in recent years. The order, a fact sheet that was shared in advance with NBC News by a White House […]

WASHINGTON — President Donald Trump on Thursday signed an executive order prohibiting “third party, pay-for-play” payments to college athletes, a move the White House is taking to curb “bidding wars” that have roiled college sports in recent years.
The order, a fact sheet that was shared in advance with NBC News by a White House official, notes that recent court rulings have dismantled the NCAA’s transfer and recruiting rules and “created a chaotic environment that threatens the financial and structural viability of college athletics.”
Advertisement
The order could send shockwaves through college football and men’s basketball, where player recruitment in the so-called transfer portal has become a multimillion-dollar market in recent years, with top teams spending tens of millions to fill out rosters.
The order would not apply to fair-market compensation for athletes who make brand endorsements, according to the White House.
The order also looks to protect women’s and nonrevenue sports by mandating that revenue sharing between universities and college athletes be implemented in a manner that protects those programs.
The president’s order also notes that a patchwork of laws in 30 states have contributed to competitive imbalances in sports.
Advertisement
It was not immediately clear how the proposed order would be enforced, or what mechanisms were in place to ensure revenue is shared more equitably between men’s and women’s and nonrevenue-generating sports.
This article was originally published on NBCNews.com
The latest plot twist in an attempt to create clearer national standards surrounding name, image and likeness in college sports surfaced on Thursday afternoon. President Donald Trump signed an executive order mandating that federal authorities clarify whether college athletes can be considered employees of the schools they play for. The move comes amid a dramatic […]

The latest plot twist in an attempt to create clearer national standards surrounding name, image and likeness in college sports surfaced on Thursday afternoon.
President Donald Trump signed an executive order mandating that federal authorities clarify whether college athletes can be considered employees of the schools they play for.
The move comes amid a dramatic increase in the money flowing into and around college athletics. It also follows key court victories won by current and former athletes angry that they were barred for decades, both from earning income based on their celebrity and from sharing in the billions of revenue they helped generate.
Facing a growing number of state laws undercutting its authority, the NCAA cleared the way for athletes to cash in with NIL deals with brands and sponsors back in July 2021.
That came mere days after a 9-0 decision from the Supreme Court that found the NCAA cannot impose caps on education-related benefits schools provide to their athletes because such limits violate antitrust law.
Trump’s action directs the secretary of labor and the National Labor Relations Board to clarify the status of collegiate athletes through guidance or rules “that will maximize the educational benefits and opportunities provided by higher education institutions through athletics.”
The NCAA’s embrace of NIL deals set the stage for another massive change that took effect July 1: The ability for schools to begin paying millions of dollars to their own athletes, up to $20.5 million per school over the next year. The $2.8 billion House settlement shifts even more power to college athletes, who have also won the ability to transfer from school to school without having to sit out a year.
The NCAA has been lobbying for several years for limited antitrust protection to keep some kind of control over this new landscape — and avoid more crippling lawsuits — but a handful of bills have gone nowhere in Congress.
The 1,100 universities that comprise the NCAA have insisted for decades that athletes are students who cannot be considered anything like a school employee. This stance has long been a part of the amateur model at the heart of college athletics, but that model is rapidly being replaced by a more professional structure fed by money that is coming from donors, brands and now the schools themselves.

Some coaches have even suggested collective bargaining is a potential solution to the chaos they see. Universities would become responsible for paying wages, benefits, and workers’ compensation and schools and conferences have insisted they will fight any such move in court.
While private institutions fall under the National Labor Relations Board, public universities must follow labor laws that vary from state to state, and it’s worth noting that virtually every state in the South has “right to work” laws that present challenges for unions.
The Associated Press contributed to this report.
Want great stories delivered right to your inbox? Create or log in to your FOX Sports account, follow leagues, teams and players to receive a personalized newsletter daily!
recommended

Get more from the College Football Follow your favorites to get information about games, news and more


Why a rising mid-major power with an NCAA Tournament team opted out of revenue-sharing — and advertised it


New 'Bosch' spin


EA Sports College Football 26 review – They got us in the first half, not gonna lie

Volleyball Releases 2025 Schedule – Niagara University Athletics


MSU Hockey News – The Only Colors


E.l.f Cosmetics Builds Sports Marketing Game Plan Toward Bigger Goals


CAREGD Trademark Hits the Streets for Mental Health Month


Buford DB Tyriq Green Commits to Georgia


Will LeBron James request a trade? 🤔 Windy says MULTIPLE TEAMS would make offers 👀 | NBA Today


Will Giannis DEPART Milwaukee⁉️ + How signing Turner & waiving Dame impacts the Bucks | NBA Today