Abstract Dornaika, F. Flexible data representation with feature Convolution for semi-supervised learning. Appl. Intell. 51 (11), 7690–7704 (2021). Introduction Research background and motivations MATH Google Scholar MATH Google Scholar Thomas, A., Ré, C. & Poldrack, R. Self-supervised learning of brain dynamics from broad neuroimaging data. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 21255–21269 (2022). Research objectives […]

Abstract
Introduction
Research background and motivations
MATH
Google Scholar
MATH
Google Scholar
Thomas, A., Ré, C. & Poldrack, R. Self-supervised learning of brain dynamics from broad neuroimaging data. Adv. Neural. Inf. Process. Syst. 35, 21255–21269 (2022).
Research objectives
Literature review: This study conducts a comprehensive and in-depth review of relevant domestic and international literature. The focus is on the research status, existing issues, and improvement strategies concerning the quality of public sports services. By systematically summarizing existing research findings, this study extracts valuable theoretical insights and practical guidance, laying a solid theoretical foundation and providing abundant practical reference examples.
-
(1)
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
-
(2)
Ying Yan: Conceptualization, methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, investigation, resources, data curation, writing—original draft preparation, writing—review and editing, visualization, supervision, project administration, funding acquisition.
-
(3)
Technical model based on supervised learning.
-
(4)
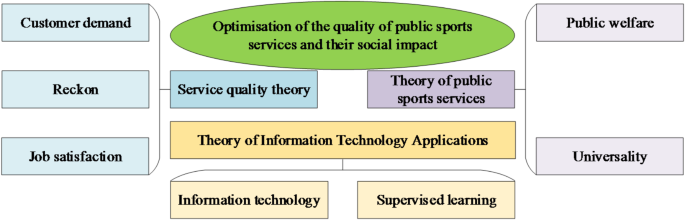
Figure 1demonstrates that the innovation of the theoretical framework lies in its comprehensiveness and foresight. It innovatively integrates public sports service theory, service quality theory, and IT application theory, constructing a multidimensional and interdisciplinary analytical framework37. This innovation not only breaks through the limitations of traditional research on single theories but also fully considers the driving role of modern IT applications in optimizing the quality of public sports services. Furthermore, this theoretical framework also emphasizes practical application, highlighting the close integration of theoretical guidance and empirical research, furnishing feasible ideas and strategies for improving the quality of public sports services38. Hence, the theoretical framework’s innovativeness plays an essential guiding role in promoting research and practice in public sports services.
Literature review
Google Scholar
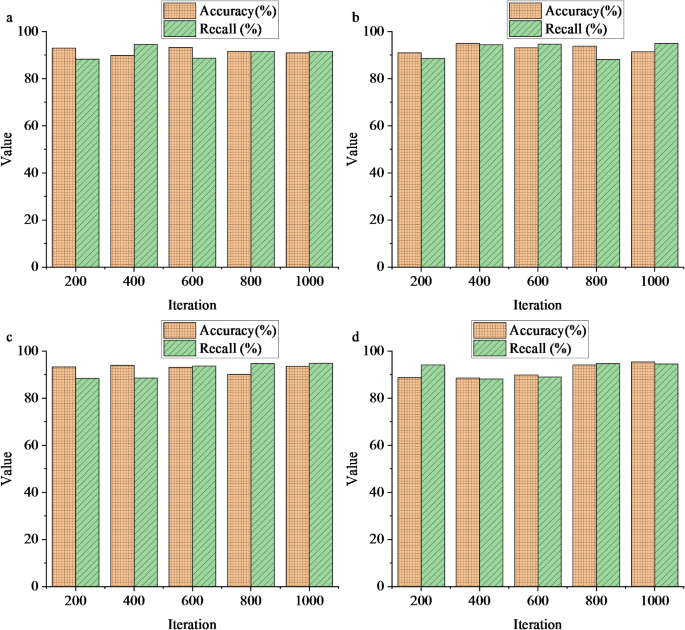
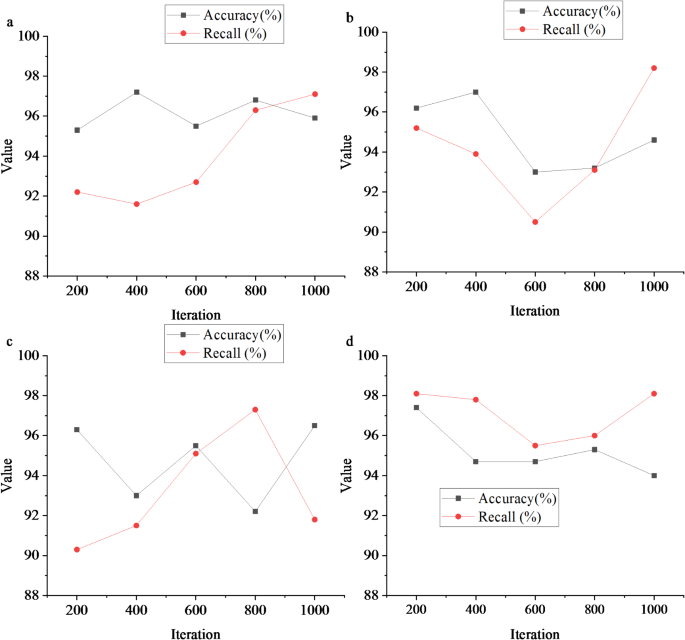
Figure 3 depicts that this study conducts a comprehensive evaluation of the model using four different data formats. These data encompass various types of public sports service data, including user feedback, facility usage, and service quality evaluations, among others. Through processing and analyzing these data, the model demonstrates excellent performance. The evaluation results indicate that the model maintains an accuracy of over 88% for handling diverse types of data, which is quite satisfactory. Accuracy is a crucial metric for measuring whether the model’s predictions are correct, and an accuracy exceeding 88% implies that the model can accurately capture data features and make correct predictions. Moreover, the recall also exceeds 88%, further confirming the effectiveness of the model in identifying relevant data. Recall measures the model’s ability to find all relevant instances, and a high recall suggests that the model can identify as many relevant data points as possible. Thus, the model constructed in this study exhibits remarkable advantages and potential in optimizing public sports service quality. It can accurately handle and analyze various types of data, affording robust support for enhancing public sports service quality. These findings validate the feasibility and effectiveness of the model and lay a solid foundation for subsequent research and applications.
Research model
PubMed
PubMed Central
MATH
Google Scholar
ADS
CAS
PubMed
PubMed Central
MATH
Google Scholar
Surek, G. A. S. et al. Video-based human activity recognition using deep learning approaches. Sensors 23 (14), 6384 (2023).
CAS
MATH
Google Scholar
Bai, Z. & Bai, X. Sports big data: management, analysis, applications, and challenges. Complexity, 2021: 1–11. (2021).
Sharma, H. K., Choudhury, T. & Kandwal, A. Machine learning based analytical approach for geographical analysis and prediction of Boston City crime using geospatial dataset. GeoJournal, 88(Suppl 1): 15–27. (2023).College of Physical Education, Hunan City University, Yiyang, 413000, Hunan, China
-
(1)
Second, the supervised learning model’s application in service quality optimization is gradually becoming prominent. This model can predict future service demands, optimize resource allocation, and improve service quality by training and learning from historical data11. In the field of public sports, some studies have attempted to apply the supervised learning model to evaluate and predict service quality, achieving certain effectiveness12. However, current research is still in its early stages, and aspects such as model selection, data processing, and result interpretation require further improvement.
-
(2)
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. All methods were performed in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations.
- (3)
-
(4)
Results of model basic evaluation (a: text; b: images; c: videos; d: comprehensive data).
MATH
Google Scholar
The influence of optimized public sports service quality on public sports participation and sports health level has been deeply explored. By comparing and analyzing the data changes before and after optimization, the actual effect of optimization measures is evaluated, and the deep reasons and mechanisms behind it are discussed, to afford a scientific basis for policy formulation.
Experimental design and performance evaluation
Datasets collection
MathSciNet
Google Scholar
PubMed
MATH
Google Scholar
Experimental environment
As a vital part of the development of modern society, public sports service is not only related to the improvement of national physique but also an important embodiment of the prosperity and development of cultural and sports undertakings1. However, with the growing public demand for sports services, how to improve the quality of public sports services to meet diversified and personalized needs has become an urgent problem to be solved2. At the same time, the swift progress of information technology (IT), especially the extensive application of big data, artificial intelligence, and other technologies, has provided new ideas and methods for the optimization of public sports services3.
Parameters setting
Evaluation of model application effects (a is text, b is image, c is video, d is comprehensive data).
Performance evaluation
MATH
Google Scholar
Ying Yan
The theoretical framework of this study is mainly based on the theory of service quality, public sports service, and IT applications. Firstly, the service quality theory is the cornerstone of this study. This theory emphasizes that service providers should pay attention to customers’ needs and expectations, and satisfy customers’ satisfaction by providing high-quality services. In the field of public sports services, this means the need to pay attention to the needs and expectations of the public on sports facilities, service processes, personnel quality, and so on, and optimize the service quality accordingly. Secondly, the public sports service theory provides concrete theoretical support for this study. The theory emphasizes the public welfare and universality of public sports services, aiming to promote the development of national fitness by offering high-quality sports services. Based on the relevant viewpoints of public sports service theory, this study analyzes the current situation and influencing factors of public sports service quality and proposes targeted optimization strategies21,22,23. Finally, the IT application theory furnishes theoretical support for applying a supervised learning model in optimizing public sports service quality. With the continuous development of IT, machine learning techniques such as supervised learning models have been widely used in various fields. In the field of public sports services, the supervised learning model can be used to conduct training and learning from historical data, predict future service demand, optimize resource allocation, and improve service quality24,25,26,27,28.Bunker et al. (2021) utilized the supervised learning model to successfully predict future public sports service demand by analyzing historical service data. The model effectively identified the seasonality, periodicity, and sudden changes in service demand based on facility usage, personnel flow data, and user feedback. This provided a scientific basis for the planning of public sports facilities, personnel allocation, and adjustment of service content, contributing to the improvement of service efficiency and quality13. Pelati et al. (2022) applied supervised learning algorithms to construct a multidimensional service quality evaluation model. This model comprehensively considered aspects such as service attitude, facility conditions, and service processes. By training and learning from a large amount of user evaluation data, the model achieved an objective and accurate assessment of service quality. The research results indicated that the supervised learning model exhibited high accuracy and stability in service quality evaluation, offering strong support for the continuous improvement of service quality14. Tang et al. (2021), through a comparative analysis of the application effects of different supervised learning models in optimizing public sports services, proposed a data-driven service optimization strategy. This strategy involved real-time monitoring of service data, utilizing model predictions of changing service demand trends and adjusting service content and methods accordingly. Practical results demonstrated that this data-driven service optimization strategy based on supervised learning models notably enhanced service satisfaction and user retention, thus playing a crucial role in improving the public sports services’ overall competitiveness15. The existing studies are summarized in Table 1.Parameter setting is a crucial step in constructing and training supervised learning models to optimize the quality of public sports services. Parameter settings determine the complexity and learning ability of the model and directly affect the model’s performance. The design results of model parameters are exhibited in Table 3.
Discussion
Ramkumar, P. N. et al. Sports medicine and artificial intelligence: a primer. Am. J. Sports Med. 50 (4), 1166–1174 (2022).Tang, Y. et al. Triple cross-domain attention on human activity recognition using wearable sensors. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top. Comput. Intell. 6 (5), 1167–1176 (2022).
Conclusion
Research contribution
Chen, L. & Li, S. Human motion target posture detection algorithm using semi-supervised learning in internet of things. IEEE Access. 9, 90529–90538 (2021).
Future works and research limitations
Chmait, N. & Westerbeek, H. Artificial intelligence and machine learning in sport research: an introduction for non-data scientists. Front. Sports Act. Living. 3, 363 (2021).
Data availability
Data analysis: This study utilizes various statistical methods. Descriptive statistics are first applied to display basic survey results and data distribution characteristics. Based on this, correlation and regression analysis are employed to investigate the extent to which different factors impact the quality of public sports services, accurately identifying key influencing factors and providing strong data support for formulating optimization strategies.
References
- PubMed
PubMed Central
MATH
Google Scholar
(2) Evaluation of model application effects. - Survey questionnaire: A multidimensional questionnaire covering aspects such as satisfaction with sports facilities, service process satisfaction, and staff quality satisfaction is designed and widely distributed to different groups. By gathering extensive user feedback and applying scientific statistical analysis methods, the study aims to gain a deep understanding of the public’s actual needs and expectations, providing reliable quantitative evidence for optimizing service quality.MATH
Google Scholar - ADS
MATH
Google Scholar
The study of the optimization of public sports service quality and its social impact has always been a hot spot in the interdisciplinary research of sports science, sociology, and management4. First, the research on the quality of public sports services has been deeply discussed by domestic and international scholars from different angles. The concept, influencing factors, and evaluation methods of service quality have become the core contents of the research5. Among them, facilities, service processes, personnel quality, and other aspects are considered to be the key factors affecting service quality6. Simultaneously, with the development of IT, the application of information services in sports services has gradually attracted attention7.
Google Scholar
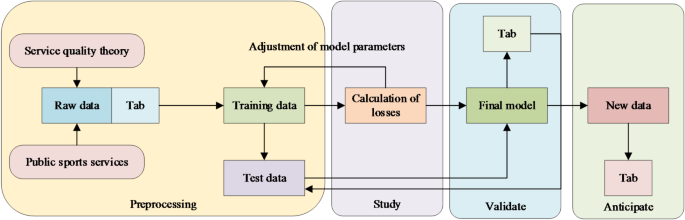
Overall, the selected dataset covers various aspects of public sports services, such as long-term facility conditions, service processes, and user feedback, which are crucial for optimizing public sports services. By applying appropriate mathematical and statistical methods to analyze this dataset, potential patterns and trends within the historical data can be identified. For instance, through regression analysis, the relationship between different variables and service demand can be explored, leading to the development of predictive models. Before delving into the construction and application of the technical model, it is essential to explain the problem based on mathematical principles. This includes precisely defining the objective function, constraints, and variables related to the optimization of public sports service quality. For example, the objective function could be to maximize overall user satisfaction, considering constraints such as limited resources and service capacity. Moreover, the design of the technical model should account for the complexity of the problem. Given the multifaceted nature of public sports services, the model must incorporate various factors and their interactions. Additionally, the model should be scalable to ensure its effectiveness and efficiency when handling large datasets and complex scenarios. Regarding the data training and testing process, a detailed and systematic explanation is required. During the training phase, a portion of the dataset is used to train the model through specific algorithms. For instance, within the supervised learning framework, labeled data is utilized to adjust model parameters to minimize the loss function. In the testing phase, an independent subset of the dataset is used to evaluate the performance of the trained model, with accuracy and recall being employed to measure its effectiveness. Through this comprehensive approach to dataset analysis, problem formulation, and model training and testing, this study aims to propose practical optimization strategies. Therefore, it can effectively enhance the overall quality of public sports services, promote the successful implementation of national fitness programs, and ultimately encourage public participation in sports activities and improve overall health levels.- Worsey, M. T. et al. One size doesn’t fit all: supervised machine learning classification in athlete-monitoring. IEEE Sens. Lett. 5 (3), 1–4 (2021).Verma, S. Sentiment analysis of public services for smart society: literature review and future research directions. Government Inform. Q. 39 (3), 101708 (2022).
- The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author Ying Yan on reasonable request via e-mail yanying@hncu.edu.cn.Himeur, Y. et al. AI-big data analytics for Building automation and management systems: a survey, actual challenges and future perspectives. Artif. Intell. Rev. 56 (6), 4929–5021 (2023).
- Ramon, X. & Rojas-Torrijos, J. L. Public service media, sports and cultural citizenship in the age of social media: an analysis of BBC sport agenda diversity on Twitter. Int. Rev. Sociol. Sport. 57 (6), 918–939 (2022).Schiappa, M. C., Rawat, Y. S. & Shah, M. Self-supervised learning for videos: A survey. ACM Comput. Surveys. 55 (13s), 1–37 (2023).
- Aiyanyo, I. D., Samuel, H. & Lim, H. Effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on classrooms: A case study on foreigners in South Korea using applied machine learning. Sustainability 13 (9), 4986 (2021).Schiappa et al. (2023) first defined the connotation of public sports service quality and constructed a comprehensive evaluation system from aspects such as facility conditions, service processes, and personnel quality. Through on-site investigations and data analysis of multiple public sports venues, the study found numerous issues in facility maintenance, service efficiency, and personnel training in current public sports services. Addressing these problems, the study proposed specific strategies such as enhancing facility maintenance, optimizing service processes, and improving personnel quality, aiming to enhance the public sports services’ overall quality8. Ramon et al. (2022) focused on the application of digital technology in innovation within public sports services. Through in-depth investigations and field interviews, they analyzed how digital technology reshaped the patterns and processes of public sports services. The research revealed that the application of digital technology not only enhanced the convenience and personalization of services but also promoted the optimization and sharing of sports resources9. Smith et al. (2023) utilized big data analysis and mining techniques to deeply process and analyze large amounts of data in the process of public sports services. By constructing a service quality evaluation model, they successfully identified critical factors influencing service quality and proposed targeted improvement measures. This study provided a scientific basis for the quality management of public sports services and laid a solid foundation for improving public satisfaction and sports health levels10.
- ADS
PubMed
PubMed Central
MATH
Google Scholar
Logacjov, A. & Bach, K. Self-supervised learning with randomized cross-sensor masked reconstruction for human activity recognition. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 128, 107478 (2024). - Based on all of the above premises, this study conducts an in-depth investigation and analysis by using a dataset for model training, testing, and evaluation. The selected dataset is the “Comprehensive Evaluation Dataset of Urban Public Sports Services”, which has been carefully collated for in-depth analysis of various aspects of urban public sports services. The dataset covers multiple dimensions such as facility conditions, service processes, personnel quality, public feedback, and usage patterns to ensure the comprehensiveness and richness of the data. Through this dataset, the operation status, service efficiency, and public satisfaction of various sports facilities can be understood in detail, to provide solid data support for improving the quality of public sports service. Specifically, the dataset can reveal the specific operation of diverse sports facilities, evaluate the effectiveness of their services, and analyze the level of public satisfaction with the services. This information is of great significance for identifying the shortcomings and room for improvement in the service. In addition, the dataset also highlights comparative analysis between different cities and communities, helping to identify commonalities and differences in the provision of public sports services. This kind of comparative analysis not only reveals the successful experience and shortcomings of public sports services in different places but also offers a reference for other cities and communities to promote public sports services’ popularization and optimization.Sarker, M. I. et al. Semi-supervised anomaly detection in video-surveillance scenes in the wild. Sensors 21 (12), 3993 (2021).
- PubMed
MATH
Google Scholar
Published:
Google Scholar
In summary, despite certain progress in the research on public sports service quality and its impact, there are still many shortcomings and unresolved issues. Building upon this foundation, this study further explores the application of supervised learning models in optimizing public sports service quality and deeply analyzes the specific effects of optimized service quality on public sports participation and sports health levels. By comprehensively employing various research methods and technical means, the aim is to provide scientific evidence and practical guidance for the public sports services’ continuous improvement and healthy development.- A perfect experimental environment is constructed to ensure the supervised learning model’s effective application in the optimization of public sports service quality. The experimental environment mainly includes hardware and software. In terms of hardware, a high-performance computer server is used, equipped with enough memory and storage space to guarantee that the data processing and calculation needs are met during the model training process. Moreover, to accelerate the model’s training process, the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) is also used to accelerate the device, which prominently improves the model’s training speed and efficiency. The experimental environment design of this study is outlined in Table 2.
Nahavandi, D. et al. Application of Artificial Intelligence in Wearable Devices: Opportunities and Challenges213106541 (Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2022).Targeted optimization strategies for public sports service quality are proposed. According to the actual situation, feasible optimization measures are formulated for the weak links in the service process.
PubMed
PubMed Central
MATH
Google Scholar
MATH
Google Scholar
Google Scholar
MATH
Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Yuan, H. et al. Self-supervised learning for human activity recognition using 700,000 person-days of wearable data. Npj Digit. Med. 7 (1), 91 (2024).
PubMed
PubMed Central
MATH
Google Scholar
PubMed
PubMed Central
MATH
Google Scholar
Yan, Y. The optimization and impact of public sports service quality based on the supervised learning model and artificial intelligence.
Sci Rep 15, 9923 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-94613-x
PubMed Central
MATH
Google Scholar
MATH
Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Google Scholar
MATH
Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Pelati, A., Meo, M. & Dini, P. Traffic anomaly detection using deep semi-supervised learning at the mobile edge. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 71 (8), 8919–8932 (2022).
Google Scholar
Ying Yan
MATH
Google Scholar
MATH
Google Scholar
ADS
CAS
PubMed
PubMed Central
MATH
Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Google Scholar
Wang, S. et al. Seeded random walk for multi-view semi-supervised classification. Knowl. Based Syst. 222, 107016 (2021).
The purpose of this study is to deeply explore the optimization path of public sports service quality and its social impact. Specifically, the objectives of this study are as follows:
Funding
Author information
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Keiper, M. C. et al. Artificial intelligence in sport management education: playing the AI game with ChatGPT. J. Hospitality Leisure Sport Tourism Educ. 33, 100456 (2023).
Ethics statement
Correspondence to
Ying Yan.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duarte, V., Zuniga-Jara, S. & Contreras, S. Machine learning and marketing: A systematic literature review. IEEE Access. 10, 93273–93288 (2022).MATH
Google Scholar
- Download citation
- School of Educational Studies, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Gelugor, Penang, 11800, Malaysia
- Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
- PubMed
MATH
Google Scholar