NIL
The Rise Of Women's Sports



Tracy Call, CEO of Media Bridge, co-founded Highlight Reel with Griffin Archer to reshape sports marketing through an integrated approach.
Women’s sports aren’t just having a moment; they’re leading a movement. Viewership is breaking records, attendance is climbing, and athletes are becoming household names. Yet many brands still treat sports sponsorships as side projects rather than a fundamental part of their marketing strategy.
For too long, sponsorships have been an exercise in logo placement and premium seating. Brands slap their name on a jersey or a scoreboard and call it a day. But there’s an opportunity to do so much more. At my agency, and at the sports marketing firm we recently cofounded, we believe that instead of being an ego play, women’s sports sponsorships should be fully integrated into a brand’s marketing mix, leveraging creative storytelling and delivering measurable impact.
The Opportunity: Go Beyond Traditional Sponsorships
Women’s sports teams offer incredible platforms for brands to engage passionate and loyal fan bases. However, many sponsorship deals still rely on templated packages that don’t fully maximize brand engagement. Brands have a chance to work more collaboratively with teams to build activations that create meaningful interactions rather than just brand visibility.
What if, instead of buying a one-size-fits-all package, brands co-created activations tailored to their unique objectives? What if success wasn’t just measured in impressions but in conversions, engagement and long-term brand loyalty?
A Smarter Approach To Women’s Sports Sponsorships
Sports sponsorships should function like any other media channel: They should be data-driven, strategically integrated and designed for measurable impact.
Here’s how brands should be thinking about women’s sports partnerships:
Start With Research, Not Personal Preference
You might love basketball, but if your target customer is watching tennis or volleyball, that’s where your investment should be. At my agency, we always start with the data. It’s not about what we like; it’s about aligning brands with the sports and athletes their audience already cares about.
Ask your agency or media partners for audience insights specific to women’s sports. Tap into social listening to see where the real-time conversations are happening. And don’t be afraid to go straight to the source—most women’s leagues have valuable fan data they’re ready to share.
Move Beyond The Logo
Visibility alone doesn’t build brand loyalty. True connection comes from storytelling, shared values and memorable experiences.
Partner with athletes to co-create content on platforms where their voices feel most personal, often social or community-based events. Align with causes that matter to their fans, and follow through with real action, whether that’s local activations, charitable support or collaborative campaigns. Focus on creating memorable moments through behind-the-scenes access, fan surprises or purpose-driven storytelling that invites people into the heart of your brand. That’s how you build lasting connections in women’s sports.
Measure Everything
Courtside tickets may impress executives, but what’s the actual return? Make sure you track lead generation, purchase behavior, social engagement and brand lift. If the sponsorship isn’t delivering, it’s time to pivot.
Foster True Partnerships With Teams
Sports teams are valuable partners, and collaboration is key. By working closely with teams, you can ensure that your sponsorships are fully realized, creating campaigns that extend beyond the arena and into digital, social and experiential marketing strategies.
As a former Team USA bobsled athlete and rugby player, I know firsthand that what women’s sports need most is financial support. In bobsled, we paid for our own gear and travel—and even the sled transportation for some races. A single sponsor often meant the difference between competing or staying home. When brands invest, it’s deeply felt. And because most female athletes aren’t used to that kind of backing, their loyalty tends to run deep, often delivering a higher ROI than expected. Treat the team like a partner, not an ad placement, and the impact will go far beyond the game.
Integrate Across Channels
A sports sponsorship isn’t a one-and-done strategy; it should fuel content, social engagement, digital marketing and in-store promotions. The most successful brands amplify their sponsorships across every touchpoint.
To get the most out of a women’s sports sponsorship, integration is key. Tailor your message by channel. What works in a stadium won’t always land the same on-air or online. Use TV and radio to highlight the emotion and momentum of the partnership, tying your brand to the energy of the game. On digital channels, lean into behind-the-scenes content or athlete takeovers that feel personal and native to the platform. Keep the message consistent, but adapt the delivery to fit each medium. That’s how you meet fans where they are and make the sponsorship pay off.
The Future Of Sports Marketing: More Strategic, More Inclusive
Women’s sports and emerging leagues have some of the most passionate and engaged fan bases today. They aren’t just worthwhile investments; they are the future of sports marketing. Brands that recognize this shift and approach sponsorships strategically (not as passion plays) will see the greatest returns.
The old sports marketing playbook is evolving. It’s time for brands to move beyond sponsorship as a static investment and start maximizing its potential as an integrated, measurable and impactful marketing strategy.
Forbes Agency Council is an invitation-only community for executives in successful public relations, media strategy, creative and advertising agencies. Do I qualify?
NIL
Georgia taking Missouri DE Damon Wilson II to court in NIL contract dispute
Updated Dec. 6, 2025, 12:47 p.m. ET
Georgia Athletics is taking Missouri football defensive end Damon Wilson II to court in a novel, nearly first-of-its-kind case over an NIL contract dispute, the Columbia Daily Tribune confirmed through a university source and court documents filed in Georgia by the Bulldogs.
UGA is attempting to take Wilson into arbitration and is seeking $390,000 in liquidated damages from the star edge rusher, who transferred to the Tigers in January 2025, over what the university views as an unfulfilled contract in Athens. The lawsuit is not against the University of Missouri, only Wilson.
According to an ESPN report, Georgia is arguing Wilson signed a contract — a common practice in the NIL era — with what was then UGA’s main NIL and marketing arm, Classic City Collective, in December 2024.
That collective has since shut down, as UGA has partnered with Learfield to negotiate and facilitate NIL deals in the revenue-sharing era.

The report, citing documents attached to UGA’s legal filings, show Wilson signed a 14-month deal worth $500,000 with the Bulldogs. He was set to earn monthly payments of $30,000 through the end of the contract, as well as two $40,000 bonus payments.
Before announcing his intention to transfer in January, he reportedly was paid $30,000.
The contract states if Wilson left the team or transferred, which he ended up doing by transferring to Missouri, then he would owe the collective issuing the payments a lump sum equal to the amount remaining on his deal.
The bonus payments seemingly were not included, which brings that total to the $390,000 Georgia is now seeking in court.
Wilson, per the report, was only paid a fraction of that sum, but the university is arguing he owes the full amount in damages. It’s unclear why Georgia is arguing it is owed the full amount in liquidated damages.
The Tribune has reached out to a Georgia Athletics spokesperson for comment. At the time of publishing, UGA had not responded to the request for a statement.
According to documents viewed by the Tribune through the Georgia courts records system, UGA filed an “application to compel arbitration” on Oct. 17 in the Clarke County Superior Court, which includes Athens and the University of Georgia. Wilson was served with a summons to appear in court, according to documents, on Nov. 19, three days before the Tigers faced Oklahoma.
A similar case occurred at Arkansas last spring, when quarterback Madden Iamaleava transferred out of Fayetteville after spring camp. It’s unclear whether or not that case has been resolved.
Wilson spent his freshman and sophomore seasons at Georgia. He transferred to Mizzou ahead of spring camp in 2025 and has emerged as one of the top pass rushers in the SEC.
Per Pro Football Focus, Wilson generated 49 pressures on opposing quarterbacks this season, which was the second-most in the SEC behind only Colin Simmons at Texas. He’s listed at 6-4, 250 pounds and could declare for the 2026 NFL Draft, where he would likely be a Day 1 or 2 pick.
The lawsuit raises a contentious point.
By suing Wilson for allegedly not fulfilling the terms of his contract, the school could be treading close to arguing Wilson was paid to play. That’s not how NIL deals currently work. The deals and their payments are typically for an athletes’ likeness for brand deals and marketing. Think of it as advertising money, not salaries.
There’s a reason that’s the case. By paying players for play, there’s an argument they are university employees. University and athletic department leaders are widely against making that distinction, because it would disrupt the amateurism model in place for college athletics.
Wilson’s contract likely includes “liquidated damages” language, which are intended to stop players from transferring.
Missouri currently has multiple players on two-year contracts. Part of that is in the hope that they do not move on after one season.
If Georgia’s arbitration case against Wilson is successful, that would be a groundbreaking ruling in college athletics that could give more weight to liquidated damages clauses in athlete contracts.
NIL
Predicting the College Football Playoff after Texas Tech beats BYU for the Big 12 title
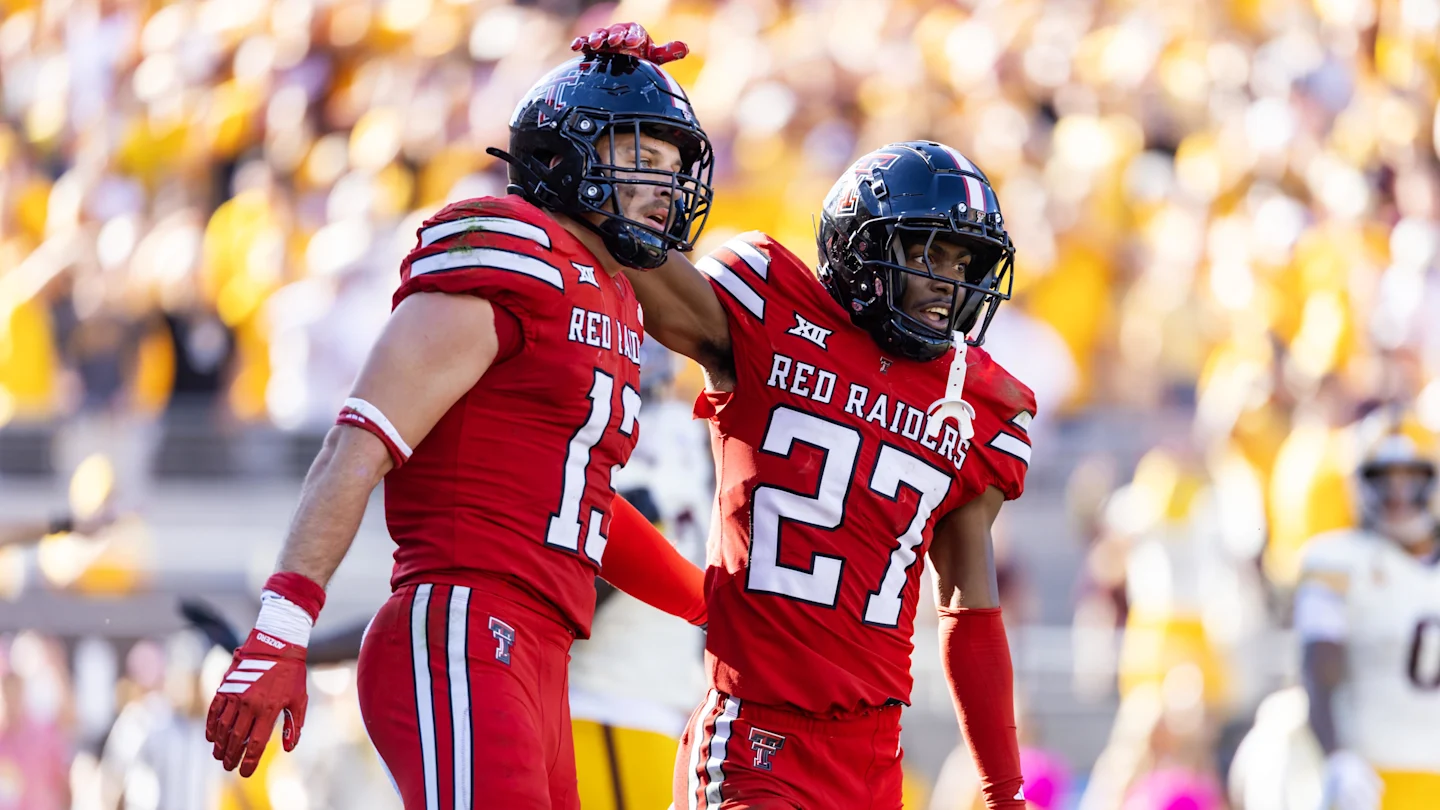

Defense wins championships, they say. That was true of Texas Tech, whose dominant unit overwhelmed BYU behind two key takeaways to win the Big 12 Championship Game and book the Red Raiders a first-round bye in the College Football Playoff.
Ben Roberts intercepted Bear Bachmeier twice, and the Texas Tech offense turned both into points to finally pull away from BYU and win its first-ever conference championship.
With the win, they’ll present a decisive case to the selection committee to stay within the top-four, especially given one of either No. 1 Ohio State or No. 2 Indiana will have to lose the Big Ten championship later today.
Where do things stand in the latest bracket projection? Let’s project what 12 teams will make the College Football Playoff, as of Texas Tech’s big win on Saturday.
Predicting the College Football Playoff bracket

Subject to change pending other Championship Week results
1. Ohio State. We project the Buckeyes will stay perfect by narrowly defeating Indiana to win the Big Ten championship and secure the top overall seed in the playoff.
2. Georgia. Our current expectation is that the Bulldogs will avenge their regular season loss to Alabama and win their second-straight SEC championship.
3. Texas Tech. One of college football’s best defenses left no doubt as to its reputation after swarming BYU to win the Big 12 championship, securing a first-round bye.
4. Indiana. Although we think the Hoosiers will lose the Big Ten title game, it won’t be by much, and they have the overall resume to stay within the top four.
5. Oregon. The one-loss Ducks will stay in the top-five, parked behind the Indiana squad that gave them that defeat earlier this season.
6. Ole Miss. The committee signaled that Lane Kiffin’s exit hasn’t affected the Rebels so far, so it’s likely they’ll stay at 6 when the final bracket is unveiled.
7. Texas A&M. That loss to Texas in the finale deprived the Aggies of a shot at the SEC championship, but the rest of their combined achievements should ensure they won’t have fallen far enough to not host a game in the first round.
8. Oklahoma. One of the nation’s toughest defenses put the Sooners back in playoff contention with a late-season push, but we’ll see how well John Mateer and this offense is able to navigate once the postseason starts.
9. Notre Dame. We expect Alabama loses the SEC championship, allowing the Irish room to move up by one spot.
10. Alabama. Here is where we could see some controversy. There’s a chance the committee keeps the Tide in the bracket if they lose close against Georgia, especially after the selectors jumped Bama over the Irish in the last poll, signaling real confidence in them, win or lose.
But watch for Miami, which will move up in the rankings after BYU’s loss, and there’s a very good case that the Hurricanes deserve it more. Miami would have one fewer loss than Alabama, and that head-to-head win over Notre Dame, too. What do we think? If Georgia beats Alabama, Miami deserves it. The committee may think otherwise, using whatever argument they pick that day.
11. Virginia. James Madison fans are rooting against the Hoos in the ACC championship, because if Virginia loses to Duke, that could pave the way for the selectors to add a second Group of Five team, with JMU ready to take advantage. We still think Virginia beats Duke, though.
12. Tulane. A dominant defensive performance allowed the Green Wave to take out North Texas and win the American championship, and likely entrench their position as the highest-ranked Group of Five team.
What the College Football Playoff bracket would look like
12 Tulane at 5 Oregon
Winner plays 4 Indiana
11 Virginia at 6 Ole Miss
Winner plays 3 Texas Tech
10 Alabama at 7 Texas A&M
Winner plays 2 Georgia
9 Notre Dame at 8 Oklahoma
Winner plays 1 Ohio State
More college football from SI: Top 25 Rankings | Schedule | Teams
Follow College Football HQ: Bookmark | Rankings | Picks
NIL
Nick Saban Calls for the Establishment of a College Football Commissioner

Nick Saban might no longer be the coach of the most dominant program in college football, but his presence still looms large on the sport as a whole. In his new role with ESPN’s College GameDay over the past two years, Saban has branded himself as a voice of reason of sorts in the Wild West era of NIL, the playoffs, and this year, a wild coaching carousel.
On conference championship Saturday, Saban once again pitched that the sport needs some established leadership in a more formal role: a commissioner.
“I think that we need to have a commissioner who’s kind of over all the conferences, as well as a competition committee who sort of defines the rules of how we’re going to play the game. Because that’s what we don’t have right now,” Saban said.
“We used to have contracts, for coaches and for players, that defined what’s your academic responsibilities, when can you transfer, what’s your obligation to the school. We don’t have that now. And if you really don’t support that, you’re kind of supporting a little bit of anarchy, which we have right now. So I think having a commissioner, national commissioner, having a governing body, certainly would enhance [the game]. Because I do think that the College Football Playoff has kind of camouflaged some of these issues, because there’s so much interest in college football because of the playoff.”
Nick Saban wants to see a commissioner for college football ✍️ pic.twitter.com/WtHgBcdHca
— College GameDay (@CollegeGameDay) December 6, 2025
The pitch for a college football commissioner is not exactly a new one, but the value of such a central figure for the sport has been highlighted by an overactive coaching carousel and an extremely tight race for the College Football Playoff.
FREE. SI College Football Newsletter. Get SI’s College Football Newsletter. dark
The college football schedule has come under scrutiny with multiple coaches set to take their team to the playoff but jump ship to a new team next year. Some of those coaches are getting the chance to coach out their run with their current schools, but Lane Kiffin, who left Ole Miss for LSU, is not.
A commissioner, along with in Saban’s pitch a central governing body, could establish a schedule that prevents schools from poaching coaches until the end of the current season. They could also potentially provide more direct guidance to schools as the NIL era continues to take shape before our eyes.
Somewhat ironically, Saban has been floated by many as the perfect man to take on the role of commissioner. Saban doesn’t seem interested, or at least isn’t currently advocating for the gig, but would be a pretty easy choice for any newly established central hub of leadership in the sport.
Penn State head coach James Franklin talks about NIL, the transfer portal, and why Nick Saban should be the commissioner of college football.
“If every decision we make is based on money, then we’re heading in the wrong direction.”
1/2 pic.twitter.com/uSS1QHz1Wh
— Colton Pool (@CPoolReporter) December 29, 2024
That said, one of the reasons a “commissioner” keeps getting floated as a potential solution to the current problems in college football is that the role is undefined enough to sound like it could make a difference.
While it’s easier to think that the issues of the calendar and the coaching carousel and NIL just came up out of the blue and their negative impacts on the sport are the result of a lack of a controlling body, they are actually the result of decisions, made by people who currently have power over said decisions, largely driven by dollars. Unless the hypothetical commissioner was given an inordinate amount of power, those problems won’t just disappear overnight.
That said, some might think that an inordinate amount of power in the hands of one benevolent figure who loves the sport may be preferable to that power being spread across varied hands with even more varied interests. For now, the idea of a commissioner of college football remains an interesting thought experiment, but if Saban wants to start campaigning for the gig, he’d certainly have a strong base of support.
More College Football from Sports Illustrated
Listen to SI’s new college sports podcast, Others Receiving Votes, below or on Apple and Spotify. Watch the show on SI’s YouTube channel.
NIL
Georgia takes Missouri DE Damon Wilson to court for $390,000 in damages after transfer
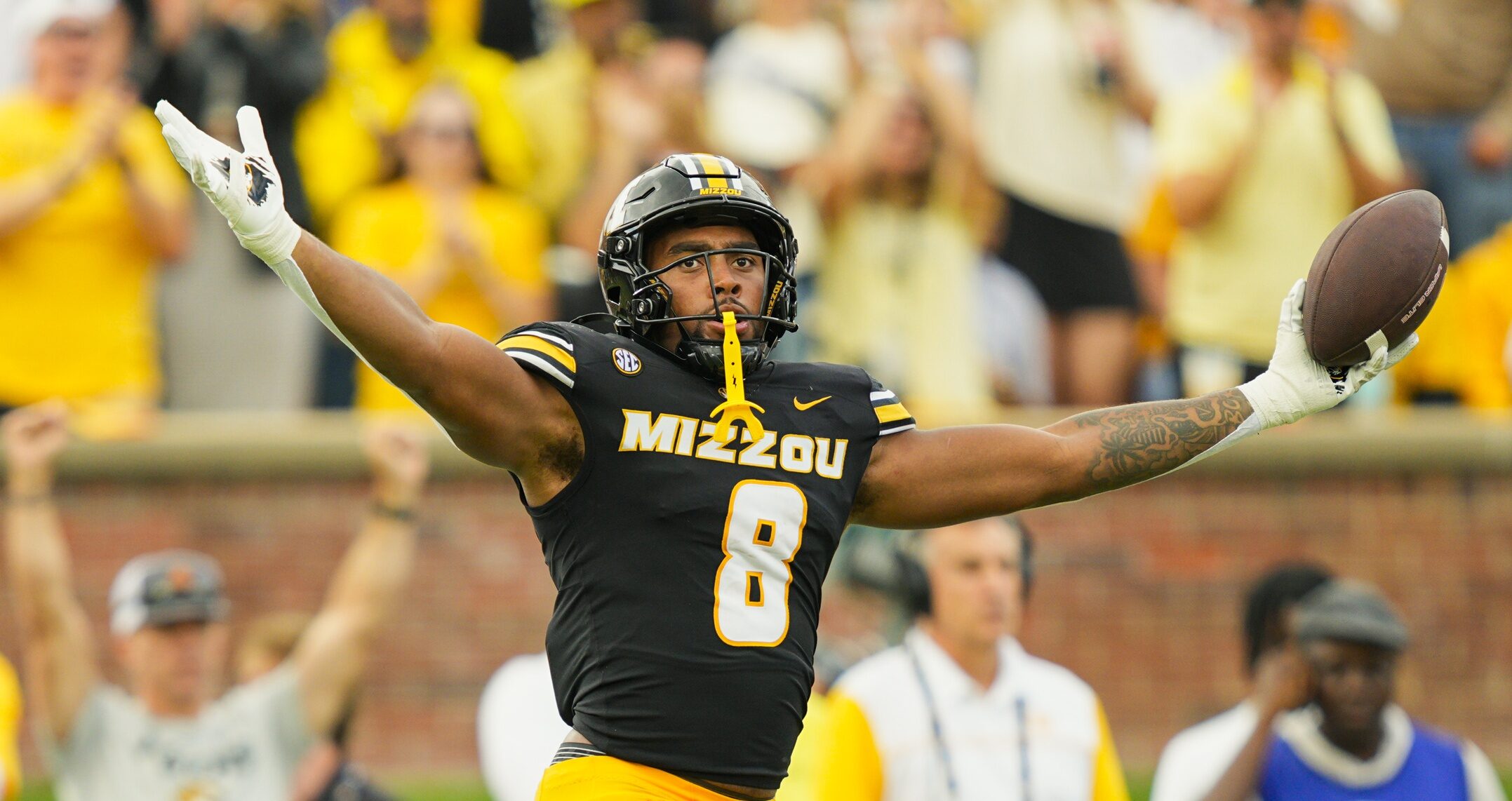

Georgia‘s athletic department is headed to court in a potentially precedent-setting legal effort to recoup approximately $390,000 in damages from former Bulldogs defensive end Damon Wilson, according to ESPN’s Dan Murphy. Wilson is Missouri‘s top pass rusher this season after transferring in from Georgia this past January.
Georgia filed a civil suit Nov. 19 requesting an Athens-Clarke County judge to compel Wilson into arbitration to settle a clause in an agreement he had with the Bulldogs’ team collective that effectively served as a buyout fee for exiting his NIL deal early when he transferred to Mizzou following the conclusion of last season. A copy of the lawsuit was obtained by On3‘s UGASports.com.
SUBSCRIBE to the On3 NIL and Sports Business Newsletter
Wilson played for the Bulldogs in 2023 and 2024, and signed a new NIL agreement with Georgia’s Classic City Collective two weeks prior to entering the NCAA Transfer Portal this past January. Through its collective, Georgia initially paid Wilson a total of $30,000 before his transfer, and now claims Wilson still owes the school a lump sum of $390,000 that was due within 30 days of his decision to leave the team, per ESPN.
The particular clause cited in Wilson’s deal with the Classic City Collective is for “liquidated damages” that many schools and collectives have inserted into their NIL agreements to both protect their investment in players and deter transfers, per ESPN. Georgia is believed to be among the first college athletic departments to publicly try to enforce the “liquidated damages” clause by filing suit against the player.
“When the University of Georgia Athletic Association enters binding agreements with student-athletes, we honor our commitments and expect student-athletes to do the same,” Georgia athletics spokesman Steven Drummond told ESPN in a statement Friday afternoon.
Wilson signed a term sheet with the Classic City Collective in early December 2024, shortly before the Bulldogs’ College Football Playoff quarterfinal loss to Notre Dame. Wilson’s 14-month contract with the collective was worth $500,000 to be distributed in monthly payments of $30,000 with two additional $40,000 bonus payments to be paid out in February and June 2025 once this past year’s transfer portal windows closed for remaining committed to Georgia, according to legal documents obtained by On3.
Wilson’s contract with Georgia’s collective reportedly dictated that should Wilson either withdraw from the team or enter the transfer portal during the term of the deal, he’d owe Classic City Collective a lump sum equal to the remaining money he would’ve received had he stayed with the Bulldogs through the length of the term sheet. The collective’s damages calculation does not include the two bonus payments that weren’t ultimately paid out. The Classic City Collective ultimately signed over the rights to those damages to Georgia’s athletic department on July 1 after most schools took over player payments following the June passing of the House Settlement.
Wilson leads Missouri with nine sacks this year and ranks third on the team with 9.5 tackles for loss and 20 total tackles in his first season in Columbia. Wilson had 3.5 total sacks in two seasons at Georgia.
NIL
Predicting the College Football Playoff after Tulane wins the American title

All that Tulane had to do was take down North Texas to win the American Conference championship, and it was all but assured a place in the College Football Playoff picture.
That they did, coming off a strong defensive performance to all but clinch what should be the highest position among Group of Five teams in the forthcoming CFP rankings as Selection Day draws near.
Coming into Championship Week, there was some newfound confusion around the final two seeds in the latest playoff bracket, with the committee leaving them blank as they await developments in the Group of Five and the ACC Championship Game.
With still plenty of football yet to be played this weekend, here is our latest projection for what the playoff field will look like after Tulane won the American title.
Predicting the College Football Playoff field after Tulane’s win

1. Ohio State. Our current projection is that the Buckeyes are able to stay undefeated and pass the test against perfect Indiana to win the Big Ten championship on the back of the top-ranked defense in college football and secure the No. 1 seed.
2. Georgia. Kirby Smart may be 1-7 against Alabama, but his defense could have a decisive advantage against a Crimson Tide offense that doesn’t look like its dominant self to win the SEC championship for a second-straight season.
3. Texas Tech. Arguably college football’s best defense, and inarguably the best in school history, should still have an edge against a BYU team it beat by 22 points a couple weeks ago, this time to win the Big 12 championship.
4. Indiana. The projected loss we foresee against the Buckeyes should be very close, within the narrow point spread, enough to stay tucked inside the top four for a team that has looked unstoppable and leads the nation in scoring margin this season.
5. Oregon. The one-loss Ducks should stay in the top-five, but behind the Indiana team that gave them that loss, by 10 points at Eugene earlier this season.
6. Ole Miss. Lane Kiffin’s departure for LSU didn’t hurt the Rebels’ position in the rankings, and they should stay in the picture to host a first-round game.
7. Texas A&M. No shot at the SEC championship after that loss against rival Texas, but the Aggies have done enough to warrant hosting a first-round game.
8. Oklahoma. The Sooners, especially their smothering defense, made a statement in the latter half of the season to move into the right side of the playoff bracket.
9. Notre Dame. A loss by Alabama should enable the Irish to move up one spot, even if arguments still persist, and credibly so, that Miami might deserve it more given its head to head win over the Golden Domers and their comparable resumes.
10. Alabama. Despite there being other teams on the bubble that could have an argument — namely BYU, Miami, Texas, and Vanderbilt — the selectors will prefer the loser of the SEC Championship Game over them, provided it’s close to make that decision easier.
11. Virginia. James Madison fans are cheering for Duke to beat Virginia for the ACC championship, but that’s not a result we expect, allowing the Cavaliers to sneak in at the bottom of the field. If Duke does it, Tulane moves to 11 and James Madison to 12.
12. Tulane. An inspired defense and some help from a hapless North Texas offense allowed the Green Wave to win the American Conference championship to secure the highest position in the rankings by any Group of Five team.
What the College Football Playoff bracket could look like
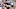
First Round Games
12 Tulane at 5 Oregon
Winner plays 4 Indiana
11 Virginia at 6 Ole Miss
Winner plays 3 Texas Tech
10 Alabama at 7 Texas A&M
Winner plays 2 Georgia
9 Notre Dame at 8 Oklahoma
Winner plays 1 Ohio State
Read more from College Football HQ
NIL
Ty Simpson vs Gunner Stockton: Stats, NIL, Head-to-Head Comparison Ahead of 2025 SEC Championship
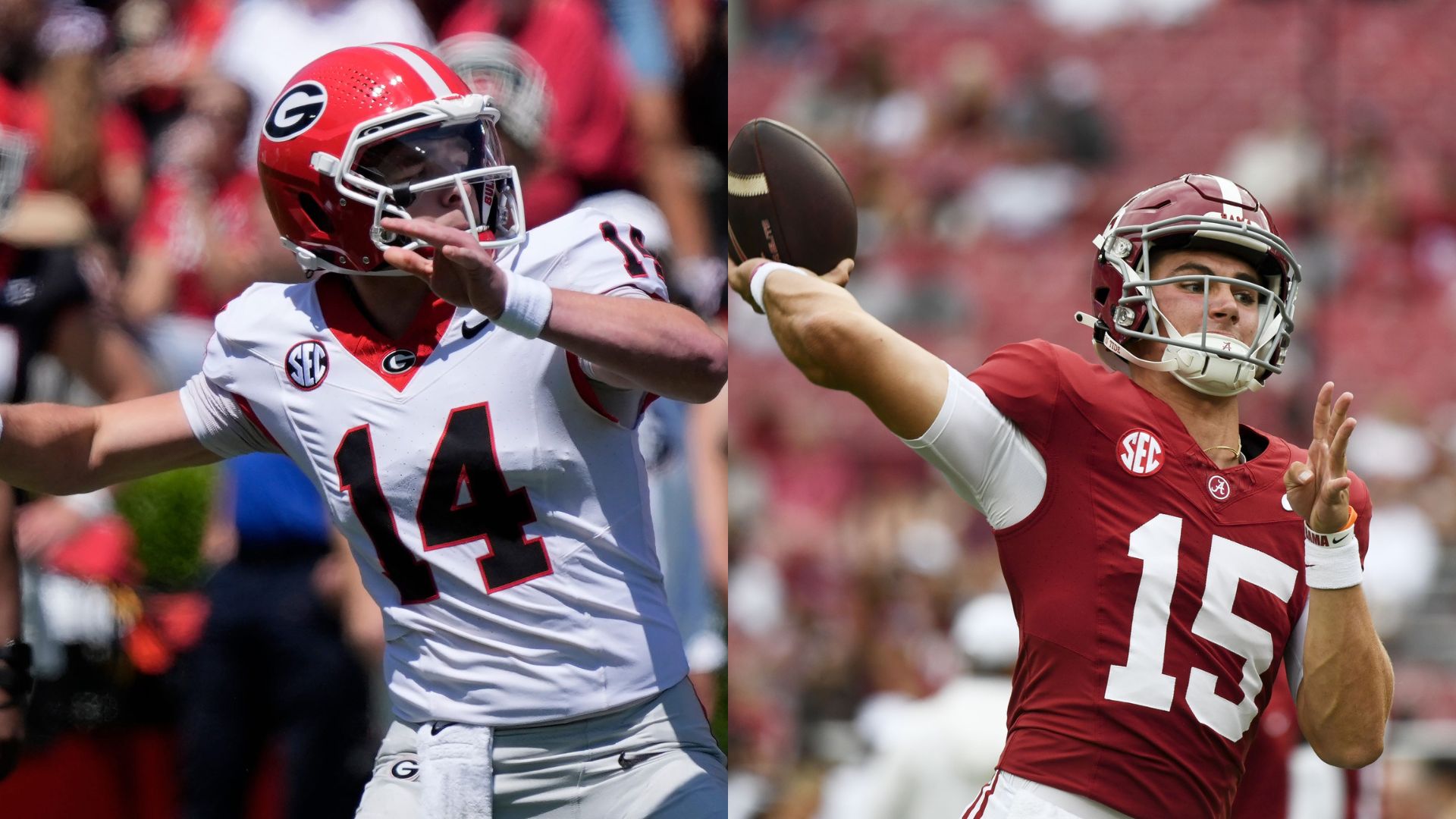

The 2025 SEC Championship will feature a showdown between two elite quarterbacks: Alabama Crimson Tide’s Ty Simpson vs Georgia Bulldogs’ Alabama Crimson Tide. Both have led their respective programs to this stage with elite play on the field, as evidenced by offensive numbers topping the SEC charts.
Let’s compare them on several fronts before the highly anticipated SEC showdown:

Ty Simpson vs Gunner Stockton: Stats
Both quarterbacks have one thing in common. They both had to patiently wait for their time before getting the opportunity to lead the team right from the start of the season. Simpson used to back up Jalen Milroe, while Gunner Stockton had to play behind Carson Beck.
| Player | Passing Yards | Passing TDs | INTs | Completion % (2025) | QBR (2025) |
| Ty Simpson | 3,056 | 25 | 4 | 65.8% (256-389) | 79.5 |
| Gunner Stockton | 2,535 | 20 | 5 | 70.2% (231-329) | 86.0 |
In terms of rushing, Simpson has rushed for 126 yards on 75 carries, including two touchdowns. On the other hand, Stockton seems a better rusher, as he has rushed for 403 yards on 103 carries, including eight touchdowns.
Ty Simpson vs Gunner Stockton: Head-to-Head Comparison
There is only one match where both quarterbacks dueled it out. It happened in the 2025 regular season, in which Simpson’s Alabama defeated Stockton’s Georgia 24-21. In that game, Stockton completed 13 of 20 passes for one touchdown. He also rushed for 22 yards on five carries. On the other hand, Simpson completed 24 of 38 passes for 276 yards and two touchdowns. He also rushed for 12 yards on four carries, including one score.
Ty Simpson vs Gunner Stockton: NIL deals
Alabama’s Ty Simpson recently signed a high-profile NIL deal with Gatorade for 2025. He already has a diverse NIL portfolio, including deals with Hugo Boss, EA Sports, Raising Cane’s, Hollister, Panini and Topps. He is represented by “QB Reps.” According to On3, his NIL valuation is around $948,000.
Meanwhile, Georgia’s Gunner Stockton has signed NIL deals with CAVA, HEYDUDE footwear, Athens Area Humane Society, Associated Credit Union (ACU), and The Dairy Alliance (part of their “Milk’s Got Game” campaign). According to On3, his NIL valuation is around $524,000.
Read More News:
Fans Push Nick Saban As ‘Man for the Job’ As Ex Alabama HC Makes Bold CFB Commissioner Proposal
Netflix’s ‘Any Given Saturday’ Reveals Brian Kelly’s Behind-the-Scenes Pitch to Keep Garrett Nussmeier at LSU
$1.1M NIL-Valued Star Claps Back at HC Brian Kelly’s “Death Valley Jr.” Jab Ahead of Clemson vs LSU College Football Showdown
College Sports Network has you covered with the latest news, analysis, insights, and trending stories in college football, men’s college basketball, women’s college basketball, and college baseball!
-

 Rec Sports2 weeks ago
Rec Sports2 weeks agoFirst Tee Winter Registration is open
-

 Rec Sports1 week ago
Rec Sports1 week agoFargo girl, 13, dies after collapsing during school basketball game – Grand Forks Herald
-

 Motorsports2 weeks ago
Motorsports2 weeks agoCPG Brands Like Allegra Are Betting on F1 for the First Time
-

 Sports2 weeks ago
Sports2 weeks agoVolleyball Recaps – November 18
-

 Motorsports2 weeks ago
Motorsports2 weeks agoF1 Las Vegas: Verstappen win, Norris and Piastri DQ tighten 2025 title fight
-

 Sports2 weeks ago
Sports2 weeks agoTwo Pro Volleyball Leagues Serve Up Plans for Minnesota Teams
-

 Sports2 weeks ago
Sports2 weeks agoSycamores unveil 2026 track and field schedule
-

 Sports2 weeks ago
Sports2 weeks agoUtah State Announces 2025-26 Indoor Track & Field Schedule
-

 Motorsports1 week ago
Motorsports1 week agoRedemption Means First Pro Stock World Championship for Dallas Glenn
-

 NIL6 days ago
NIL6 days agoBowl Projections: ESPN predicts 12-team College Football Playoff bracket, full bowl slate after Week 14




















































