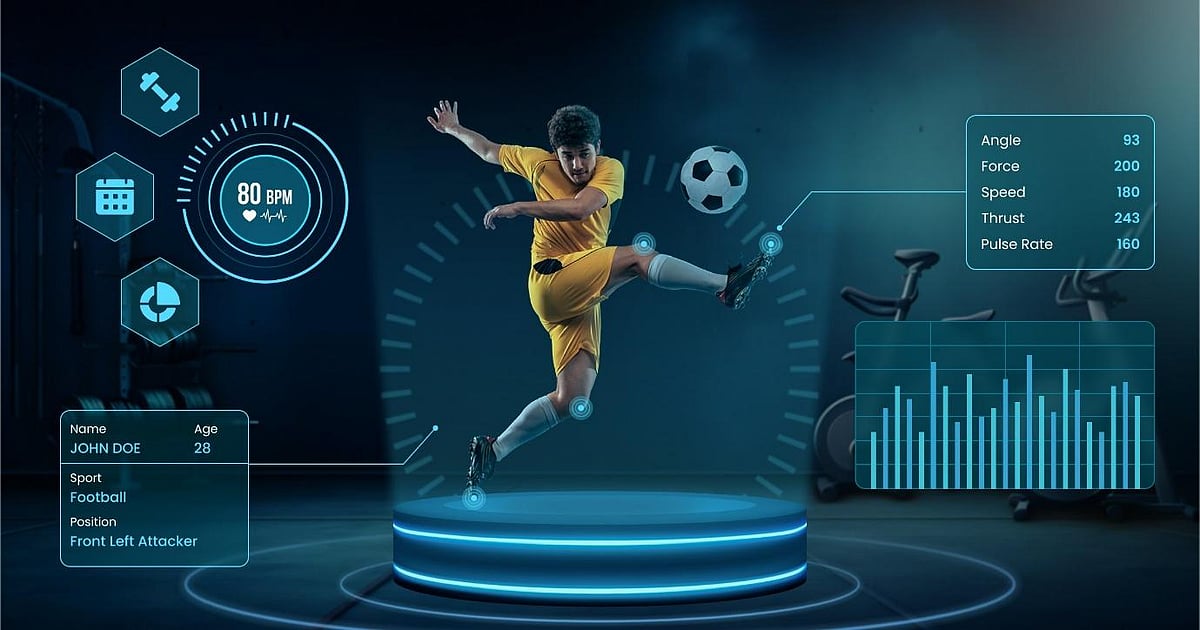
In the ever-evolving world of sports science, one of the most promising innovations is emerging from an unlikely source: sweat. Once regarded merely as a sign of physical exertion, sweat is now being studied as a rich source of biometric data. Sweat sensors—wearable microdevices that analyze the chemical composition of sweat in real-time—are reshaping how we understand athlete performance, hydration, fatigue, and overall health. As this technology matures, its implications for the Indian sports ecosystem are profound, offering new opportunities for performance optimization, injury prevention, and talent development.
Understanding Sweat Sensor Technology
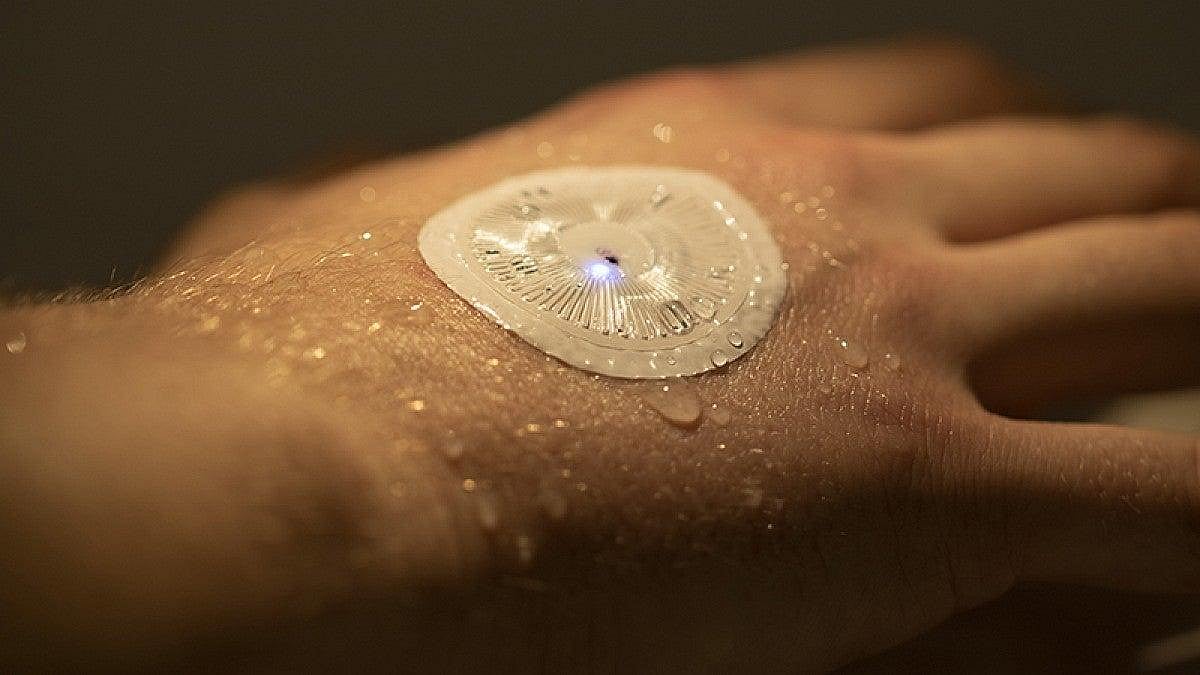
Sweat sensors have evolved into various sophisticated forms, each serving specific monitoring purposes. The most prevalent are electrochemical sensors, which combine high performance with cost-effectiveness and miniaturization capabilities. These are complemented by optical sensors and microfluidic devices that maintain close skin contact for accurate sweat collection and analysis. The technology has advanced to include flexible and stretchable electronics that can be comfortably worn during athletic activities, providing continuous monitoring of sweat composition and offering valuable insights into metabolic activity and overall health status.
Applications in Sports: Optimizing Health and Performance
Athletes put their bodies through extreme physical and mental strain. Sweat sensors are increasingly being used to tailor training regimens and recovery strategies to individual needs, providing insights into:
1. Hydration Monitoring
Dehydration can severely impair physical performance and cognitive function. In hot and humid climates like India’s, this risk is heightened. Sweat sensors can detect real-time sodium and chloride levels, alerting coaches and athletes when electrolyte levels are off-balance, allowing for proactive hydration strategies.
2. Fatigue and Recovery Management
Elevated lactate levels in sweat indicate when muscles are shifting from aerobic to anaerobic metabolism, which correlates with fatigue. By identifying these shifts, coaches can adjust training loads to prevent overtraining and injuries. Tracking cortisol levels also provides insight into mental stress, ensuring athletes aren’t burning out psychologically.
3. Injury Prevention
Injuries are often preceded by changes in biochemical markers. For example, electrolyte imbalances can increase cramp risk, while low hydration is linked to ligament fatigue. Real-time data can help trainers mitigate these risks through immediate interventions.
4. Nutrition and Metabolism Insights
By tracking glucose, urea, and ammonia levels, sweat sensors provide data on how effectively an athlete is metabolizing nutrients. This enables personalized dietary adjustments to boost endurance and muscle recovery.
Major Developments and Global Adoption
Globally, tech giants and sports organizations are rapidly investing in sweat sensor technology. Companies like Epicore Biosystems, Eccrine Systems, and Gatorade (GX Sweat Patch) are already producing commercial devices used in elite sports. For example:
-
The U.S. Olympic Committee tested sweat sensors during athlete training camps to customize hydration strategies.
-
The NFL and NBA are exploring wearable biosensors to optimize player readiness and reduce injuries.
-
Stanford and Northwestern Universities have collaborated on developing skin-integrated, flexible sweat sensors for both athletes and healthcare applications.
In India, the adoption is still nascent, but promising. Indian sports scientists and startup ecosystems are gradually exploring wearable technology, particularly in high-performance centers like the Sports Authority of India (SAI) and private institutions such as the JSW Sports Excellence Program and Reliance Foundation’s youth sports initiatives.
Impact on Sports Medicine and Training
The integration of sweat sensors into sports medicine has revolutionized how teams approach athlete health monitoring. These devices provide continuous, real-time data that allows for immediate interventions when necessary. This capability is particularly valuable in preventing dehydration and optimizing performance during training and competition. Recent studies have shown promising correlations between sweat biomarkers and blood levels for certain parameters, offering a non-invasive alternative to traditional blood testing. This advancement is particularly significant for continuous monitoring during training sessions and competitions.
Potential for Indian Sports
The Indian sports technology market is experiencing significant growth, projected to reach USD 1,479.2 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 13.32%. This growth presents a tremendous opportunity for the integration of sweat sensor technology into Indian sports programs. For the Indian sports ecosystem, sweat sensors could address several crucial challenges:
-
Performance Optimization: With India’s diverse climate conditions, accurate hydration and electrolyte monitoring become crucial for athlete performance.
-
Cost-Effective Monitoring: The technology offers a more accessible alternative to traditional medical testing, particularly beneficial for emerging athletes and smaller sports programs.
-
Data-Driven Training: The Indian sports analytics market is expected to grow from USD 193.28 million in 2024 to USD 2000 million by 2035, indicating a strong potential for the integration of sweat sensor data into comprehensive athlete monitoring systems.
-
Empowering Female Athletes: Women’s physiological responses to training, recovery, and hydration differ from men’s, yet most training protocols don’t account for this. Sweat sensors offer gender-specific insights, enabling better support for female athletes, crucial in promoting equitable participation and excellence.
-
Altitude Training Programs: Indian athletes training at high-altitude facilities could use sweat sensors to monitor adaptation responses and optimize acclimatization protocols, particularly beneficial for endurance sports like long-distance running and cycling.
-
Healthcare Integration: Rising chronic diseases, including diabetes and cardiovascular issues, make sweat glucose monitoring particularly relevant for Indian athletes. Insurance providers are already partnering with wearable manufacturers to monitor health and reduce claims, positioning this technology as a vital component of the healthcare ecosystem
Future Prospects
The future of sweat sensor technology looks promising, with ongoing developments in sensor accuracy, durability, and data integration. Researchers are working on expanding the range of biomarkers that can be monitored, potentially including hormones and other complex molecules. For Indian sports, this technology could be particularly transformative. As the country continues to invest in sports infrastructure and technology, sweat sensors could become an integral part of athlete development programs, helping India produce more competitive athletes across various sports disciplines.
Sweat sensor technology represents a significant advancement in athlete health monitoring, offering non-invasive, real-time insights into physiological and biochemical states. While challenges remain in terms of validation and standardization, the potential benefits for athlete health and performance optimization are substantial. For India’s growing sports ecosystem, this technology could be a game-changer in developing world-class athletes and improving overall sports performance across disciplines.






















 | First Take
| First Take
 #HeroesOfTheGame
#HeroesOfTheGame






































