NIL
The evolving landscape of college athlete pay

Cat Flood recounted the DM she got from the Pennsylvania Beef Council around two years ago that started her down the road of cashing in on college volleyball stardom. The nonprofit wanted her to promote its mission of “building beef and veal demand with consumers of all ages.”
She recorded a series of videos for her Instagram, one of which got over a million views. In the post, she invited followers along a day in her life — notably, eating jerky for her first snack, steak for lunch and later on, more jerky. The council paid her $1,000.
Deals like this are commonplace in today’s college athletics landscape, where for four years, athletes have been profiting from use of their name, image and likeness [NIL].
“NIL made us all influencers,” Flood said.
As one of the University of Pittsburgh’s most popular athletes, Flood — who recently graduated — benefited from NIL deals, averaging one or two a month, and saw how their introduction changed the nature of college sports.
And more change is on the horizon with the June 6 approval of a landmark NCAA settlement letting colleges pay their athletes that takes effect July 1. Universities in the former Power Five conferences (recently reduced to four), including Pitt and Penn State, will each have to split $20.5 million annually between players for a decade. The yearly amount will increase incrementally.
While the settlement ushers in more money for athletes, it’s unlikely to be spread evenly, and certain NIL deals will be scrutinized for the first time. Uncertainty about how the millions will be distributed and exactly how the settlement terms will be enforced has rattled college athletes and spurred state lawmakers alike.
PublicSource spoke to several athletes, state representatives and NIL experts about their thoughts on the second big change in compensation in just this decade. Here’s what they had to say.
Antonio Epps, Duquesne University
School division: Division I, outside of Power 4 conferences
Year: Senior
Sport: Football
Recent NIL deal: None
Dream NIL deal: Pizza Hut

Before NIL came into play, Epps said, “there was always talk about how being a college athlete was very similar to working a 9-5, in a sense.”
He was a sophomore when the NCAA allowed athletes to have NIL deals and became a part of Duquesne’s Red and Blue NIL collective. Through this, he’s able to make money from merch and generally feels NIL has been a good thing.
“It can help out a lot of people who didn’t have as much money coming into college,” he said.
Duquesne is one of the schools that can choose to opt into sharing a portion of their athletics department revenue with athletes, but isn’t required to do so.
A university spokesperson confirmed that Duquesne is opting in.
Epps said that although the conversation has been about athletes, they’re being left in the dark when it comes to understanding what impact this will have on them.
“A lot of the conversations that happen, happen around us, but a lot of us are not told the [parameters] of what is being said.”
When the NIL policy first went into effect in 2021, it was expected that money would largely come from endorsement rights opportunities — think brand deals like Flood’s Pennsylvania Beef Council posts. Then collectives emerged, said University of Illinois labor and law professor Michael LeRoy.
Collectives are groups that pool donations to pay athletes for use of their NIL, while facilitating deals for them. While these are usually school-specific, they’re operated independently, though there’s often some level of collaboration with the college.
Once athletes sign contracts with collectives, there’s an expectation that they’ll get paid, but which players are paid and how much is up to the discretion of the collective’s head. Last fall, the founder of Pitt’s collective, Alliance 412, along with the university’s football coach, stopped paying all members of the team, instead compensating only some to incentivize better performance.
The NCAA settlement retains a longstanding ban on compensation solely related to athletic performance or participation. Nonetheless, the NIL system has been called “pay for play,” because it seemingly rewards performance in many cases.
“There’s so much pent-up demand among supporters and the businesses … neither the laws nor the rules have caught up with the market supply of NIL money for athletes,” LeRoy said.
A majority of NIL funds come from collectives, not endorsements, sponsorships or appearances, according to Philadelphia-based NIL agent and attorney Stephen Vanyo. When he’s looking at contracts with collectives for clients, he said a player’s NIL value is being assessed based on what they will bring to a team. This is subjective, but factors include stats and social media following.
None of the athletes PublicSource interviewed disclosed their NIL values. Some of them did not have the figures.
LeRoy, who has researched NIL earnings, said that men outearn women 10:1 in deals, with the most money going to men’s football and basketball players. The settlement is expected to do little to remedy this, opening the doors for lawsuits against schools under Title IX, which requires schools to provide equal financial assistance opportunities to men and women athletes.
With no stipulations on how colleges have to divvy up the $20.5 million, experts have predicted that as much as 70-90% will go to men’s football, men’s basketball and women’s basketball, in that order.
Cat Flood, University of Pittsburgh
School division: Division I, ACC
Year: Graduated in 2025
Sport: Volleyball
Recent NIL deal: Saxbys
Dream NIL deal: World Wildlife Fund or Free People

Last year, Pitt’s volleyball team was ranked third in the country by the NCAA, finishing the 2024-2025 season 33-2.
Flood joined the team in 2020 after one visit to a university volleyball clinic. “I fell in love with it on the spot,” she said.
Recruiting, to her, was all about considering, “Where am I going to have the best four years?” not where she could get the most money in NIL deals. She never joined Alliance 412.
“I didn’t love the idea of NIL, I had seen what it had done to a lot of players,” she said. “They were playing for the money, they were transferring for the money.” She preferred to use NIL to promote local businesses in mutually beneficial, ethical arrangements.
However, after the volleyball team’s continued success, she began to regret not taking NIL more seriously. She saw NIL funds flowing to men’s football and men’s basketball, which she believed was fair due to viewership. But she noted that despite her squad being “the best team at the university … the women’s side was getting nothing.”
With players now getting paid a portion of the revenue that college athletics departments receive, she wants to see women’s volleyball benefit.
“I hope that we bark up some NIL trees.”
In the year it’s taken for the settlement terms to be negotiated and finalized, schools have prepared to start paying athletes. One way was by presenting recruits with NIL contracts that would only become effective after the settlement’s approval.
Alex Guminiski, a Pittsburgh-based NIL agent and attorney, has seen over 20 of these so far — some for Pitt recruits — but due to confidentiality clauses, couldn’t give more details. He stressed, though, that “it’s not pay for play,” but rather “licensing deals.”
“The school is asking the player to grant the school the license to use their NIL in all sorts of media,” Guminiski said.
LeRoy, the professor who obtained similar contracts from schools in the Big Ten and SEC conferences, said players are being asked to give away “an irrevocable right” to their collegiate NIL. These terms aren’t negotiable, he added.
“They are going to be paid for this, and in many cases, paid well. But again, people likely don’t know what they’re signing.”
LeRoy worries about the exploitation of athletes, especially those without an agent. He sees these contracts as a way to sidestep the perennial question of whether college athletes are employees of the schools they play for — another area many experts believe will play out in the courts.
Vanyo called the settlement “another half measure” because of the legal challenges it is likely to ignite. He said the only sustainable solution for stabilizing the industry is to allow athletes to unionize and collectively bargain, as players in professional leagues do. Then, there’d be what he described as a “semblance of fairness.”
“It’s the only thing we’ve seen work in the American sports model,” he said.
Ryan Prather Jr., Robert Morris University
School division: Division I, outside of Power 4 conferences
Year: Junior
Sport: Basketball
Recent NIL deal: C4 Energy
Dream NIL deal: Nike

Ryan Prather Jr. has had a long journey to Pittsburgh. After playing at the University of Akron through his first two years of college, he decided to transfer and commit to RMU in 2024.
“I wanted somewhere I could go and showcase what I could do,” he said.
He changed schools in part to be closer to home and family, but also due to the opportunities he could envision. After transferring, he joined RomoRise, an NIL collective specifically for RMU students, and has taken advantage of the deals presented to him.
As the settlement is sure to prompt changes to deals, Prather said, “It definitely has an effect on anyone who’s trying to play in college … they come in with a certain amount in their head.”
Prather said he understood the benefit of college athletes getting paid to do what they love. “The money helps you out in the long run because if you use up your money and save it up and invest, you can start early rather than waiting until after college for your career to get started.”
The downside: “It’s kind of hard at the same time because no team is going to stick with each other.” With teams changing every year due to players leaving, it can be difficult to produce a cohesive team environment.
“More money doesn’t always mean a better situation.”
The NCAA has been trying to wrangle what it views as an out-of-control stream of money going to athletes via NIL deals over the past few years, in part because athletes are transferring schools at record numbers, which some believe is due to money offered by collectives.
Under the settlement’s rules, third-party NIL deals valued at or above $600 will be reported to a clearinghouse run by consulting firm Deloitte. The goal, LeRoy said, is to regulate the market.
The clearinghouse will determine if deals fall under “pay for play” and evaluate their fair market values. Deals have to be approved before an athlete can receive the funds.
Little is known about the specific criteria needed for compliance, but experts told PublicSource that there isn’t a set fair market value for any NIL deal, and trying to determine one is next to impossible.
Vanyo said fair market value in the industry is simply “what somebody’s willing to pay.”
“In no other industry do we have … a clearinghouse that then says, ‘OK, this is a fair salary,’” he continued.
Some experts describe the clearinghouse as a way to scale back how much some athletes are earning.
“While nobody knows for sure how this is going to come out, the clear implication is that most of the NIL deals, particularly in men’s revenue sports — football and men’s basketball — will not be accepted as fair market value,” LeRoy said. A new College Sports Commission, separate from the NCAA, could then reject such deals.
It’s been reported that Deloitte officials said 70% of past deals from collectives would be rejected under the clearinghouse.
Unsurprisingly, legal challenges by those with rejected deals are expected to follow.
Aurielle Brunner, Chatham University
School division: Division III, Presidents’ Athletic Conference
Year: Graduated in 2025
Sport: Track and field, Soccer, Basketball
Recent NIL deal: P3R, a local event management organization
Dream NIL deal: Nike

Brunner believes college athletes are valued professionals and views the settlement as a “huge step for sports.”
She holds 10 All-American awards for her track and field success. As Chatham University’s most decorated athlete of all time, she quickly stood out in the local college sports scene and became one of the school’s first players to secure an NIL deal.
She’s part of an NIL Athlete program with the Pittsburgh-based sports event planners P3R, which spotlights players in underrepresented sports to advance the company’s mission to “keep Pittsburgh moving.”
Brunner said NIL opportunities are “a great way to get college athletes out there and into the world.”
Her role involves filming a monthly video sharing workouts, answering fan questions and talking about her accomplishments. For this, she receives $500 a year.
“Any amount was great for a college athlete playing three sports,” said Brunner.
She’s very aware of the disparity between athletes’ earnings and isn’t a fan of the clearinghouse and tighter NIL deal regulations introduced by the settlement. While Division III schools aren’t included, she’s confident that some of the funding changes will trickle down.
Several state legislatures have passed bills aimed at making it easier for athletes and schools to navigate the new revenue-sharing model.
Days before the settlement was finalized, three Pennsylvania House representatives introduced legislation targeting NIL earnings. Rep. Aerion Andrew Abney, whose district includes Pitt’s Oakland campus, said his bill would put the state on par with others that have prohibited the NCAA’s compensation limits on money from NIL collectives.
He said the bill would allow schools in the state “to have the same type of, if not more, of a competitive edge” than those in neighboring states by protecting student athletes against exploitation. As a trustee on Pitt’s board, he sent the legislation to the university for review.
Across the aisle, House Republican Leader Rep. Jesse Topper, of Bedford and Fulton counties, and Rep. Perry Stambaugh, R-Juniata and Perry counties, issued a memo highlighting their forthcoming legislation that aims to develop long-term financial security for college athletes. Their bill would require schools to provide financial literacy courses to players and offer them the opportunity to put NIL earnings in trust accounts.
“We do need to bring a little order,” said Topper, to what he called the “Wild, Wild West” of NIL.
“We see what’s going on with the courts. The more that we can as public policymakers set rules and guidelines through policy, the less uncertainty that’s out there,” he said.
When interviewed by PublicSource, neither Topper nor Abney had seen the other’s legislation. Abney said he shared his bill with the Republicans and was positive that there would be something to glean from both, as the legislature also tries to finalize a budget.
“At the end of the day, there’s got to be something in … their legislation and my legislation that we can, during this budget negotiation, find a solution to this topic.”
Maddy Franklin reports on higher ed for PublicSource, in partnership with Open Campus, and can be reached at madison@publicsource.org.
Ayla Saeed is an editorial intern at PublicSource and can be reached at ayla@publicsource.org.
This story was fact-checked by Jake Vasilias.
NIL
Bankruptcy trustee presses case against Deion Sanders’ son Shilo
Dec. 17, 2025, 10:04 p.m. ET
- Shilo Sanders is in a legal dispute with a bankruptcy trustee over approximately $250,000 in alleged unauthorized fund transfers.
- The core issue is whether Sanders’ NIL earnings belong to him or to the bankruptcy estate for his creditors.
- Sanders filed for Chapter 7 bankruptcy in October 2023 to discharge over $11 million in debt from a 2022 civil court judgment.
The trustee in the bankruptcy case of former Colorado football player Shilo Sanders filed a response in court Dec. 17 that supports his argument that Sanders violated bankruptcy law by making unauthorized transfers to himself of approximately $250,000.
The court filing is the latest volley in bankruptcy case of Sanders, who filed a Chapter 7 petition in October 2023 seeking to get out of more than $11 million in debt.
The trustee in the case, David Wadsworth, sued Shilo Sanders in October, seeking recovery of the money and an accounting from Sanders. Sanders’ attorney then filed a motion to dismiss that complaint in November by arguing that the trustee had it all wrong.
The latest filing from Wadsworth’s attorney rebuts that notion as litigation related to the bankruptcy case continues on multiple fronts in addition to this one. Sanders’ debt stems from a civil court judgment in Dallas in 2022.
“The Defendants are wrong,” the trustee’s attorney, Peter Cal, said in court documents.
What is at issue in Shilo Sanders’ bankruptcy case this time?
The court-appointed trustee in this case is in charge of rounding up Sanders’ non-exempt assets for the bankruptcy estate to divide among his creditors. The trustee has alleged having trouble doing that and filed a complaint against Sanders related to money he traced in Sanders’ business accounts for earnings from his name, image and likeness (NIL). Those businesses are named as defendants with Sanders in the complaint – Big 21 and Headache Gang.
The big issue is who the money in question belongs to – the bankruptcy estate or Sanders. Sanders’ earnings before he filed the bankruptcy petition generally belong to the bankruptcy estate for the benefit of creditors, while earnings that came from work after the bankruptcy filing belong to Sanders.
Sanders’ attorney, Keri Riley, stated in court documents that the money in question belonged to Sanders because they were “post-petition earnings.”
The trustee disputed that in his response Dec. 17 and said such factual disputes can’t be resolved at this stage of the litigation.
Sanders “relies on the unsupported argument that all funds in the Big 21 Bank Account were post-petition earnings of the Debtor (Sanders),” the trustee’s attorney stated. “The Court should not consider the argument because it relies upon a factual assertion that is not included in the (trustee’s) Complaint.”
The trustee’s attorney then includes a footnote.
“Because there were funds in the Big 21 Bank Account on the Petition Date, the Defendants’ argument is demonstrably wrong,” the footnote states.
Timing of Shilo Sanders’ NIL earnings in dispute
The trustee’s attorney also noted that “even if the earnings are paid to the Debtor post-petition, they are considered prepetition earnings when they arose from a prepetition contractual interest.”
He argued the trustee pleaded his case well enough for the trustee’s complaint against Sanders to move forward. A bankruptcy judge will decide on that.
“It is more than plausible that at least certain of the post-petition deposits were based on the Debtor’s prepetition NIL contracts and, therefore, are subject to turnover,” the trustee’s filing states.
The trustee said he wants Sanders to “account for the distributions” after “improperly” exercising control over property of the bankruptcy estate.
How did the Shilo Sanders bankruptcy case originate?
A security guard at Sanders’ school in Dallas sued Sanders and his parents in 2016, alleging Shilo caused him permanent and severe injuries when he tried to confiscate his phone at school in 2015, when Shilo was 15. The parents were dismissed from the case before trial, but when the case finally went to trial in 2022, Shilo didn’t show up for it and got hit with a $11.89 million default judgment as a result.
The security guard, John Darjean, then moved to collect on that judgment in 2023, leading Sanders to file for bankruptcy to try to get out of it.
Darjean is fighting that with a separate complaint that alleges the debt should not be discharged in bankruptcy court because it stems from a “willful and malicious” injury. Sanders has claimed he acted in self-defense. That complaint remains pending, as does a separate complaint from Darjean that accuses Sanders of improperly omitting or concealing assets in his bankruptcy closures, which he denied.
What is Shilo Sanders doing now?
Sanders, 25, is out of football after being waived by the Tampa Bay Buccaneers before the season. He recently said he was moving to Miami and is pursuing other interests, such as acting and rap music.
He graduated from Jackson State before transferring to play for his dad at Colorado in 2023. Earlier this year, he also earned a master’s degree at Colorado in organizational leadership.
He is the middle of Deion Sanders’ three sons. His younger brother Shedeur is quarterback of the Cleveland Browns.
Follow reporter Brent Schrotenboer @Schrotenboer. Email: bschrotenb@usatoday.com
NIL
$45 million college football head coach reportedly offers Lane Kiffin unexpected role

The College Football Playoff travels to Oxford on Saturday with an unusual subplot: an 11-win Ole Miss team entering the postseason without the coach who compiled that record, Lane Kiffin.
Meanwhile, Tulane, which Ole Miss faces Saturday at 3:30 p.m. ET at Vaught-Hemingway Stadium, also has an outgoing coach, as Jon Sumrall has opted to finish the season in New Orleans before taking over at Florida.
Kiffin’s 2025 Rebels closed the regular season at 11–1, securing a CFP berth behind a high-powered offense that averaged 498.1 total yards per game, the third-most in college football.
Within days of the Egg Bowl, Kiffin accepted LSU’s offer, a reported seven-year contract worth roughly $91 million, and announced he would not coach Ole Miss in the playoff.
Ole Miss promptly elevated defensive coordinator Pete Golding to lead the program into the bracket.
On Wednesday, Sumrall broke down the matchup and joked that he had offered Kiffin a spot in Tulane’s coaches’ box.
“They’ve got a lot more stability for the game than people realize. They’re going to be who they’ve been; they’re just not going to have Lane on the sideline,” Sumrall said. “I’ve reached out to Lane to see if he wants to sit in our coaches’ box for the game, but he hasn’t given me an answer yet.”

Tulane arrives after winning the American Athletic Conference and finishing 11–2.
The Green Wave boasts one of the nation’s best turnover margins (+10) and a defense that has tightened steadily since an early setback in Oxford on Sept. 20, a 45–10 loss.
Adding to the narrative, Sumrall, who signed a reported six-year, roughly $45 million deal to become Florida’s next head coach, has said he will remain with Tulane through the postseason before joining the Gators full-time.
Tulane has already designated passing-game coordinator Will Hall as Sumrall’s successor once the playoff run concludes.
This moment reflects a new normal in college football’s accelerated coaching market, with major hires unfolding as teams prepare for postseason play.
Read More at College Football HQ
- $3.7 million college football head coach named clear candidate for Michigan vacancy
- College football program signs $1.2 million deal with NFL legend
- College Football Playoff team losing all-conference player to transfer portal
- $2.1 million college football QB announces return to Big Ten program
NIL
$36 million college football coach reportedly out of race for Michigan vacancy

Michigan is the last remaining Power Four college football program to find a new head coach in the 2026 cycle.
The Wolverines fired head coach Sherrone Moore on Dec. 10 with cause and are now one week into the coaching search. Alabama head coach Kalen DeBoer, Arizona State head coach Kenny Dillingham, and Missouri head coach Eli Drinkwitz are among those being floated as potential replacements.
One name that previously received attention for the vacancy was Washington head coach Jedd Fisch. On3 and ESPN college football insider Josh Pate reported Fisch’s interest in the Michigan head coaching vacancy has declined in the last few days.
“There’s been some sentiment today that maybe Jedd Fisch’s name has cooled,” Pate said. “I think that’s accurate. The critical take-home points are that I don’t know if Jedd Fisch is going to be a factor in the Michigan search moving forward… I don’t think Jedd Fisch is going to be an option for them.”
Fisch’s waning interest is a relief to Washington, as it is all too familiar with head coaches leaving for other jobs. The Huskies lost Kalen DeBoer to Alabama in the 2024 offseason when Nick Saban announced his retirement from the Crimson Tide.
The Florida alumnus spent the first 24 seasons in the coaching ranks as an assistant at a high school, in the Arena Football League, at six different NFL franchises and five different college football programs. He served as Michigan’s passing game coordinator in 2015 and 2016 under Jim Harbaugh, part of the reason he is linked to the Wolverines’ current opening.
The only head-coaching capacity Fisch had served in before he took the Arizona vacancy was as UCLA’s interim coach in the 2017 Cactus Bowl against Kansas State.
Arizona finished 1-11 in 2021, the lone win against California (10-3) in November. The Wildcats improved to 5-7 in 2022, a record that included an upset victory over a ranked UCLA team. Fisch followed up a 3-3 start in 2023 with seven consecutive wins, including an Alamo Bowl win over Oklahoma (38-24).
Fisch filled the Washington vacancy left by DeBoer in the 2024 offseason. An up-and-down first season led to a 6-7 season, capped by a Sun Bowl loss to Louisville (35-34).
The Huskies put together a stronger effort in 2025. Washington concluded the regular season at 8-4 and defeated Boise State (38-10) in the LA Bowl in SoFi Stadium.
NIL
Eli Drinkwitz: NIL Buyouts And Tampering Are Making ‘College Football Sick’

Just two weeks away from the transfer portal opening in college football, coaches across the country are trying to maintain a roster while opposing schools look for any possible way to steal a player, no matter if it comes with paying a buyout.
On Monday, we all witnessed multiple starting quarterbacks decide to declare their intentions to enter the portal. This included DJ Lagway, Dylan Raiola, Brendan Sorsby and Sam Leavitt.
All of these guys would have had the opportunity to play next season at their current schools, with maybe Lagway being an outlier because of the new staff in Gainesville. But, we are certainly in a drastically different era of college athletics.
Transfer Portal Carousel: Quarterbacks, NIL Deals And The Rise Of A WILD College Football Free Agency Market
“There’s a warning that the system that we’re in is really sick right now, and college football is sick,” Eli Drinkwitz said. “There’s showing signs of this thing really cracking moving forward, and we need to get something under control.”
Contracts: How ‘Buyouts’ Are Handled, Or Trying To Be
At the moment, there are players deciding that entering the transfer portal is the best route to take when it comes to cashing in, with chances of making it to the NFL not guaranteed. This also means that certain players are deciding to enter the transfer portal while still under contract with a school like Missouri.
In reality, there are no rules at the moment. Some might think the new College Sports Commission is setting guidelines for future enforcement, but there is still no agreement signed that would have them running the show.
After Sherrone Moore Scandal, Michigan Board Orders Investigation Into Athletic Department
We have seen players re-signing with schools, while others are being shopped around to others. So, what happens if an athlete has signed an agreement with one school, but is looking at the opportunity of transferring?
Here’s the best way to explain what we’re seeing right now in college athletics when it comes to a player leaving one school after already being paid through a “front-loaded” deal before new rules were put into place over the summer.
Let Me Try To Summarize It
“Hey, College Player, you’re being paid $4 million. Here’s $3.8 million before the house settlement is passed. Once you hit the portal, we can terminate the deal, but if it’s terminated because you left, you owe us the money. If another collective cuts the check at the new school, the player would then have that taken out of their new school’s contract.
“And, if the player decides to balk at paying their previous school back, this is where lawsuits could continue. The athletes have already taken this money, but they still owe their previous school for the contract that has not been fulfilled. Somebody has to pay back that money, or what they agreed to under the particular contract.”
I hope that explains it, for the folks still trying to grasp all this.
As we’ve reported before, this is where certain contract language will have “buyout” clauses. But, who is enforcing this? This is what Eli Drinkwitz was trying to emphasize on Tuesday.
“I don’t know, some of the players that have entered the portal were under two-year contracts, and their anticipation is that another school will pay their buyout, or they’ll pay it back themselves,” Drinkwitz told reporters. “So, you know, contracts are contracts. I think there’s been an assumption that, not gonna go there. So we’ll see, we’ll see, you know. Right now, there are perceived rules, and then we’ll figure out what are the real rules moving forward.”
As you can tell, there is no clarity, and as much as some of these coaches would have loved the help of Congress, they might end up waiting a while before enforcement can actually take place.
It’s No Longer Tampering. College Athletes Are Being Shopped
Most coaches in this era would rather handle situations behind the scenes, rather than calling out an opposing school during a press conference setting.
Why? Because there is “tampering” going on at every school. Now, it might not be as rampant at some compared to others, but it’s happening. This could come in the form of a grad-assistant reaching out to the high school coach of a player enrolled at another school.
It happens when the player is not directly contacted, but goes through a third party. Agents are so prevalent in college athletics that they are also shopping players around to the highest bidder. And, we’re not talking about well-run companies that have made a name for themselves over the past six years.
The term “street agent” is used a lot in the industry, which is essentially a person who is working on a campus, acting as if they are running the business affairs of a particular athlete. They have zero training, besides being able to operate a social media account.
But, some of these athletes know no better, and will trust their futures with someone who acts as though they have their best interest at heart. I’m sorry, but having your buddy handle your business affairs, and most importantly life decisions, is not the smartest move.
“You know, tampering is at, I mean, the highest level. There is no such thing as tampering. It’s just, because there’s nobody that’s been punished for tampering. And so everybody on my roster is being called,” Drinkwitz said. “I had a dad call me and say that, and I called the head coaches at their schools, that this school and this school, and this school called, they are offering this much money.
“And, you know, you’re putting a lot of pressure on young men. You know, we’re paying them as 1099 employees, a lot of money, not offering any type of retirement, not offering any type of health benefits.”
I think it’s fair to say we have a long way to go, as schools are still trying to navigate this era of college athletics.
NIL
Bowl Season Attendance Plummets As Star Players Opt Out, Teams Decline Invites

Fighting Irish choose to forgo postseason play after being left out of College Football Playoff, as LA Bowl attendance drops
Remember the good old days of college football bowl season?
Almost every day throughout December, there were good, fun bowl games pitting quality teams against each other. There was no debate over whether star players would be involved, no “opt outs,” no teams turning down invitations. Lesser games still had big attendance figures, as fans built winter vacations around warmer destinations. It built up throughout the month, culminating in the key bowl games around New Year’s Day. The Rose Bowl served as a de facto end of the season, with the biggest and most historic stage.
Now? That’s all a distant relic of a difficult-to-remember past. And it’s only going to get worse.
The start to the 2025 bowl season has been a strong reminder that the old days of college football are never coming back. In some respects, that’s for the better. In some, it’s for the worse. For example, in the days after the end of the conference championship games, discussion focused primarily on the Notre Dame Fighting Irish.
The Irish were left out of the College Football Playoff in favor of the Alabama Crimson Tide and Miami Hurricanes. The committee, as it so often does, simply made up its criteria on the fly, engaged in its usual lack of logical consistency, and predetermined the outcomes it wanted. In short, Notre Dame was treated unfairly. Instead of accepting that, however, the Irish took their ball and went home.
RELATED: Would This Proposal Fix College Football And Broken Playoff Committee?
They announced on social media they would decline any bowl invitation, choosing to forgo important postgame practices and more development time as a team. And while it’s easy to criticize, that type of decision is only going to become more common. Because there’s simply no point to most bowls anymore.

Notre Dame head football coach Marcus Freeman. MICHAEL CLUBB/SOUTH BEND TRIBUNE / USA TODAY NETWORK via Imagn Images
College Football Playoff, NIL, NFL, Ending Bowl Season For Good
It wasn’t just Notre Dame. One of the first higher-profile bowl games of the season was the LA Bowl pitting the Washington Huskies against the Boise State Broncos at SoFi Stadium. Warm weather destination, two schools with large, dedicated fan bases, a gigantic brand-new state-of-the-art venue, and…nobody showed up.
The official announced attendance was just more than 23,000, but it sure seemed like less than that. Crowd shots before kickoff showed dozens of fans sprinkled around the lower bowl, with the middle and upper sections virtually empty.
It filled in more as the game started, but just barely.
Then there’s the Alamo Bowl, with 9-3 USC taking on 8-4 TCU in San Antonio. In prior decades, it wouldn’t be a point of discussion how many big-name players for SC would be available. Yet sure enough, head coach Lincoln Riley announced over the weekend that several starters would not be participating.
Safety Kamari Ramsey is out after declaring for the NFL Draft. So is Biletnikoff Award winner Makai Lemon. And circus catch specialist Ja’kobi Lane. Starting tight end Lake McRee won’t play, neither will starting linebacker Eric Gentry. This isn’t an outlier, it’s become common practice across the sport. Starting players heading for the NFL sitting out instead of playing in a relatively decent bowl game. And the reasons make sense; why jeopardize your health for an exhibition game that isn’t the College Football Playoff?
It’s the same for fans too. Why buy tickets for an exhibition bowl game where half the starters from the regular season aren’t playing? These are valid questions, and it raises the more important overarching one: what is the future of bowl games?
Notre Dame, one of the game’s biggest brand names isn’t going to play in a bowl game at all. Star players left and right won’t be playing. Nobody’s buying tickets to half these games anymore to see backups taking on backups. NIL and the transfer portal makes it so that many players will avoid bowls, since they’re halfway out the door already anyway.
It’s just not sustainable, and with the game trending in the direction it’s going, there’s little to suggest it’s ever going to go back to the way it was.
Expanding the College Football Playoff isn’t a popular choice, for good reason. But it might be the only path forward to allow more teams, players and fanbases to continue after the regular season. Home playoff games in a 16-team or 20-team or whatever it is field would sell out stadiums and keep players engaged. Bowls could be revived in importance. Ratings would be huge. And most importantly, more money would get infused into the sport.
Like it or not, that’s what college football runs on these days. And the current bowl system isn’t printing enough of it.
NIL
Mitch Barnhart says the NIL money is there but he refuses to show the receipt

If you’re a Kentucky fan trying to make sense of NIL, revenue sharing and JMI, you’re not alone. The athletic director running the whole thing admits it’s “clunky” right now.
From losing ground with high school basketball recruits like Tyran Stokes and Christian Collins, BBN is at all-time high in recruiting anxiety.
In a long sit-down with the Lexington Herald-Leader, Mitch Barnhart tried to explain how Kentucky is operating in this new College Sports Commission / NILGo world. The message was basically this: yes, it’s confusing; no, Kentucky isn’t freelancing; and he believes the structure he’s put in place is actually a strength, not a handicap.
Convincing the fanbase of that isn’t going to be easy without recruits showing up.
‘Clunky’ rules, moving caps and a promise to stay in the guardrails at Kentucky
Barnhart said the current landscape is really two different eras smashed together: what was done before July 1, and everything that’s been built since the House settlement, the College Sports Commission and NILGo went live.
Different schools had different pre-July 1 spending patterns. That history impacts how much cap space they have now. Some have more room. Some have less. That’s part of why it looks like schools are operating under different rulebooks.
Barnhart’s word for the rollout was “clunky.” There are participation agreements that not every school has signed yet, rules that have to go through courts and attorneys general, and separate 30-day windows for both the House plaintiffs and state AGs before some policies can even be implemented. Some rules are in effect. Others are still in line.
In the middle of all that, Barnhart keeps coming back to the same idea: Kentucky is trying to be “steady,” stay within the “guardrails,” and trust that “progress is being made” as the national framework catches up.
That might not satisfy fans who look around and see other schools clearly pushing those guardrails, but it’s the lane he’s chosen. Pope backed that up by saying they will always “err” on the side of caution when it comes to NIL.
NILGo, averages and a ‘hot market’ in Lexington
On the actual NIL payouts, Barnhart said all deals now flow through NILGo, and Kentucky has already had “several hundred” go through the system. At the Champions Blue meeting in October, he pegged the average deal around $3,000, with the biggest near $50,000. He said those numbers are still “trending in the same way.”
He pointed to Kentucky volleyball as a prime example of what a “hot market” looks like. A Final Four run has made that roster more visible in Lexington, and as their “notoriety” has grown, so has their NIL value. Barnhart sounded genuinely excited talking about watching those opportunities grow for non-revenue athletes.
For fans who worry Kentucky isn’t doing anything, that’s the counter: NIL deals are happening, they’re in seven figures across the department, and not just in football and men’s basketball.
The question, of course, is whether that level of activity is enough to land and keep the kind of top-end basketball talent BBN expects. So far, the answer to that question seems to be no.
Why Mitch Barnhart is all-in on JMI
A huge chunk of the interview was essentially a defense of the JMI model that fans hate.
Barnhart’s pitch goes like this: JMI arrives with more than 200 corporate partners already on board and a seasoned sales force generating $35–40 million a year in advertising and sponsorships. That group is now tasked with not just selling Kentucky athletics, but also matching student-athletes with those brands.
From his perspective, that’s an enormous head start. You’ve got a big, experienced sales staff already embedded on campus, already working with companies that “are very, very interested in your program,” and now they can turn that machine toward NIL.
He also made a key point that’s been blurry for fans: JMI isn’t skimming a cut off those NILGo deals. “There’s no fee,” Barnhart said. “We’re fee-free.”
So what’s the trade-off? Marks and flexibility.
If a student-athlete wants to use Kentucky logos and IP in their deals, that path runs through JMI. If they sign with a company that competes with an existing UK sponsor, Barnhart said they’re “certainly” encouraged to give Kentucky partners first crack, but athletes can still go ahead with outside deals they just can’t use the marks.
That is a huge deal. Being able to use the UK brand, and the notoriety that comes with Kentucky basketball is a huge draw for NIL-minded athletes. Not being able to use those can be a deal breaker.
He pointed to cases like Trent Noah, who has hometown relationships he wants to honor, and players who arrive with pre-existing high school NIL deals. The message there was, “We work through it,” even if it’s messy. Noah decided to not opt-in with JMI and has deals all through the commonwealth, you just won’t see the UK logo anywhere.
The flip side is obvious: if you don’t like or trust JMI, you’re going to see this entire structure as restrictive, even if the AD keeps calling it a “really cool” family.
Barnhart speaks on conflicts of interest and long relationships
Barnhart didn’t dodge the question about perceived conflicts between UK staff and JMI personnel. He just doesn’t see a problem.
To him, the long-standing ties that span from the Jim Host era to IMG to now 11 years with JMI and a new extension through year 25, are a feature, not a bug. He framed it as a tight-knit group of people who love Kentucky and know the market, not as an insider network that needs to be broken up.
A lot of fan angst comes from the Rachel Newman Baker-Brandon Baker relationship. Rachel is an assistant AD at UK while Brandon is Vice President Partnerships at JMI with the title UK Sports & Campus Marketing. According to JMI, “Brandon’s role is focused on aligning key partners’ marketing objectives with the goals and vision of the university. He directs the team that oversees all key partnerships and renewal business, as well as gameday activations, partner hospitality, and stadium/arena signage.”
“If it was a conflict,” Barnhart essentially argued, why have revenues and rights deals grown so aggressively?
That answer is unlikely to quiet any critics of the relationship between UK and JMI. Some fans hear “family” and “long-term relationships” and immediately think of a closed ecosystem that’s hard to challenge. But Barnhart is clearly not backing away from that model. If anything, he’s doubling down on it as a competitive advantage.
Why Barnhart won’t show his revenue-sharing cards at Kentucky
Maybe the most interesting part of the interview was his insistence on keeping revenue-sharing numbers private.
Barnhart pushed back on the idea that it’s about secrecy. He called it “flexibility.”
In his view, there are two separate buckets: revenue sharing and NIL. He thinks fans and some schools have blurred those lines by bragging about a big “NIL” number that’s really a mix of both.
He wants the freedom to slide resources between those buckets depending on the sport, the year and the player. Maybe a high-profile recruit is better served taking more in rev share and less in NIL, or vice versa. Maybe football needs a bigger push one offseason to address a critical position, while basketball doesn’t. Maybe in another year it’s the opposite.
If he puts hard public numbers on what each program gets, he worries he’ll lock himself into boxes that hurt Kentucky competitively and create a circus of fans comparing individual payouts.
He also says there’s a protective piece: he doesn’t want each athlete “pegged” publicly by a dollar figure or constantly compared to teammates.
You can debate whether that explanation is satisfying, or whether transparency would actually help calm the waters, but it’s at least a clear window into his thinking.
For fans it is just Mitch Barnhart saying they have the money, but won’t show a receipt.
Balancing Kentucky football, Kentucky basketball and the rest of the athletics department
Kentucky’s situation is unusual. Both football and men’s basketball are profitable. Most schools can’t say that.
Barnhart admitted that balancing those two in this new world is tricky. Pre-July 1, he says everyone loved the rosters. Post-July 1, the math is just harder across the board, not only at Kentucky.
His bigger picture vision is to use the power of the Kentucky basketball brand to lift everything. If NIL and rev-share decisions are made wisely, he believes success in men’s hoops and football can raise the tide for baseball, women’s basketball, volleyball and everyone else.
That’s the optimistic version. The pessimistic version is what some fans are already feeling: if basketball misses on elite recruits and football falls behind the SEC arms race, nobody gets lifted and everything falls apart.
On general managers, Mark Pope and ‘talent evaluation’
Barnhart also weighed in on the “general manager” debate that’s hovered over Kentucky basketball.
Will Stein came in and immediately wanted a GM for football. Barnhart was fine with that. For a first-time head coach juggling a new staff, a playoff run and a roster rebuild, he called it “probably a pretty smart decision.”
With Mark Pope, he’s not forcing the issue. Barnhart said he’s going to “lean into” Pope’s preference and give him the flexibility to decide whether he wants that role or not down the line.
Then he slipped in a line that will jump out to fans: “Our talent assessment was fine until we lost a couple games, and then everybody started wondering about our talent assessment, correct?” Well, Mitch that is usually how it works.
In other words: he doesn’t think one rough stretch means the eval process is broken, and he doesn’t believe a GM is some magic fix. But he did leave the door open to adjustments later if Pope decides he wants to structure things differently.
Will Mitch Barnhart still be the one steering this or will he retire?
Finally, the obvious question: how much longer does he want to do this?
Barnhart acknowledged the ambassador clause in his contract that would allow him to step aside after December 31 and shift roles. He didn’t commit one way or the other.
He talked instead about loving competition, loving Kentucky and the fact that he and his family came planning to stay 6–8 years and never left. He admitted the job has changed, where it used to be 75% competition and 25% “other stuff,” he thinks those numbers have flipped. Now it’s more about sustaining the enterprise of college sports than just trying to win Saturday.
He also admitted the personal connection piece is harder in an era where 35–40% of the roster turns over every year. Meeting every recruit, knowing every family? That’s tougher now.
But the thrill of competition is still there for him. “The day that changes,” he said, is probably the day someone else should take over.
That’s the backdrop to everything he just laid out: a clunky system, a controversial partnership model, a fanbase demanding top-tier results, and an athletic director who insists Kentucky has “a good plan” for all of it, and says he still wants to be the one fighting to make it work.
-

 Motorsports3 weeks ago
Motorsports3 weeks agoJo Shimoda Undergoes Back Surgery
-

 NIL2 weeks ago
NIL2 weeks agoBowl Projections: ESPN predicts 12-team College Football Playoff bracket, full bowl slate after Week 14
-

 Motorsports1 week ago
Motorsports1 week agoSoundGear Named Entitlement Sponsor of Spears CARS Tour Southwest Opener
-

 Rec Sports3 weeks ago
Rec Sports3 weeks agoHow this startup (and a KC sports icon) turned young players into card-carrying legends overnight
-

 Rec Sports3 weeks ago
Rec Sports3 weeks agoRobert “Bobby” Lewis Hardin, 56
-
Sports3 weeks ago
Wisconsin volleyball sweeps Minnesota with ease in ranked rivalry win
-

 Motorsports3 weeks ago
Motorsports3 weeks agoPohlman admits ‘there might be some spats’ as he pushes to get Kyle Busch winning again
-

 Motorsports1 week ago
Motorsports1 week agoDonny Schatz finds new home for 2026, inks full-time deal with CJB Motorsports – InForum
-
 Motorsports3 weeks ago
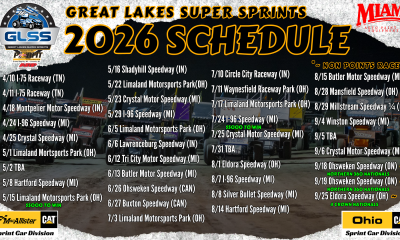
Motorsports3 weeks agoIncreased Purses, 19 Different Tracks Highlight 2026 Great Lakes Super Sprints Schedule – Speedway Digest
-

 Rec Sports2 weeks ago
Rec Sports2 weeks agoHow Donald Trump became FIFA’s ‘soccer president’ long before World Cup draw































