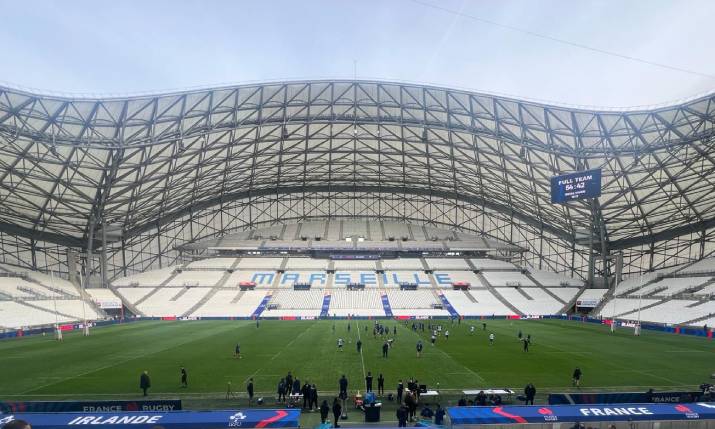

Stade Orange Vélodrome in Marselle being prepared for 2024 Six Nations opening match between France and Ireland in February
Of all the rapidly changing trends witnessed by sports – and in particular their fans – over the past decade, one of the most significant is what has become of sports stadiums. Indeed, it could be argued that the term ‘modern sports stadium’ is somewhat old fashioned as the homes of sports teams have evolved into multi-use events facilities.
Any stadium that is being constructed from new or being upgraded is done so with the clear message that the end result won’t be what passed before to satisfy fans. The new or enhanced stadium is now a true communications hub, capable of meeting the connectivity demands of those who visit them: that is of the transmission of masses of video content to and from not just fans but also broadcasters, and not just content from sports fans but also those going to music events.
For all sports stadiums, providing a modern, high-quality communications network is very much a team game, principally involving a leading comms operator that not only understands current demands but can demonstrate how to manage the inevitable data explosion. Few countries’ sports arenas have had to deal with this issue more than those in France. And – as exemplified with its work for the last Rugby World cup and Olympic Games, as well as routine Ligue 1 games – few companies have provided solutions to meet this demand more than Orange.
Calling growth in data at today’s sports arenas ‘robust’ would be very much an understatement. A 2024 study from Ericsson calculated that arena venues had seen a 67% growth in data usage compared with a year previously, noting specifically that fans in stadiums now demand high-performance, robust and reliable mobile coverage to share, interact with and stream content. The next survey will almost certainly see this figure surpassed considerably. At the Stade Orange Vélodrome in Marseilles, this will be a certainty.
The home of Olympique de Marseille (OM) – traditionally seen as France’s second team behind the enriched Paris Saint-Germain – is unique in that not only does it have naming rights sponsorship from a leading global comms operator, it is also the home of a test bed for mobile and fixed communications technology and services. Orange’s relationship with OM really began in earnest in the 4G days of June 2016 as part of a grand strategy to create a totally renovated connected stadium in time for that year’s Euros tournament.
Recalling the connectivity demands of the time, Guillaume Chabas, head of innovation at Orange Business and head of the 5G Lab at Orange Vélodrome, said the first step was to create something significant with the wireless connection and create and purpose some applications for new usage. In 2016, 4G was the mobile standard but on its own it was not enough. WiFi connectivity had to be implemented to upgrade network capacity because 4G was not enough to meet anticipated network loads.
Six years later – just months away from a Rugby World Cup that would see Orange Vélodrome act as a key host stadium – 5G had very much entered the room and not just metaphorically. The end of the 2021/22 football season saw fans in the hospitality boxes and premium seats able to make use of the Orange 5G network to see the first use cases that the next-generation mobile infrastructure could support. Indeed, Orange Vélodrome was also France’s first 5G-equipped stadium, taking advantage of a non-standalone core network that comprised a 3.5GHz mid-band network complemented by experimental mmWave 5G in the 26GHz range. There was also AWS Edge Capacity connected to an experimental 5G area and to a cloud/hybrid edge.
Initial supported technologies and services included virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), video analytics based on artificial intelligence (AI), and real-time monitoring of stadium resources. One of the most impressive and interesting of these was the Augmented Match service, a mixed-reality mobile app developed jointly by Orange and Immersiv.io that allowed fans to access real-time technical and statistical information about the players on the field. This gave the option of data on the players – such as distance ran, goals scored, general pedigree etc – transposed upon the official TV feed of the game for those watching on a smartphone. The players’ positions were displayed in real time along with other data, such as shots, dribbles, passes and defence.
The app ran over the experimental 26GHz 5G network along with edge computing, using Computer Vision to detect player position, with 5G ensuring a very high-speed connection, necessary to provide the lowest possible latency to avoid any lag between the actions on the field, AR data and even digital twins of the players.
It’s no surprise to discover that Chabas and his team were also actively involved in the 2024 Paris Olympics for which select maritime events were hosted in the nearby marina in Marseilles. In terms of challenges, and indeed environment, the Marseilles nautical events brought about unique conditions for network broadcast. The company leant in on the established Stade Orange fibre network that routinely sees use in transporting high-quality broadcast video during OM home fixtures. A key part of the broadcast service was based on using specially optimised Samsung S24 smartphones as TV cameras directly on boats, supported by an Orange private 5G network.
Fast forward to 2025 and the Orange Vélodrome is upping the connectivity ante to stay relevant for today’s fans. “From the way athletes train to how fans experience the game, technology is transforming sports at every level. While unlocking new business opportunities, it creates immersive entertainment and democratises sports, making them more interactive and inclusive,” says Chabas.
Orange has now deployed four key applications to boost broadcasting and ultimately the fan experience, namely an evolved Immersiv.io app that brings AR overlays and live stats and replays directly into the stadium; Touch2See which is designed to enable visually impaired fans to ‘feel’ the game through tactile tablets; 5G+ for Camera, said to offer “seamless” media production; and Team Connect, based on a private 5G network that is said to enable private 5G media production. Specifically, the app is designed to allow real-time, high-performance interference-free live broadcasting and critical event communications during events using dedicated frequencies and cloud services to streamline operations.
Going forward, Chabas see more innovation from the connectivity set up. Key projects being investigated include potential advanced monetisation opportunities from video feeds by which AI could recognise key brands’ sports equipment. Prioritised electronic payment services are regarded as another key area. But essentially, the key will be delivering an advanced comms infrastructure to make these potentials real, with AI very much at the forefront in the new immersive world of sports broadcast.
“As 5G, AI, and immersive technologies evolve, the future of sport is not just something you watch; it’s something you live,” Chabas concludes.








 Role at VMI:
Role at VMI:













 COLLECTIVE COLLAPSE OF EPIC PROPORTIONS! | First Take
COLLECTIVE COLLAPSE OF EPIC PROPORTIONS! | First Take





































 (via @zackystrong.pt/TT)
(via @zackystrong.pt/TT)

